Vésteinn Snæbjarnarson
Taxonomy-Aware Evaluation of Vision-Language Models
Apr 07, 2025
Abstract:When a vision-language model (VLM) is prompted to identify an entity depicted in an image, it may answer 'I see a conifer,' rather than the specific label 'norway spruce'. This raises two issues for evaluation: First, the unconstrained generated text needs to be mapped to the evaluation label space (i.e., 'conifer'). Second, a useful classification measure should give partial credit to less-specific, but not incorrect, answers ('norway spruce' being a type of 'conifer'). To meet these requirements, we propose a framework for evaluating unconstrained text predictions, such as those generated from a vision-language model, against a taxonomy. Specifically, we propose the use of hierarchical precision and recall measures to assess the level of correctness and specificity of predictions with regard to a taxonomy. Experimentally, we first show that existing text similarity measures do not capture taxonomic similarity well. We then develop and compare different methods to map textual VLM predictions onto a taxonomy. This allows us to compute hierarchical similarity measures between the generated text and the ground truth labels. Finally, we analyze modern VLMs on fine-grained visual classification tasks based on our proposed taxonomic evaluation scheme.
Counterfactual Generation from Language Models
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Understanding and manipulating the causal generation mechanisms in language models is essential for controlling their behavior. Previous work has primarily relied on techniques such as representation surgery -- e.g., model ablations or manipulation of linear subspaces tied to specific concepts -- to intervene on these models. To understand the impact of interventions precisely, it is useful to examine counterfactuals -- e.g., how a given sentence would have appeared had it been generated by the model following a specific intervention. We highlight that counterfactual reasoning is conceptually distinct from interventions, as articulated in Pearl's causal hierarchy. Based on this observation, we propose a framework for generating true string counterfactuals by reformulating language models as Generalized Structural-equation. Models using the Gumbel-max trick. This allows us to model the joint distribution over original strings and their counterfactuals resulting from the same instantiation of the sampling noise. We develop an algorithm based on hindsight Gumbel sampling that allows us to infer the latent noise variables and generate counterfactuals of observed strings. Our experiments demonstrate that the approach produces meaningful counterfactuals while at the same time showing that commonly used intervention techniques have considerable undesired side effects.
Activation Scaling for Steering and Interpreting Language Models
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:Given the prompt "Rome is in", can we steer a language model to flip its prediction of an incorrect token "France" to a correct token "Italy" by only multiplying a few relevant activation vectors with scalars? We argue that successfully intervening on a model is a prerequisite for interpreting its internal workings. Concretely, we establish a three-term objective: a successful intervention should flip the correct with the wrong token and vice versa (effectiveness), and leave other tokens unaffected (faithfulness), all while being sparse (minimality). Using gradient-based optimization, this objective lets us learn (and later evaluate) a specific kind of efficient and interpretable intervention: activation scaling only modifies the signed magnitude of activation vectors to strengthen, weaken, or reverse the steering directions already encoded in the model. On synthetic tasks, this intervention performs comparably with steering vectors in terms of effectiveness and faithfulness, but is much more minimal allowing us to pinpoint interpretable model components. We evaluate activation scaling from different angles, compare performance on different datasets, and make activation scalars a learnable function of the activation vectors themselves to generalize to varying-length prompts.
LoQT: Low Rank Adapters for Quantized Training
May 26, 2024



Abstract:Training of large neural networks requires significant computational resources. Despite advances using low-rank adapters and quantization, pretraining of models such as LLMs on consumer hardware has not been possible without model sharding, offloading during training, or per-layer gradient updates. To address these limitations, we propose LoQT, a method for efficiently training quantized models. LoQT uses gradient-based tensor factorization to initialize low-rank trainable weight matrices that are periodically merged into quantized full-rank weight matrices. Our approach is suitable for both pretraining and fine-tuning of models, which we demonstrate experimentally for language modeling and downstream task adaptation. We find that LoQT enables efficient training of models up to 7B parameters on a consumer-grade 24GB GPU. We also demonstrate the feasibility of training a 13B parameter model using per-layer gradient updates on the same hardware.
Context versus Prior Knowledge in Language Models
Apr 06, 2024



Abstract:To answer a question, language models often need to integrate prior knowledge learned during pretraining and new information presented in context. We hypothesize that models perform this integration in a predictable way across different questions and contexts: models will rely more on prior knowledge for questions about entities (e.g., persons, places, etc.) that they are more familiar with due to higher exposure in the training corpus, and be more easily persuaded by some contexts than others. To formalize this problem, we propose two mutual information-based metrics to measure a model's dependency on a context and on its prior about an entity: first, the persuasion score of a given context represents how much a model depends on the context in its decision, and second, the susceptibility score of a given entity represents how much the model can be swayed away from its original answer distribution about an entity. Following well-established measurement modeling methods, we empirically test for the validity and reliability of these metrics. Finally, we explore and find a relationship between the scores and the model's expected familiarity with an entity, and provide two use cases to illustrate their benefits.
Byte-Level Grammatical Error Correction Using Synthetic and Curated Corpora
May 29, 2023



Abstract:Grammatical error correction (GEC) is the task of correcting typos, spelling, punctuation and grammatical issues in text. Approaching the problem as a sequence-to-sequence task, we compare the use of a common subword unit vocabulary and byte-level encoding. Initial synthetic training data is created using an error-generating pipeline, and used for finetuning two subword-level models and one byte-level model. Models are then finetuned further on hand-corrected error corpora, including texts written by children, university students, dyslexic and second-language writers, and evaluated over different error types and origins. We show that a byte-level model enables higher correction quality than a subword approach, not only for simple spelling errors, but also for more complex semantic, stylistic and grammatical issues. In particular, initial training on synthetic corpora followed by finetuning on a relatively small parallel corpus of real-world errors helps the byte-level model correct a wide range of commonly occurring errors. Our experiments are run for the Icelandic language but should hold for other similar languages, particularly morphologically rich ones.
Transfer to a Low-Resource Language via Close Relatives: The Case Study on Faroese
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:Multilingual language models have pushed state-of-the-art in cross-lingual NLP transfer. The majority of zero-shot cross-lingual transfer, however, use one and the same massively multilingual transformer (e.g., mBERT or XLM-R) to transfer to all target languages, irrespective of their typological, etymological, and phylogenetic relations to other languages. In particular, readily available data and models of resource-rich sibling languages are often ignored. In this work, we empirically show, in a case study for Faroese -- a low-resource language from a high-resource language family -- that by leveraging the phylogenetic information and departing from the 'one-size-fits-all' paradigm, one can improve cross-lingual transfer to low-resource languages. In particular, we leverage abundant resources of other Scandinavian languages (i.e., Danish, Norwegian, Swedish, and Icelandic) for the benefit of Faroese. Our evaluation results show that we can substantially improve the transfer performance to Faroese by exploiting data and models of closely-related high-resource languages. Further, we release a new web corpus of Faroese and Faroese datasets for named entity recognition (NER), semantic text similarity (STS), and new language models trained on all Scandinavian languages.
Discriminative Class Tokens for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Mar 30, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image diffusion models have enabled the generation of diverse and high-quality images. However, generated images often fall short of depicting subtle details and are susceptible to errors due to ambiguity in the input text. One way of alleviating these issues is to train diffusion models on class-labeled datasets. This comes with a downside, doing so limits their expressive power: (i) supervised datasets are generally small compared to large-scale scraped text-image datasets on which text-to-image models are trained, and so the quality and diversity of generated images are severely affected, or (ii) the input is a hard-coded label, as opposed to free-form text, which limits the control over the generated images. In this work, we propose a non-invasive fine-tuning technique that capitalizes on the expressive potential of free-form text while achieving high accuracy through discriminative signals from a pretrained classifier, which guides the generation. This is done by iteratively modifying the embedding of a single input token of a text-to-image diffusion model, using the classifier, by steering generated images toward a given target class. Our method is fast compared to prior fine-tuning methods and does not require a collection of in-class images or retraining of a noise-tolerant classifier. We evaluate our method extensively, showing that the generated images are: (i) more accurate and of higher quality than standard diffusion models, (ii) can be used to augment training data in a low-resource setting, and (iii) reveal information about the data used to train the guiding classifier. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/idansc/discriminative_class_tokens}
Assessing Neural Network Robustness via Adversarial Pivotal Tuning
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:The ability to assess the robustness of image classifiers to a diverse set of manipulations is essential to their deployment in the real world. Recently, semantic manipulations of real images have been considered for this purpose, as they may not arise using standard adversarial settings. However, such semantic manipulations are often limited to style, color or attribute changes. While expressive, these manipulations do not consider the full capacity of a pretrained generator to affect adversarial image manipulations. In this work, we aim at leveraging the full capacity of a pretrained image generator to generate highly detailed, diverse and photorealistic image manipulations. Inspired by recent GAN-based image inversion methods, we propose a method called Adversarial Pivotal Tuning (APT). APT first finds a pivot latent space input to a pretrained generator that best reconstructs an input image. It then adjusts the weights of the generator to create small, but semantic, manipulations which fool a pretrained classifier. Crucially, APT changes both the input and the weights of the pretrained generator, while preserving its expressive latent editing capability, thus allowing the use of its full capacity in creating semantic adversarial manipulations. We demonstrate that APT generates a variety of semantic image manipulations, which preserve the input image class, but which fool a variety of pretrained classifiers. We further demonstrate that classifiers trained to be robust to other robustness benchmarks, are not robust to our generated manipulations and propose an approach to improve the robustness towards our generated manipulations. Code available at: https://captaine.github.io/apt/
Cross-Lingual QA as a Stepping Stone for Monolingual Open QA in Icelandic
Jul 05, 2022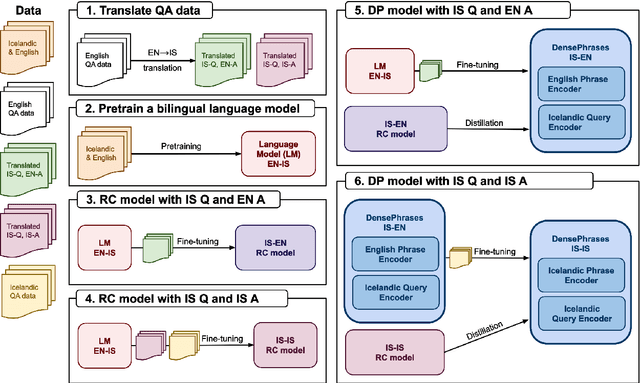
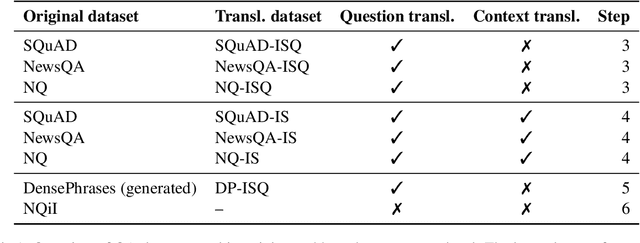
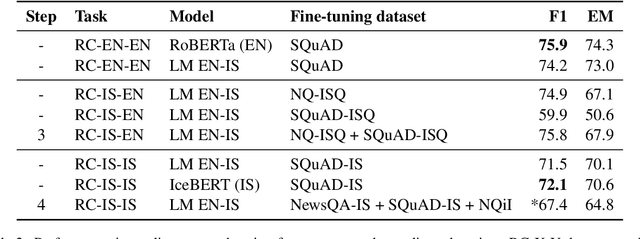
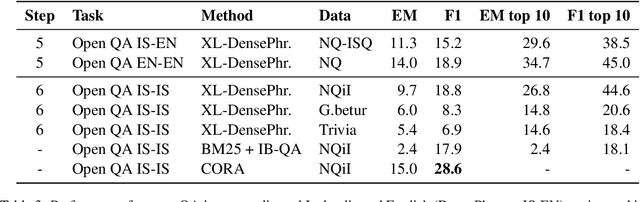
Abstract:It can be challenging to build effective open question answering (open QA) systems for languages other than English, mainly due to a lack of labeled data for training. We present a data efficient method to bootstrap such a system for languages other than English. Our approach requires only limited QA resources in the given language, along with machine-translated data, and at least a bilingual language model. To evaluate our approach, we build such a system for the Icelandic language and evaluate performance over trivia style datasets. The corpora used for training are English in origin but machine translated into Icelandic. We train a bilingual Icelandic/English language model to embed English context and Icelandic questions following methodology introduced with DensePhrases (Lee et al., 2021). The resulting system is an open domain cross-lingual QA system between Icelandic and English. Finally, the system is adapted for Icelandic only open QA, demonstrating how it is possible to efficiently create an open QA system with limited access to curated datasets in the language of interest.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge