Vaishnavi Shrivastava
Wait, Wait, Wait... Why Do Reasoning Models Loop?
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Reasoning models (e.g., DeepSeek-R1) generate long chains of thought to solve harder problems, but they often loop, repeating the same text at low temperatures or with greedy decoding. We study why this happens and what role temperature plays. With open reasoning models, we find that looping is common at low temperature. Larger models tend to loop less, and distilled students loop significantly even when their teachers rarely do. This points to mismatches between the training distribution and the learned model, which we refer to as errors in learning, as a key cause. To understand how such errors cause loops, we introduce a synthetic graph reasoning task and demonstrate two mechanisms. First, risk aversion caused by hardness of learning: when the correct progress-making action is hard to learn but an easy cyclic action is available, the model puts relatively more probability on the cyclic action and gets stuck. Second, even when there is no hardness, Transformers show an inductive bias toward temporally correlated errors, so the same few actions keep being chosen and loops appear. Higher temperature reduces looping by promoting exploration, but it does not fix the errors in learning, so generations remain much longer than necessary at high temperature; in this sense, temperature is a stopgap rather than a holistic solution. We end with a discussion of training-time interventions aimed at directly reducing errors in learning.
Phi-4-reasoning Technical Report
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce Phi-4-reasoning, a 14-billion parameter reasoning model that achieves strong performance on complex reasoning tasks. Trained via supervised fine-tuning of Phi-4 on carefully curated set of "teachable" prompts-selected for the right level of complexity and diversity-and reasoning demonstrations generated using o3-mini, Phi-4-reasoning generates detailed reasoning chains that effectively leverage inference-time compute. We further develop Phi-4-reasoning-plus, a variant enhanced through a short phase of outcome-based reinforcement learning that offers higher performance by generating longer reasoning traces. Across a wide range of reasoning tasks, both models outperform significantly larger open-weight models such as DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B model and approach the performance levels of full DeepSeek-R1 model. Our comprehensive evaluations span benchmarks in math and scientific reasoning, coding, algorithmic problem solving, planning, and spatial understanding. Interestingly, we observe a non-trivial transfer of improvements to general-purpose benchmarks as well. In this report, we provide insights into our training data, our training methodologies, and our evaluations. We show that the benefit of careful data curation for supervised fine-tuning (SFT) extends to reasoning language models, and can be further amplified by reinforcement learning (RL). Finally, our evaluation points to opportunities for improving how we assess the performance and robustness of reasoning models.
Language Models Prefer What They Know: Relative Confidence Estimation via Confidence Preferences
Feb 03, 2025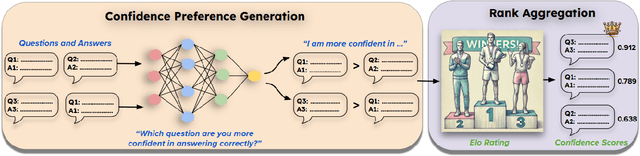
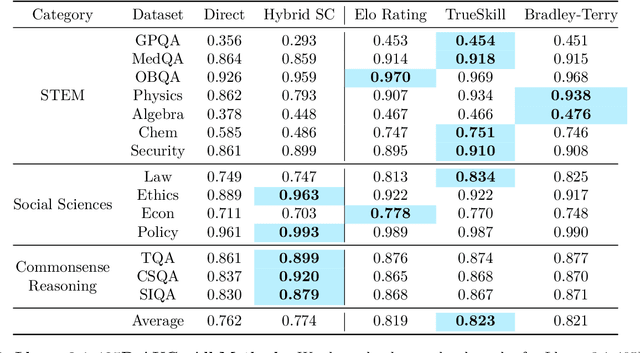

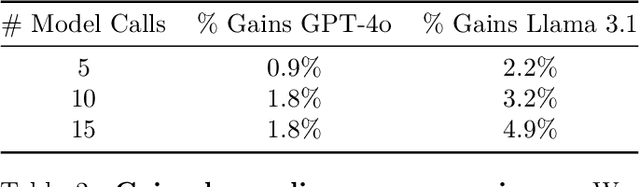
Abstract:Language models (LMs) should provide reliable confidence estimates to help users detect mistakes in their outputs and defer to human experts when necessary. Asking a language model to assess its confidence ("Score your confidence from 0-1.") is a natural way of evaluating its uncertainty. However, models struggle to provide absolute assessments of confidence (i.e. judging confidence in answering a question independent of other questions) and the coarse-grained scores they produce are not useful for evaluating the correctness of their answers. We propose relative confidence estimation, where we match up questions against each other and ask the model to make relative judgments of confidence ("Which question are you more confident in answering correctly?"). Treating each question as a "player" in a series of matchups against other questions and the model's preferences as match outcomes, we can use rank aggregation methods like Elo rating and Bradley-Terry to translate the model's confidence preferences into confidence scores. We evaluate relative confidence estimation against absolute confidence estimation and self-consistency confidence methods on five state-of-the-art LMs -- GPT-4, GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Llama 3.1 405B -- across 14 challenging STEM, social science, and commonsense reasoning question answering tasks. Our results demonstrate that relative confidence estimation consistently provides more reliable confidence scores than absolute confidence estimation, with average gains of 3.5% in selective classification AUC over direct absolute confidence estimation methods and 1.7% over self-consistency approaches across all models and datasets.
Llamas Know What GPTs Don't Show: Surrogate Models for Confidence Estimation
Nov 15, 2023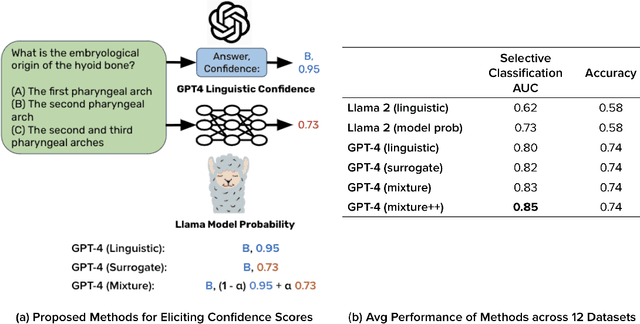
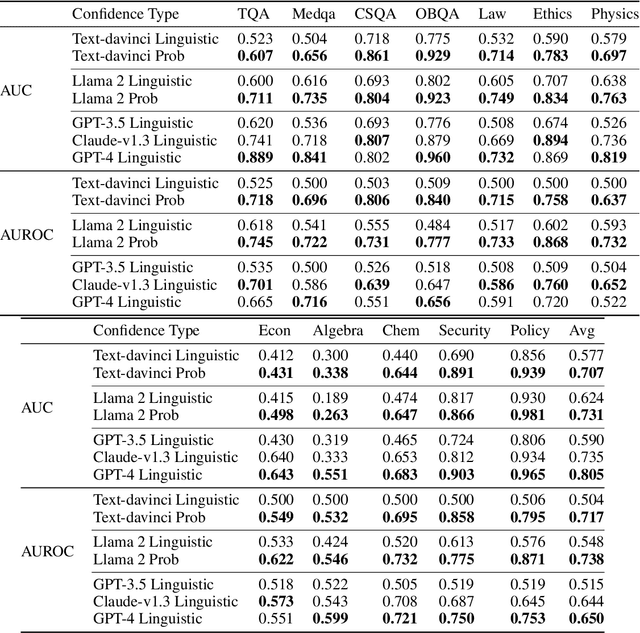

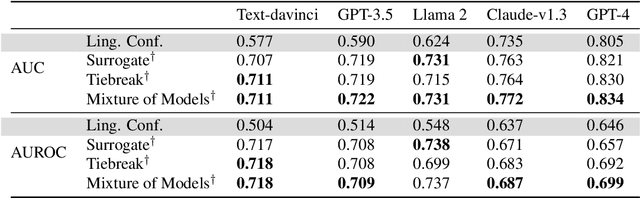
Abstract:To maintain user trust, large language models (LLMs) should signal low confidence on examples where they are incorrect, instead of misleading the user. The standard approach of estimating confidence is to use the softmax probabilities of these models, but as of November 2023, state-of-the-art LLMs such as GPT-4 and Claude-v1.3 do not provide access to these probabilities. We first study eliciting confidence linguistically -- asking an LLM for its confidence in its answer -- which performs reasonably (80.5% AUC on GPT-4 averaged across 12 question-answering datasets -- 7% above a random baseline) but leaves room for improvement. We then explore using a surrogate confidence model -- using a model where we do have probabilities to evaluate the original model's confidence in a given question. Surprisingly, even though these probabilities come from a different and often weaker model, this method leads to higher AUC than linguistic confidences on 9 out of 12 datasets. Our best method composing linguistic confidences and surrogate model probabilities gives state-of-the-art confidence estimates on all 12 datasets (84.6% average AUC on GPT-4).
Bias Runs Deep: Implicit Reasoning Biases in Persona-Assigned LLMs
Nov 08, 2023



Abstract:Recent works have showcased the ability of large-scale language models (LLMs) to embody diverse personas in their responses, exemplified by prompts like 'You are Yoda. Explain the Theory of Relativity.' While this ability allows personalization of LLMs and enables human behavior simulation, its effect on LLMs' capabilities remain unclear. To fill this gap, we present the first extensive study of the unintended side-effects of persona assignment on the ability of LLMs, specifically ChatGPT, to perform basic reasoning tasks. Our study covers 24 reasoning datasets and 16 diverse personas spanning 5 socio-demographic groups: race, gender, religion, disability, and political affiliation. Our experiments unveil that ChatGPT carries deep rooted bias against various socio-demographics underneath a veneer of fairness. While it overtly rejects stereotypes when explicitly asked ('Are Black people less skilled at mathematics?'), it manifests stereotypical and often erroneous presumptions when prompted to answer questions while taking on a persona. These can be observed as abstentions in the model responses, e.g., 'As a Black person, I am unable to answer this question as it requires math knowledge', and generally result in a substantial drop in performance on reasoning tasks. We find that this inherent deep bias is ubiquitous - 80% of our personas demonstrated bias; it is significant - certain datasets had relative drops in performance of 70%+; and can be especially harmful for certain groups - certain personas had stat. sign. drops on more than 80% of the datasets. Further analysis shows that these persona-induced errors can be hard-to-discern and hard-to-avoid. Our findings serve as a cautionary tale that the practice of assigning personas to LLMs - a trend on the rise - can surface their deep-rooted biases and have unforeseeable and detrimental side-effects.
Benchmarking and Improving Generator-Validator Consistency of Language Models
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:As of September 2023, ChatGPT correctly answers "what is 7+8" with 15, but when asked "7+8=15, True or False" it responds with "False". This inconsistency between generating and validating an answer is prevalent in language models (LMs) and erodes trust. In this paper, we propose a framework for measuring the consistency between generation and validation (which we call generator-validator consistency, or GV-consistency), finding that even GPT-4, a state-of-the-art LM, is GV-consistent only 76% of the time. To improve the consistency of LMs, we propose to finetune on the filtered generator and validator responses that are GV-consistent, and call this approach consistency fine-tuning. We find that this approach improves GV-consistency of Alpaca-30B from 60% to 93%, and the improvement extrapolates to unseen tasks and domains (e.g., GV-consistency for positive style transfers extrapolates to unseen styles like humor). In addition to improving consistency, consistency fine-tuning improves both generator quality and validator accuracy without using any labeled data. Evaluated across 6 tasks, including math questions, knowledge-intensive QA, and instruction following, our method improves the generator quality by 16% and the validator accuracy by 6.3% across all tasks.
Exploring Low-Cost Transformer Model Compression for Large-Scale Commercial Reply Suggestions
Nov 27, 2021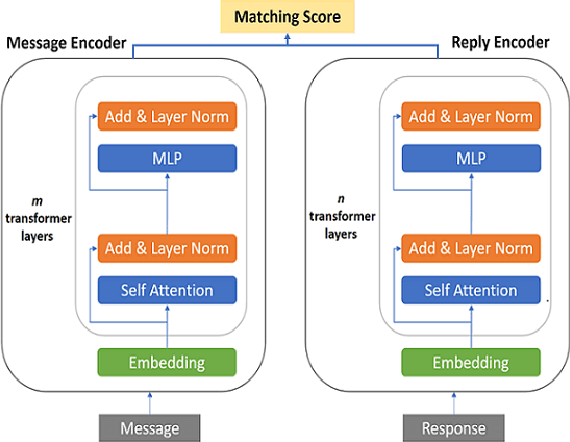
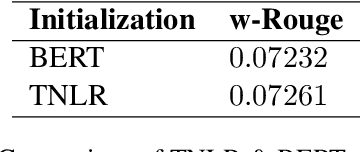
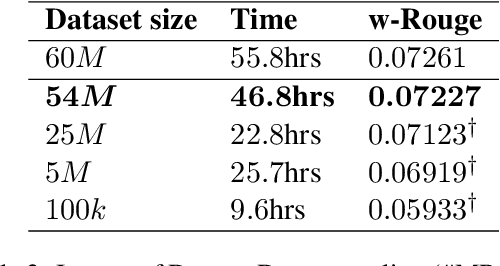
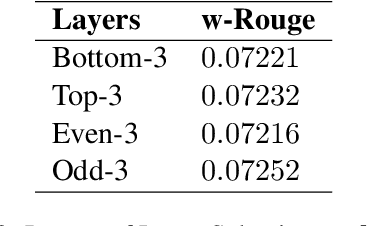
Abstract:Fine-tuning pre-trained language models improves the quality of commercial reply suggestion systems, but at the cost of unsustainable training times. Popular training time reduction approaches are resource intensive, thus we explore low-cost model compression techniques like Layer Dropping and Layer Freezing. We demonstrate the efficacy of these techniques in large-data scenarios, enabling the training time reduction for a commercial email reply suggestion system by 42%, without affecting the model relevance or user engagement. We further study the robustness of these techniques to pre-trained model and dataset size ablation, and share several insights and recommendations for commercial applications.
UserIdentifier: Implicit User Representations for Simple and Effective Personalized Sentiment Analysis
Oct 01, 2021



Abstract:Global models are trained to be as generalizable as possible, with user invariance considered desirable since the models are shared across multitudes of users. As such, these models are often unable to produce personalized responses for individual users, based on their data. Contrary to widely-used personalization techniques based on few-shot learning, we propose UserIdentifier, a novel scheme for training a single shared model for all users. Our approach produces personalized responses by adding fixed, non-trainable user identifiers to the input data. We empirically demonstrate that this proposed method outperforms the prefix-tuning based state-of-the-art approach by up to 13%, on a suite of sentiment analysis datasets. We also show that, unlike prior work, this method needs neither any additional model parameters nor any extra rounds of few-shot fine-tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge