Xiaoyu Deng
Causality-Aware Temporal Projection for Video Understanding in Video-LLMs
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Recent Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) have shown strong multimodal reasoning capabilities, yet remain challenged by video understanding tasks that require consistent temporal ordering and causal coherence. Many parameter-efficient Video-LLMs rely on unconstrained bidirectional projectors to model inter-frame interactions, which can blur temporal ordering by allowing later frames to influence earlier representations, without explicit architectural mechanisms to respect the directional nature of video reasoning. To address this limitation, we propose V-CORE, a parameter-efficient framework that introduces explicit temporal ordering constraints for video understanding. V-CORE consists of two key components: (1) Learnable Spatial Aggregation (LSA), which adaptively selects salient spatial tokens to reduce redundancy, and (2) a Causality-Aware Temporal Projector (CATP), which enforces structured unidirectional information flow via block-causal attention and a terminal dynamic summary token acting as a causal sink. This design preserves intra-frame spatial interactions while ensuring that temporal information is aggregated in a strictly ordered manner. With 4-bit QLoRA and a frozen LLM backbone, V-CORE can be trained efficiently on a single consumer GPU. Experiments show that V-CORE achieves strong performance on the challenging NExT-QA benchmark, reaching 61.2% accuracy, and remains competitive across MSVD-QA, MSRVTT-QA, and TGIF-QA, with gains concentrated in temporal and causal reasoning subcategories (+3.5% and +5.2% respectively), directly validating the importance of explicit temporal ordering constraints.
LP-DETR: Layer-wise Progressive Relations for Object Detection
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents LP-DETR (Layer-wise Progressive DETR), a novel approach that enhances DETR-based object detection through multi-scale relation modeling. Our method introduces learnable spatial relationships between object queries through a relation-aware self-attention mechanism, which adaptively learns to balance different scales of relations (local, medium and global) across decoder layers. This progressive design enables the model to effectively capture evolving spatial dependencies throughout the detection pipeline. Extensive experiments on COCO 2017 dataset demonstrate that our method improves both convergence speed and detection accuracy compared to standard self-attention module. The proposed method achieves competitive results, reaching 52.3\% AP with 12 epochs and 52.5\% AP with 24 epochs using ResNet-50 backbone, and further improving to 58.0\% AP with Swin-L backbone. Furthermore, our analysis reveals an interesting pattern: the model naturally learns to prioritize local spatial relations in early decoder layers while gradually shifting attention to broader contexts in deeper layers, providing valuable insights for future research in object detection.
ChallengeMe: An Adversarial Learning-enabled Text Summarization Framework
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:The astonishing performance of large language models (LLMs) and their remarkable achievements in production and daily life have led to their widespread application in collaborative tasks. However, current large models face challenges such as hallucination and lack of specificity in content generation in vertical domain tasks. Inspired by the contrast and classification mechanisms in human cognitive processes, this paper constructs an adversarial learning-based prompt framework named ChallengeMe, which includes three cascaded solutions: generation prompts, evaluation prompts, and feedback optimization. In this process, we designed seven core optimization dimensions and set the threshold for adversarial learning. The results of mixed case studies on the text summarization task show that the proposed framework can generate more accurate and fluent text summaries compared to the current advanced mainstream LLMs.
A New Perspective on Privacy Protection in Federated Learning with Granular-Ball Computing
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) facilitates collaborative model training while prioritizing privacy by avoiding direct data sharing. However, most existing articles attempt to address challenges within the model's internal parameters and corresponding outputs, while neglecting to solve them at the input level. To address this gap, we propose a novel framework called Granular-Ball Federated Learning (GrBFL) for image classification. GrBFL diverges from traditional methods that rely on the finest-grained input data. Instead, it segments images into multiple regions with optimal coarse granularity, which are then reconstructed into a graph structure. We designed a two-dimensional binary search segmentation algorithm based on variance constraints for GrBFL, which effectively removes redundant information while preserving key representative features. Extensive theoretical analysis and experiments demonstrate that GrBFL not only safeguards privacy and enhances efficiency but also maintains robust utility, consistently outperforming other state-of-the-art FL methods. The code is available at https://github.com/AIGNLAI/GrBFL.
CoVis: A Collaborative Framework for Fine-grained Graphic Visual Understanding
Nov 27, 2024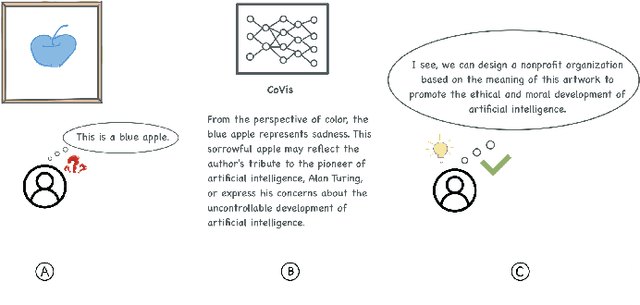
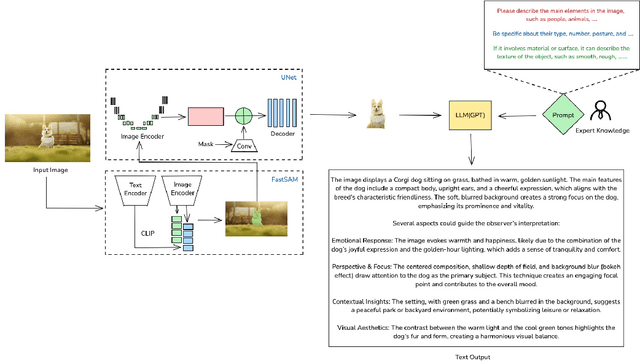
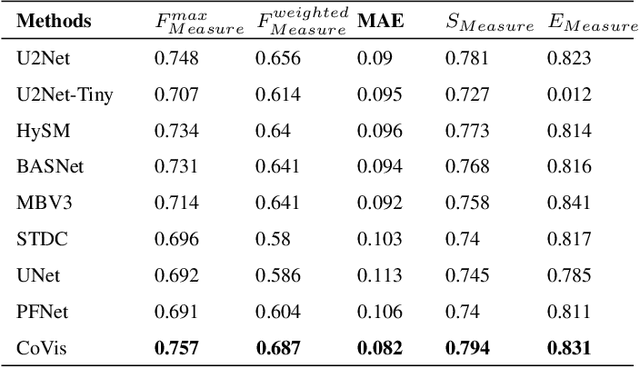

Abstract:Graphic visual content helps in promoting information communication and inspiration divergence. However, the interpretation of visual content currently relies mainly on humans' personal knowledge background, thereby affecting the quality and efficiency of information acquisition and understanding. To improve the quality and efficiency of visual information transmission and avoid the limitation of the observer due to the information cocoon, we propose CoVis, a collaborative framework for fine-grained visual understanding. By designing and implementing a cascaded dual-layer segmentation network coupled with a large-language-model (LLM) based content generator, the framework extracts as much knowledge as possible from an image. Then, it generates visual analytics for images, assisting observers in comprehending imagery from a more holistic perspective. Quantitative experiments and qualitative experiments based on 32 human participants indicate that the CoVis has better performance than current methods in feature extraction and can generate more comprehensive and detailed visual descriptions than current general-purpose large models.
Optimizing Automated Picking Systems in Warehouse Robots Using Machine Learning
Aug 29, 2024
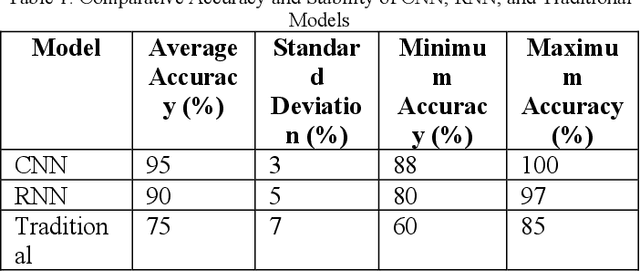
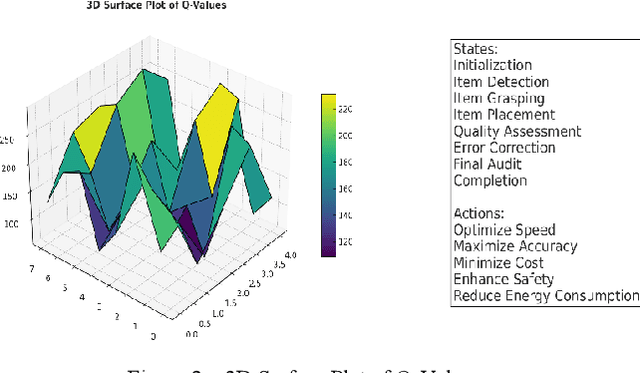

Abstract:With the rapid growth of global e-commerce, the demand for automation in the logistics industry is increasing. This study focuses on automated picking systems in warehouses, utilizing deep learning and reinforcement learning technologies to enhance picking efficiency and accuracy while reducing system failure rates. Through empirical analysis, we demonstrate the effectiveness of these technologies in improving robot picking performance and adaptability to complex environments. The results show that the integrated machine learning model significantly outperforms traditional methods, effectively addressing the challenges of peak order processing, reducing operational errors, and improving overall logistics efficiency. Additionally, by analyzing environmental factors, this study further optimizes system design to ensure efficient and stable operation under variable conditions. This research not only provides innovative solutions for logistics automation but also offers a theoretical and empirical foundation for future technological development and application.
Combating Uncertainty and Class Imbalance in Facial Expression Recognition
Dec 15, 2022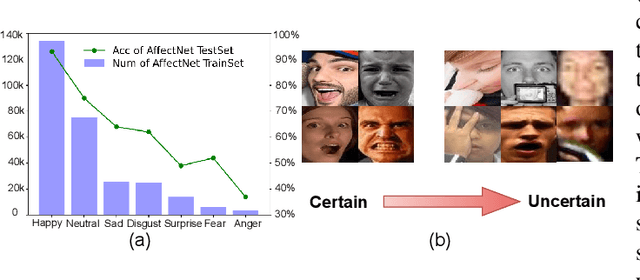
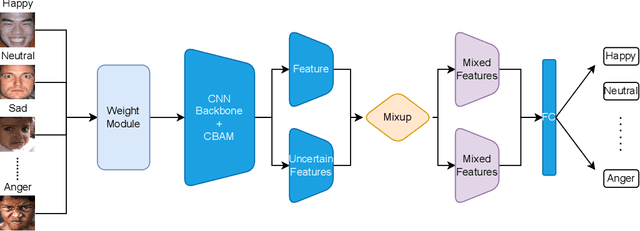
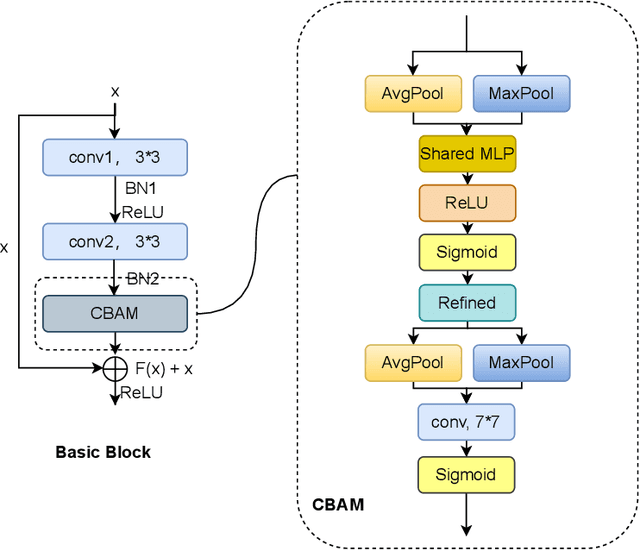
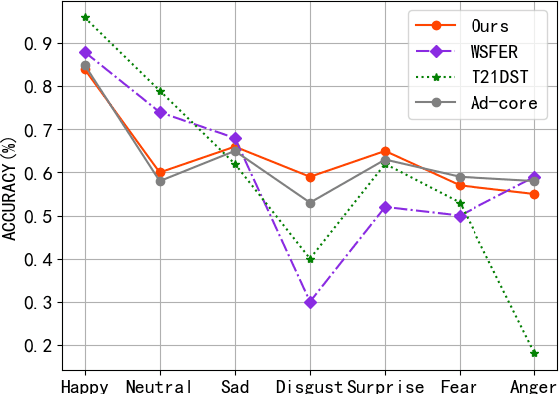
Abstract:Recognition of facial expression is a challenge when it comes to computer vision. The primary reasons are class imbalance due to data collection and uncertainty due to inherent noise such as fuzzy facial expressions and inconsistent labels. However, current research has focused either on the problem of class imbalance or on the problem of uncertainty, ignoring the intersection of how to address these two problems. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a framework based on Resnet and Attention to solve the above problems. We design weight for each class. Through the penalty mechanism, our model will pay more attention to the learning of small samples during training, and the resulting decrease in model accuracy can be improved by a Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM). Meanwhile, our backbone network will also learn an uncertain feature for each sample. By mixing uncertain features between samples, the model can better learn those features that can be used for classification, thus suppressing uncertainty. Experiments show that our method surpasses most basic methods in terms of accuracy on facial expression data sets (e.g., AffectNet, RAF-DB), and it also solves the problem of class imbalance well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge