Wenxin Hu
Can Large Language Models Recall Reference Location Like Humans?
Feb 26, 2024Abstract:When completing knowledge-intensive tasks, humans sometimes need not just an answer but also a corresponding reference passage for auxiliary reading. Previous methods required obtaining pre-segmented article chunks through additional retrieval models. This paper explores leveraging the parameterized knowledge stored during the pre-training phase of large language models (LLMs) to independently recall reference passage from any starting position. We propose a two-stage framework that simulates the scenario of humans recalling easily forgotten references. Initially, the LLM is prompted to recall document title identifiers to obtain a coarse-grained document set. Then, based on the acquired coarse-grained document set, it recalls fine-grained passage. In the two-stage recall process, we use constrained decoding to ensure that content outside of the stored documents is not generated. To increase speed, we only recall a short prefix in the second stage, then locate its position to retrieve a complete passage. Experiments on KILT knowledge-sensitive tasks have verified that LLMs can independently recall reference passage location in various task forms, and the obtained reference significantly assist downstream tasks.
A Positive-Unlabeled Metric Learning Framework for Document-Level Relation Extraction with Incomplete Labeling
Jun 26, 2023



Abstract:The goal of document-level relation extraction (RE) is to identify relations between entities that span multiple sentences. Recently, incomplete labeling in document-level RE has received increasing attention, and some studies have used methods such as positive-unlabeled learning to tackle this issue, but there is still a lot of room for improvement. Motivated by this, we propose a positive-augmentation and positive-mixup positive-unlabeled metric learning framework (P3M). Specifically, we formulate document-level RE as a metric learning problem. We aim to pull the distance closer between entity pair embedding and their corresponding relation embedding, while pushing it farther away from the none-class relation embedding. Additionally, we adapt the positive-unlabeled learning to this loss objective. In order to improve the generalizability of the model, we use dropout to augment positive samples and propose a positive-none-class mixup method. Extensive experiments show that P3M improves the F1 score by approximately 4-10 points in document-level RE with incomplete labeling, and achieves state-of-the-art results in fully labeled scenarios. Furthermore, P3M has also demonstrated robustness to prior estimation bias in incomplete labeled scenarios.
PEGA: Personality-Guided Preference Aggregator for Ephemeral Group Recommendation
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:Recently, making recommendations for ephemeral groups which contain dynamic users and few historic interactions have received an increasing number of attention. The main challenge of ephemeral group recommender is how to aggregate individual preferences to represent the group's overall preference. Score aggregation and preference aggregation are two commonly-used methods that adopt hand-craft predefined strategies and data-driven strategies, respectively. However, they neglect to take into account the importance of the individual inherent factors such as personality in the group. In addition, they fail to work well due to a small number of interactive records. To address these issues, we propose a Personality-Guided Preference Aggregator (PEGA) for ephemeral group recommendation. Concretely, we first adopt hyper-rectangle to define the concept of Group Personality. We then use the personality attention mechanism to aggregate group preferences. The role of personality in our approach is twofold: (1) To estimate individual users' importance in a group and provide explainability; (2) to alleviate the data sparsity issue that occurred in ephemeral groups. The experimental results demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods w.r.t. the score of both Recall and NDCG on Amazon and Yelp datasets.
C3SASR: Cheap Causal Convolutions for Self-Attentive Sequential Recommendation
Nov 10, 2022Abstract:Sequential Recommendation is a prominent topic in current research, which uses user behavior sequence as an input to predict future behavior. By assessing the correlation strength of historical behavior through the dot product, the model based on the self-attention mechanism can capture the long-term preference of the sequence. However, it has two limitations. On the one hand, it does not effectively utilize the items' local context information when determining the attention and creating the sequence representation. On the other hand, the convolution and linear layers often contain redundant information, which limits the ability to encode sequences. In this paper, we propose a self-attentive sequential recommendation model based on cheap causal convolution. It utilizes causal convolutions to capture items' local information for calculating attention and generating sequence embedding. It also uses cheap convolutions to improve the representations by lightweight structure. We evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed model in terms of both accurate and calibrated sequential recommendation. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that the proposed model can perform better in single- and multi-objective recommendation scenarios.
A Unified Positive-Unlabeled Learning Framework for Document-Level Relation Extraction with Different Levels of Labeling
Oct 17, 2022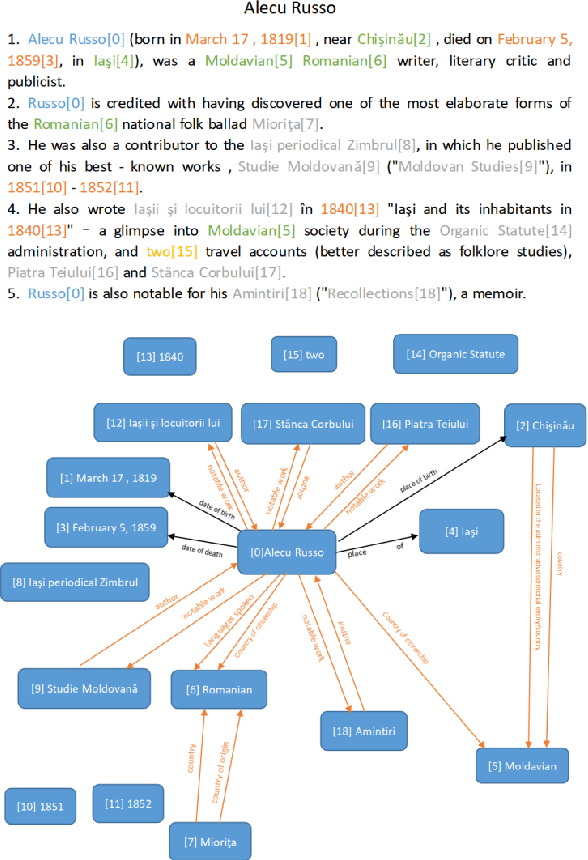
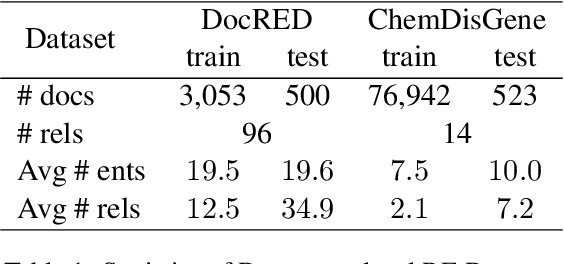
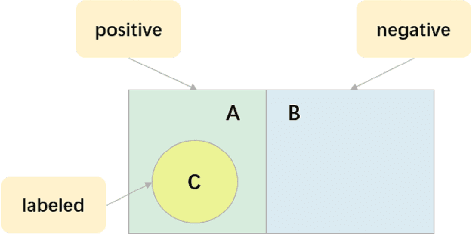
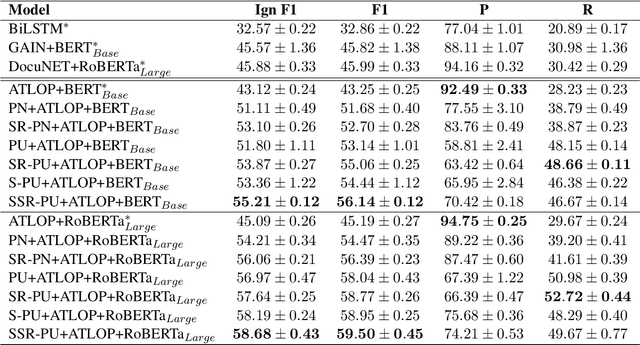
Abstract:Document-level relation extraction (RE) aims to identify relations between entities across multiple sentences. Most previous methods focused on document-level RE under full supervision. However, in real-world scenario, it is expensive and difficult to completely label all relations in a document because the number of entity pairs in document-level RE grows quadratically with the number of entities. To solve the common incomplete labeling problem, we propose a unified positive-unlabeled learning framework - shift and squared ranking loss positive-unlabeled (SSR-PU) learning. We use positive-unlabeled (PU) learning on document-level RE for the first time. Considering that labeled data of a dataset may lead to prior shift of unlabeled data, we introduce a PU learning under prior shift of training data. Also, using none-class score as an adaptive threshold, we propose squared ranking loss and prove its Bayesian consistency with multi-label ranking metrics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves an improvement of about 14 F1 points relative to the previous baseline with incomplete labeling. In addition, it outperforms previous state-of-the-art results under both fully supervised and extremely unlabeled settings as well.
Pyramid Focusing Network for mutation prediction and classification in CT images
Apr 13, 2020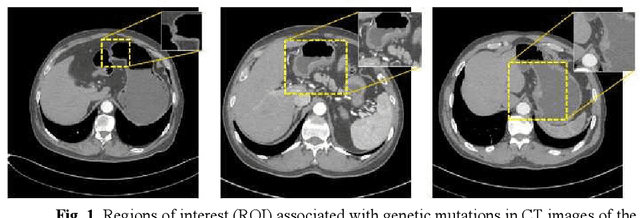
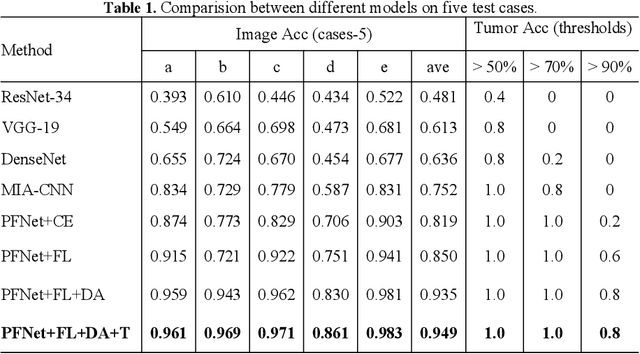
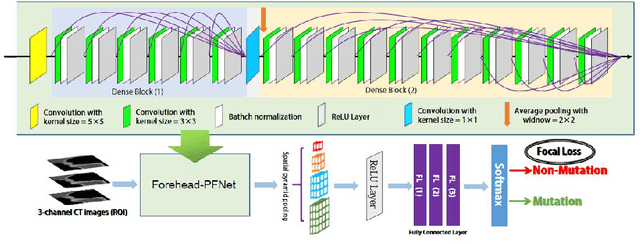
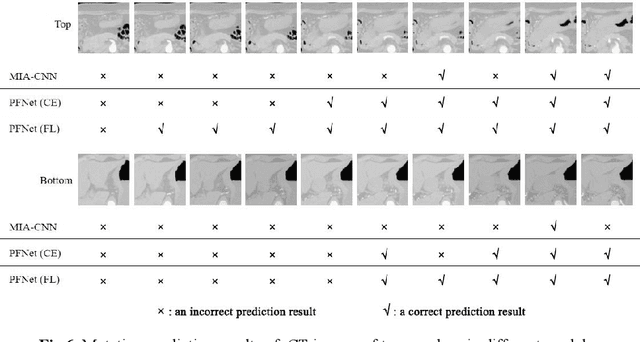
Abstract:Predicting the mutation status of genes in tumors is of great clinical significance. Recent studies have suggested that certain mutations may be noninvasively predicted by studying image features of the tumors from Computed Tomography (CT) data. Currently, this kind of image feature identification method mainly relies on manual processing to extract generalized image features alone or machine processing without considering the morphological differences of the tumor itself, which makes it difficult to achieve further breakthroughs. In this paper, we propose a pyramid focusing network (PFNet) for mutation prediction and classification based on CT images. Firstly, we use Space Pyramid Pooling to collect semantic cues in feature maps from multiple scales according to the observation that the shape and size of the tumors are varied.Secondly, we improve the loss function based on the consideration that the features required for proper mutation detection are often not obvious in cross-sections of tumor edges, which raises more attention to these hard examples in the network. Finally, we devise a training scheme based on data augmentation to enhance the generalization ability of networks. Extensively verified on clinical gastric CT datasets of 20 testing volumes with 63648 CT images, our method achieves the accuracy of 94.90% in predicting the HER-2 genes mutation status of at the CT image.
Cascaded Detail-Preserving Networks for Super-Resolution of Document Images
Nov 25, 2019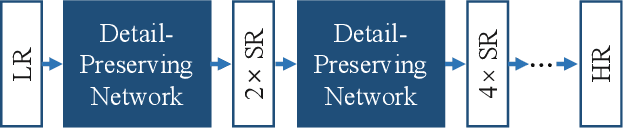
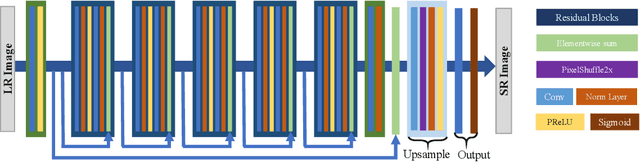
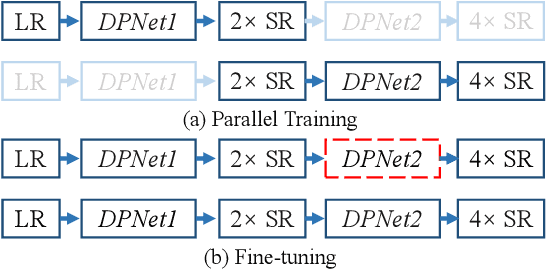

Abstract:The accuracy of OCR is usually affected by the quality of the input document image and different kinds of marred document images hamper the OCR results. Among these scenarios, the low-resolution image is a common and challenging case. In this paper, we propose the cascaded networks for document image super-resolution. Our model is composed by the Detail-Preserving Networks with small magnification. The loss function with perceptual terms is designed to simultaneously preserve the original patterns and enhance the edge of the characters. These networks are trained with the same architecture and different parameters and then assembled into a pipeline model with a larger magnification. The low-resolution images can upscale gradually by passing through each Detail-Preserving Network until the final high-resolution images. Through extensive experiments on two scanning document image datasets, we demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms recent state-of-the-art image super-resolution methods, and combining it with standard OCR system lead to signification improvements on the recognition results.
Automatically Generating Macro Research Reports from a Piece of News
Nov 21, 2019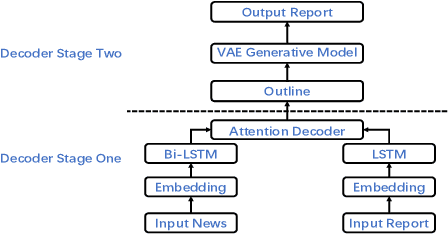
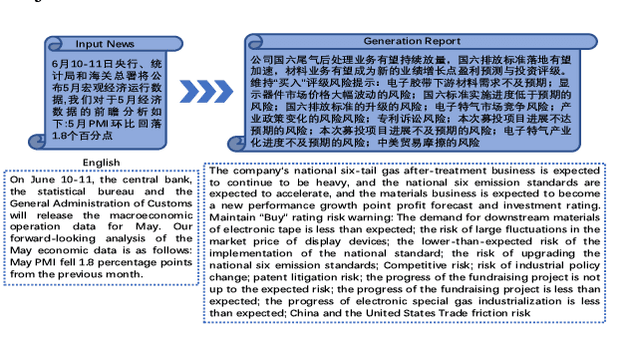
Abstract:Automatically generating macro research reports from economic news is an important yet challenging task. As we all know, it requires the macro analysts to write such reports within a short period of time after the important economic news are released. This motivates our work, i.e., using AI techniques to save manual cost. The goal of the proposed system is to generate macro research reports as the draft for macro analysts. Essentially, the core challenge is the long text generation issue. To address this issue, we propose a novel deep learning technique based approach which includes two components, i.e., outline generation and macro research report generation.For the model performance evaluation, we first crawl a large news-to-report dataset and then evaluate our approach on this dataset, and the generated reports are given for the subjective evaluation.
Adaptive Scenario Discovery for Crowd Counting
Dec 06, 2018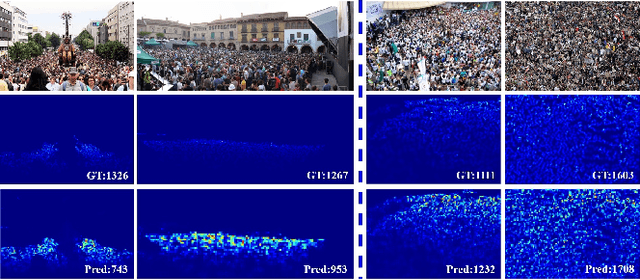
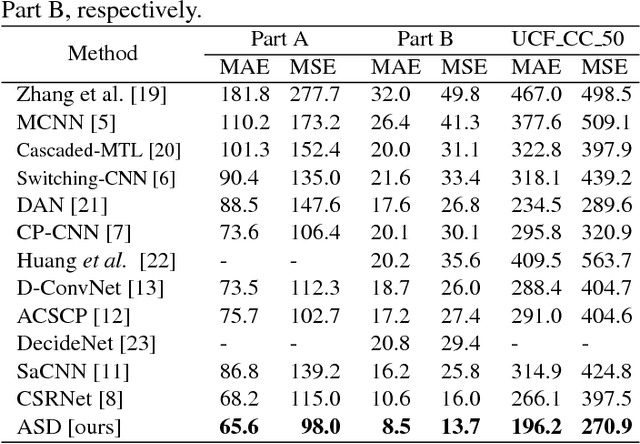
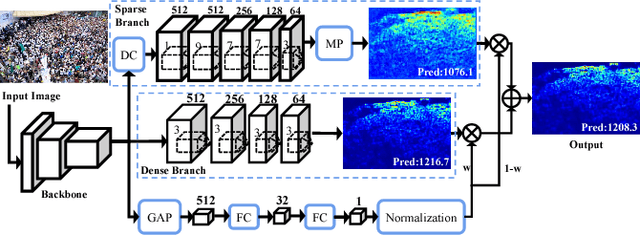
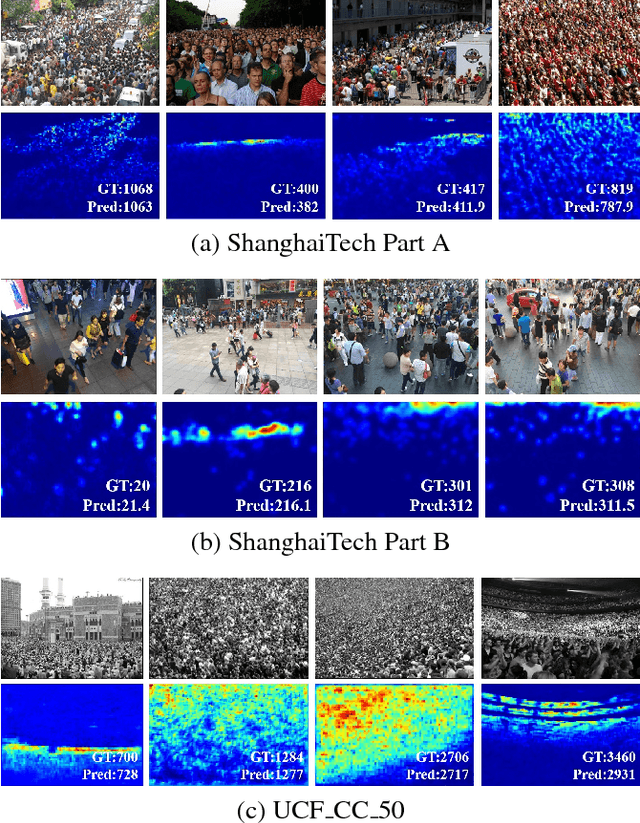
Abstract:Crowd counting, i.e., estimation number of pedestrian in crowd images, is emerging as an important research problem with the public security applications. A key ingredient in the design of crowd counting systems is the construction of counting models while being robust to various scenarios under facts such as camera perspective and physical barriers. In this paper, we present an adaptive scenario discovery framework for crowd counting. The system is structured with two parallel pathways that are trained with different sizes of receptive field to represent different scales and crowd densities. After ensuring that these components are present in the proper geometric configuration, a third branch is designed to adaptively recalibrate the pathway-wise responses by discovering and modeling the dynamic scenarios implicitly. Our system is able to represent highly variable crowd images and achieves state-of-the-art results in two challenging benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge