Bo Hong
Neural Dynamics Model of Visual Decision-Making: Learning from Human Experts
Sep 04, 2024



Abstract:Uncovering the fundamental neural correlates of biological intelligence, developing mathematical models, and conducting computational simulations are critical for advancing new paradigms in artificial intelligence (AI). In this study, we implemented a comprehensive visual decision-making model that spans from visual input to behavioral output, using a neural dynamics modeling approach. Drawing inspiration from the key components of the dorsal visual pathway in primates, our model not only aligns closely with human behavior but also reflects neural activities in primates, and achieving accuracy comparable to convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Moreover, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) identified key neuroimaging features such as structural connections and functional connectivity that are associated with performance in perceptual decision-making tasks. A neuroimaging-informed fine-tuning approach was introduced and applied to the model, leading to performance improvements that paralleled the behavioral variations observed among subjects. Compared to classical deep learning models, our model more accurately replicates the behavioral performance of biological intelligence, relying on the structural characteristics of biological neural networks rather than extensive training data, and demonstrating enhanced resilience to perturbation.
Optimizing Automated Picking Systems in Warehouse Robots Using Machine Learning
Aug 29, 2024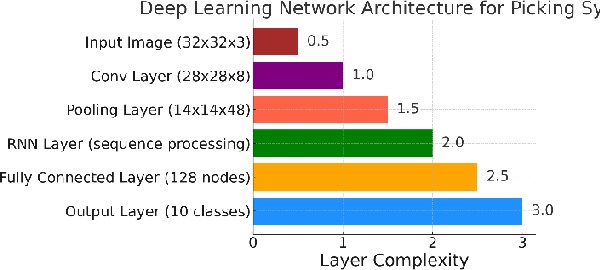
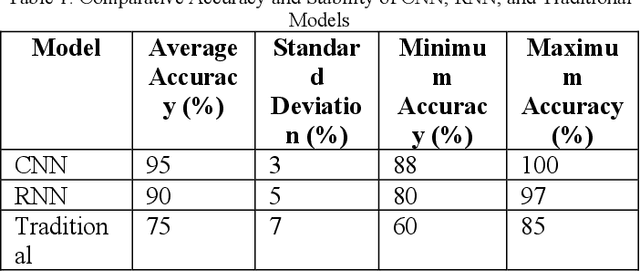

Abstract:With the rapid growth of global e-commerce, the demand for automation in the logistics industry is increasing. This study focuses on automated picking systems in warehouses, utilizing deep learning and reinforcement learning technologies to enhance picking efficiency and accuracy while reducing system failure rates. Through empirical analysis, we demonstrate the effectiveness of these technologies in improving robot picking performance and adaptability to complex environments. The results show that the integrated machine learning model significantly outperforms traditional methods, effectively addressing the challenges of peak order processing, reducing operational errors, and improving overall logistics efficiency. Additionally, by analyzing environmental factors, this study further optimizes system design to ensure efficient and stable operation under variable conditions. This research not only provides innovative solutions for logistics automation but also offers a theoretical and empirical foundation for future technological development and application.
Exploiting Diffusion Prior for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Jun 16, 2024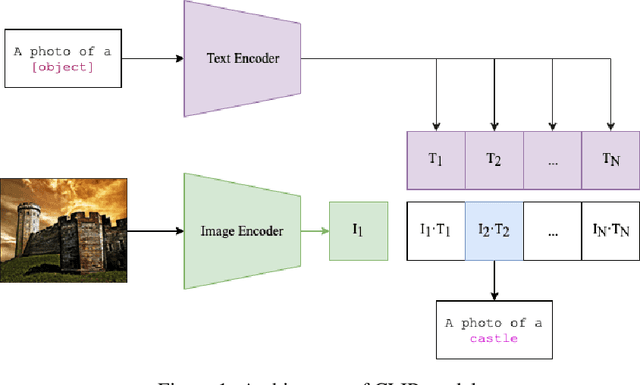
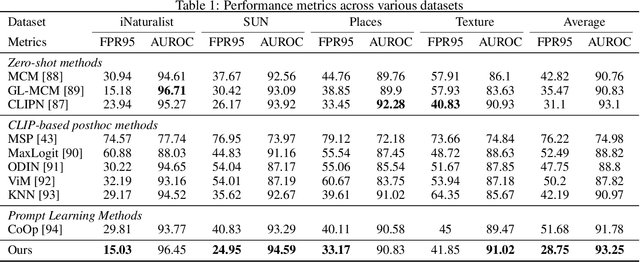
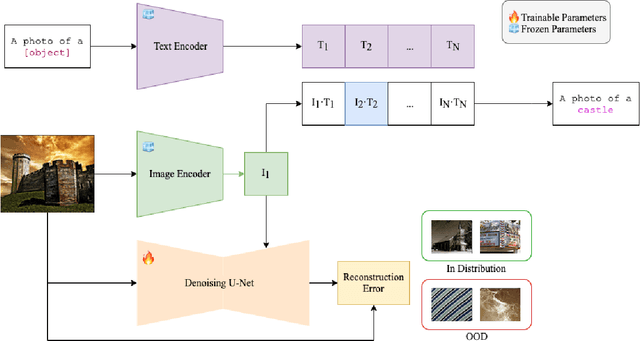
Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is crucial for deploying robust machine learning models, especially in areas where security is critical. However, traditional OOD detection methods often fail to capture complex data distributions from large scale date. In this paper, we present a novel approach for OOD detection that leverages the generative ability of diffusion models and the powerful feature extraction capabilities of CLIP. By using these features as conditional inputs to a diffusion model, we can reconstruct the images after encoding them with CLIP. The difference between the original and reconstructed images is used as a signal for OOD identification. The practicality and scalability of our method is increased by the fact that it does not require class-specific labeled ID data, as is the case with many other methods. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets demonstrates the robustness and effectiveness of our method, which have significantly improved the detection accuracy.
Cross-Task Multi-Branch Vision Transformer for Facial Expression and Mask Wearing Classification
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:With wearing masks becoming a new cultural norm, facial expression recognition (FER) while taking masks into account has become a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose a unified multi-branch vision transformer for facial expression recognition and mask wearing classification tasks. Our approach extracts shared features for both tasks using a dual-branch architecture that obtains multi-scale feature representations. Furthermore, we propose a cross-task fusion phase that processes tokens for each task with separate branches, while exchanging information using a cross attention module. Our proposed framework reduces the overall complexity compared with using separate networks for both tasks by the simple yet effective cross-task fusion phase. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed model performs better than or on par with different state-of-the-art methods on both facial expression recognition and facial mask wearing classification task.
The application of Augmented Reality (AR) in Remote Work and Education
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:With the rapid advancement of technology, Augmented Reality (AR) technology, known for its ability to deeply integrate virtual information with the real world, is gradually transforming traditional work modes and teaching methods. Particularly in the realms of remote work and online education, AR technology demonstrates a broad spectrum of application prospects. This paper delves into the application potential and actual effects of AR technology in remote work and education. Through a systematic literature review, this study outlines the key features, advantages, and challenges of AR technology. Based on theoretical analysis, it discusses the scientific basis and technical support that AR technology provides for enhancing remote work efficiency and promoting innovation in educational teaching models. Additionally, by designing an empirical research plan and analyzing experimental data, this article reveals the specific performance and influencing factors of AR technology in practical applications. Finally, based on the results of the experiments, this research summarizes the application value of AR technology in remote work and education, looks forward to its future development trends, and proposes forward-looking research directions and strategic suggestions, offering empirical foundation and theoretical guidance for further promoting the in-depth application of AR technology in related fields.
Rumor Detection with a novel graph neural network approach
Apr 02, 2024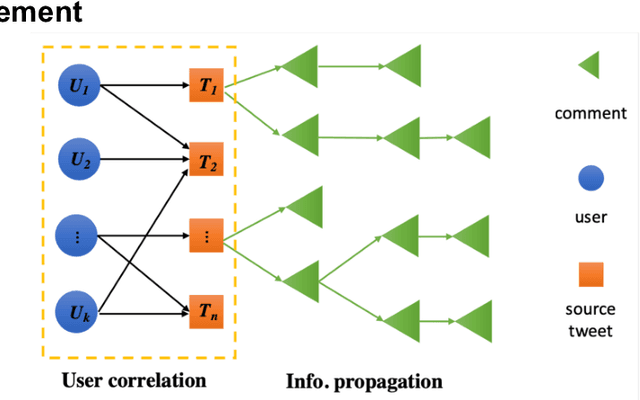
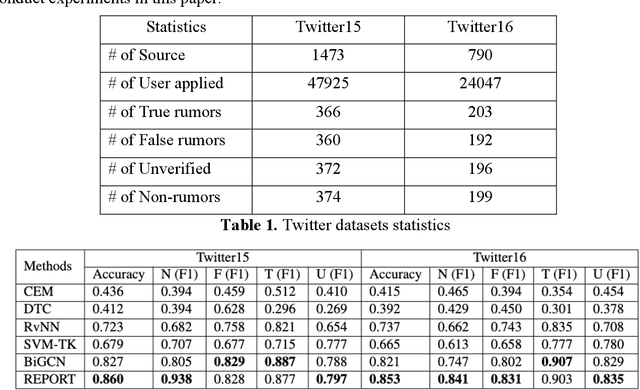

Abstract:The wide spread of rumors on social media has caused a negative impact on people's daily life, leading to potential panic, fear, and mental health problems for the public. How to debunk rumors as early as possible remains a challenging problem. Existing studies mainly leverage information propagation structure to detect rumors, while very few works focus on correlation among users that they may coordinate to spread rumors in order to gain large popularity. In this paper, we propose a new detection model, that jointly learns both the representations of user correlation and information propagation to detect rumors on social media. Specifically, we leverage graph neural networks to learn the representations of user correlation from a bipartite graph that describes the correlations between users and source tweets, and the representations of information propagation with a tree structure. Then we combine the learned representations from these two modules to classify the rumors. Since malicious users intend to subvert our model after deployment, we further develop a greedy attack scheme to analyze the cost of three adversarial attacks: graph attack, comment attack, and joint attack. Evaluation results on two public datasets illustrate that the proposed MODEL outperforms the state-of-the-art rumor detection models. We also demonstrate our method performs well for early rumor detection. Moreover, the proposed detection method is more robust to adversarial attacks compared to the best existing method. Importantly, we show that it requires a high cost for attackers to subvert user correlation pattern, demonstrating the importance of considering user correlation for rumor detection.
Image Captioning in news report scenario
Apr 02, 2024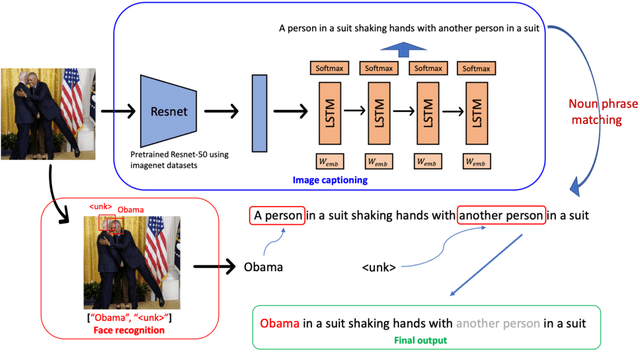
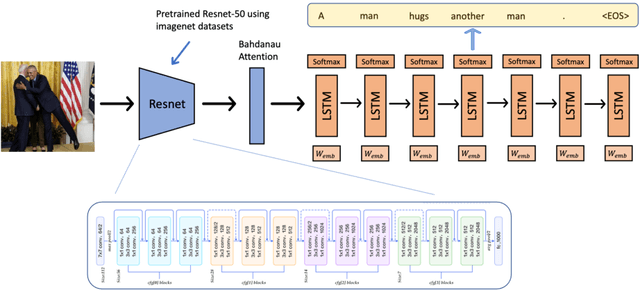


Abstract:Image captioning strives to generate pertinent captions for specified images, situating itself at the crossroads of Computer Vision (CV) and Natural Language Processing (NLP). This endeavor is of paramount importance with far-reaching applications in recommendation systems, news outlets, social media, and beyond. Particularly within the realm of news reporting, captions are expected to encompass detailed information, such as the identities of celebrities captured in the images. However, much of the existing body of work primarily centers around understanding scenes and actions. In this paper, we explore the realm of image captioning specifically tailored for celebrity photographs, illustrating its broad potential for enhancing news industry practices. This exploration aims to augment automated news content generation, thereby facilitating a more nuanced dissemination of information. Our endeavor shows a broader horizon, enriching the narrative in news reporting through a more intuitive image captioning framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge