Mads Toftrup
LoQT: Low Rank Adapters for Quantized Training
May 26, 2024



Abstract:Training of large neural networks requires significant computational resources. Despite advances using low-rank adapters and quantization, pretraining of models such as LLMs on consumer hardware has not been possible without model sharding, offloading during training, or per-layer gradient updates. To address these limitations, we propose LoQT, a method for efficiently training quantized models. LoQT uses gradient-based tensor factorization to initialize low-rank trainable weight matrices that are periodically merged into quantized full-rank weight matrices. Our approach is suitable for both pretraining and fine-tuning of models, which we demonstrate experimentally for language modeling and downstream task adaptation. We find that LoQT enables efficient training of models up to 7B parameters on a consumer-grade 24GB GPU. We also demonstrate the feasibility of training a 13B parameter model using per-layer gradient updates on the same hardware.
A reproduction of Apple's bi-directional LSTM models for language identification in short strings
Feb 11, 2021
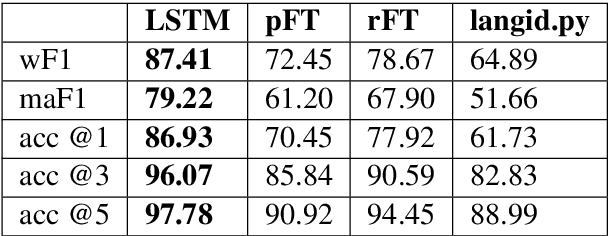
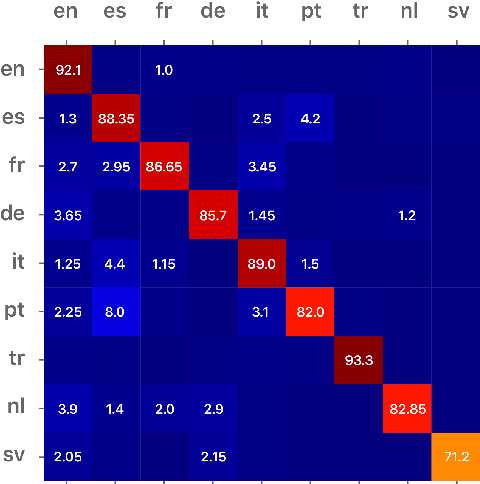
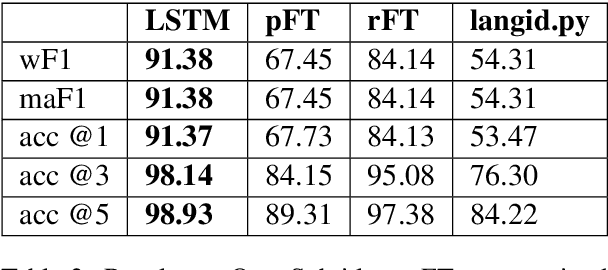
Abstract:Language Identification is the task of identifying a document's language. For applications like automatic spell checker selection, language identification must use very short strings such as text message fragments. In this work, we reproduce a language identification architecture that Apple briefly sketched in a blog post. We confirm the bi-LSTM model's performance and find that it outperforms current open-source language identifiers. We further find that its language identification mistakes are due to confusion between related languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge