Tzofi Klinghoffer
What if Eye...? Computationally Recreating Vision Evolution
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Vision systems in nature show remarkable diversity, from simple light-sensitive patches to complex camera eyes with lenses. While natural selection has produced these eyes through countless mutations over millions of years, they represent just one set of realized evolutionary paths. Testing hypotheses about how environmental pressures shaped eye evolution remains challenging since we cannot experimentally isolate individual factors. Computational evolution offers a way to systematically explore alternative trajectories. Here we show how environmental demands drive three fundamental aspects of visual evolution through an artificial evolution framework that co-evolves both physical eye structure and neural processing in embodied agents. First, we demonstrate computational evidence that task specific selection drives bifurcation in eye evolution - orientation tasks like navigation in a maze leads to distributed compound-type eyes while an object discrimination task leads to the emergence of high-acuity camera-type eyes. Second, we reveal how optical innovations like lenses naturally emerge to resolve fundamental tradeoffs between light collection and spatial precision. Third, we uncover systematic scaling laws between visual acuity and neural processing, showing how task complexity drives coordinated evolution of sensory and computational capabilities. Our work introduces a novel paradigm that illuminates evolutionary principles shaping vision by creating targeted single-player games where embodied agents must simultaneously evolve visual systems and learn complex behaviors. Through our unified genetic encoding framework, these embodied agents serve as next-generation hypothesis testing machines while providing a foundation for designing manufacturable bio-inspired vision systems.
Blurred LiDAR for Sharper 3D: Robust Handheld 3D Scanning with Diffuse LiDAR and RGB
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:3D surface reconstruction is essential across applications of virtual reality, robotics, and mobile scanning. However, RGB-based reconstruction often fails in low-texture, low-light, and low-albedo scenes. Handheld LiDARs, now common on mobile devices, aim to address these challenges by capturing depth information from time-of-flight measurements of a coarse grid of projected dots. Yet, these sparse LiDARs struggle with scene coverage on limited input views, leaving large gaps in depth information. In this work, we propose using an alternative class of "blurred" LiDAR that emits a diffuse flash, greatly improving scene coverage but introducing spatial ambiguity from mixed time-of-flight measurements across a wide field of view. To handle these ambiguities, we propose leveraging the complementary strengths of diffuse LiDAR with RGB. We introduce a Gaussian surfel-based rendering framework with a scene-adaptive loss function that dynamically balances RGB and diffuse LiDAR signals. We demonstrate that, surprisingly, diffuse LiDAR can outperform traditional sparse LiDAR, enabling robust 3D scanning with accurate color and geometry estimation in challenging environments.
Epi-NAF: Enhancing Neural Attenuation Fields for Limited-Angle CT with Epipolar Consistency Conditions
Nov 09, 2024



Abstract:Neural field methods, initially successful in the inverse rendering domain, have recently been extended to CT reconstruction, marking a paradigm shift from traditional techniques. While these approaches deliver state-of-the-art results in sparse-view CT reconstruction, they struggle in limited-angle settings, where input projections are captured over a restricted angle range. We present a novel loss term based on consistency conditions between corresponding epipolar lines in X-ray projection images, aimed at regularizing neural attenuation field optimization. By enforcing these consistency conditions, our approach, Epi-NAF, propagates supervision from input views within the limited-angle range to predicted projections over the full cone-beam CT range. This loss results in both qualitative and quantitative improvements in reconstruction compared to baseline methods.
PlatoNeRF: 3D Reconstruction in Plato's Cave via Single-View Two-Bounce Lidar
Dec 21, 2023



Abstract:3D reconstruction from a single-view is challenging because of the ambiguity from monocular cues and lack of information about occluded regions. Neural radiance fields (NeRF), while popular for view synthesis and 3D reconstruction, are typically reliant on multi-view images. Existing methods for single-view 3D reconstruction with NeRF rely on either data priors to hallucinate views of occluded regions, which may not be physically accurate, or shadows observed by RGB cameras, which are difficult to detect in ambient light and low albedo backgrounds. We propose using time-of-flight data captured by a single-photon avalanche diode to overcome these limitations. Our method models two-bounce optical paths with NeRF, using lidar transient data for supervision. By leveraging the advantages of both NeRF and two-bounce light measured by lidar, we demonstrate that we can reconstruct visible and occluded geometry without data priors or reliance on controlled ambient lighting or scene albedo. In addition, we demonstrate improved generalization under practical constraints on sensor spatial- and temporal-resolution. We believe our method is a promising direction as single-photon lidars become ubiquitous on consumer devices, such as phones, tablets, and headsets.
DISeR: Designing Imaging Systems with Reinforcement Learning
Sep 25, 2023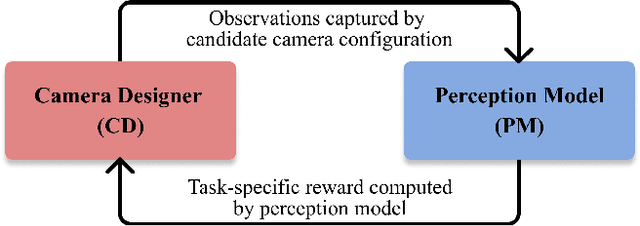
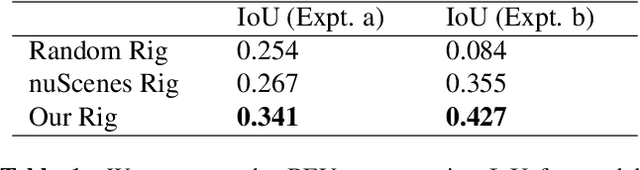
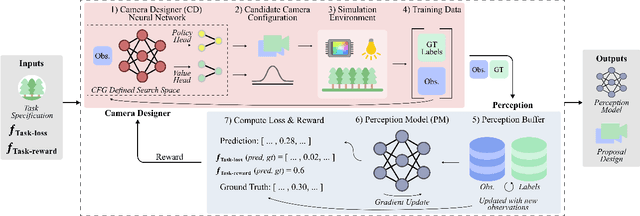

Abstract:Imaging systems consist of cameras to encode visual information about the world and perception models to interpret this encoding. Cameras contain (1) illumination sources, (2) optical elements, and (3) sensors, while perception models use (4) algorithms. Directly searching over all combinations of these four building blocks to design an imaging system is challenging due to the size of the search space. Moreover, cameras and perception models are often designed independently, leading to sub-optimal task performance. In this paper, we formulate these four building blocks of imaging systems as a context-free grammar (CFG), which can be automatically searched over with a learned camera designer to jointly optimize the imaging system with task-specific perception models. By transforming the CFG to a state-action space, we then show how the camera designer can be implemented with reinforcement learning to intelligently search over the combinatorial space of possible imaging system configurations. We demonstrate our approach on two tasks, depth estimation and camera rig design for autonomous vehicles, showing that our method yields rigs that outperform industry-wide standards. We believe that our proposed approach is an important step towards automating imaging system design.
Towards Viewpoint Robustness in Bird's Eye View Segmentation
Sep 11, 2023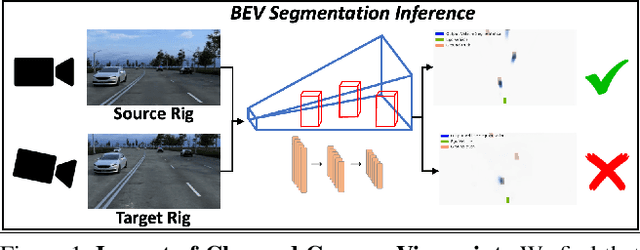
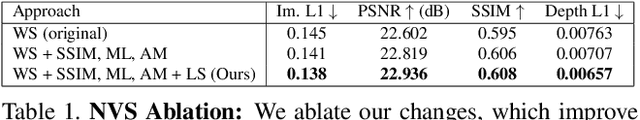

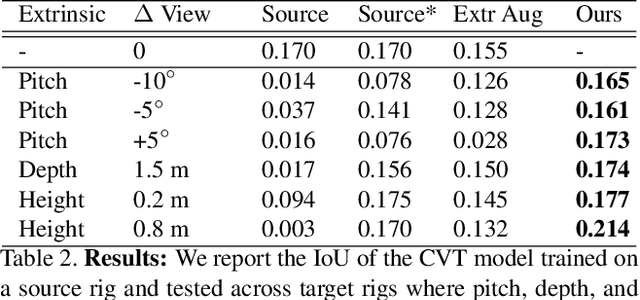
Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AV) require that neural networks used for perception be robust to different viewpoints if they are to be deployed across many types of vehicles without the repeated cost of data collection and labeling for each. AV companies typically focus on collecting data from diverse scenarios and locations, but not camera rig configurations, due to cost. As a result, only a small number of rig variations exist across most fleets. In this paper, we study how AV perception models are affected by changes in camera viewpoint and propose a way to scale them across vehicle types without repeated data collection and labeling. Using bird's eye view (BEV) segmentation as a motivating task, we find through extensive experiments that existing perception models are surprisingly sensitive to changes in camera viewpoint. When trained with data from one camera rig, small changes to pitch, yaw, depth, or height of the camera at inference time lead to large drops in performance. We introduce a technique for novel view synthesis and use it to transform collected data to the viewpoint of target rigs, allowing us to train BEV segmentation models for diverse target rigs without any additional data collection or labeling cost. To analyze the impact of viewpoint changes, we leverage synthetic data to mitigate other gaps (content, ISP, etc). Our approach is then trained on real data and evaluated on synthetic data, enabling evaluation on diverse target rigs. We release all data for use in future work. Our method is able to recover an average of 14.7% of the IoU that is otherwise lost when deploying to new rigs.
ORCa: Glossy Objects as Radiance Field Cameras
Dec 12, 2022
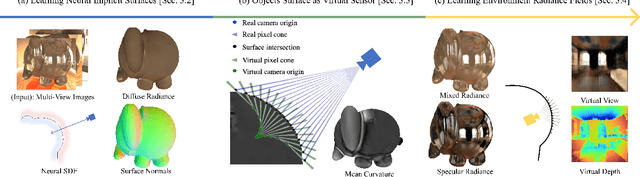
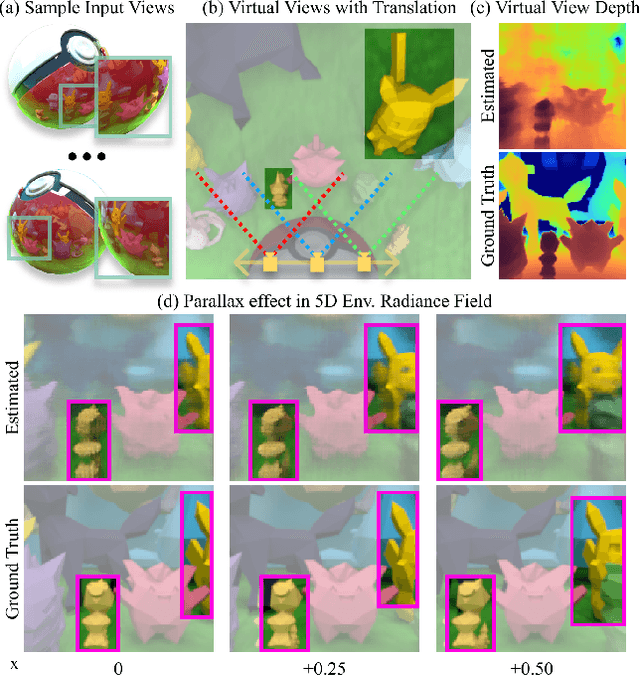
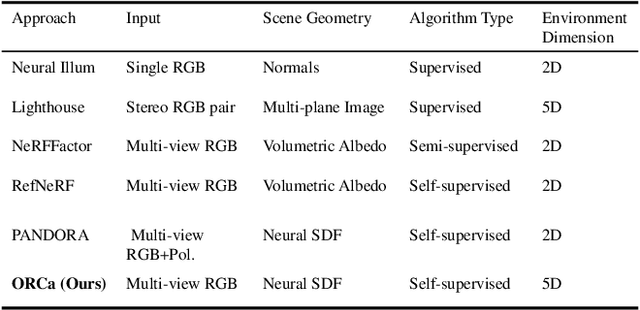
Abstract:Reflections on glossy objects contain valuable and hidden information about the surrounding environment. By converting these objects into cameras, we can unlock exciting applications, including imaging beyond the camera's field-of-view and from seemingly impossible vantage points, e.g. from reflections on the human eye. However, this task is challenging because reflections depend jointly on object geometry, material properties, the 3D environment, and the observer viewing direction. Our approach converts glossy objects with unknown geometry into radiance-field cameras to image the world from the object's perspective. Our key insight is to convert the object surface into a virtual sensor that captures cast reflections as a 2D projection of the 5D environment radiance field visible to the object. We show that recovering the environment radiance fields enables depth and radiance estimation from the object to its surroundings in addition to beyond field-of-view novel-view synthesis, i.e. rendering of novel views that are only directly-visible to the glossy object present in the scene, but not the observer. Moreover, using the radiance field we can image around occluders caused by close-by objects in the scene. Our method is trained end-to-end on multi-view images of the object and jointly estimates object geometry, diffuse radiance, and the 5D environment radiance field.
Physics vs. Learned Priors: Rethinking Camera and Algorithm Design for Task-Specific Imaging
Apr 21, 2022



Abstract:Cameras were originally designed using physics-based heuristics to capture aesthetic images. In recent years, there has been a transformation in camera design from being purely physics-driven to increasingly data-driven and task-specific. In this paper, we present a framework to understand the building blocks of this nascent field of end-to-end design of camera hardware and algorithms. As part of this framework, we show how methods that exploit both physics and data have become prevalent in imaging and computer vision, underscoring a key trend that will continue to dominate the future of task-specific camera design. Finally, we share current barriers to progress in end-to-end design, and hypothesize how these barriers can be overcome.
Physically Disentangled Representations
Apr 11, 2022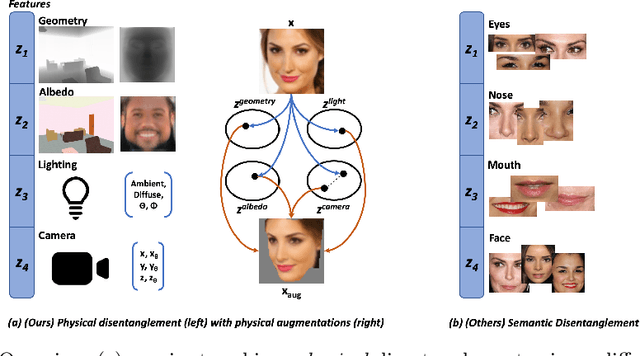

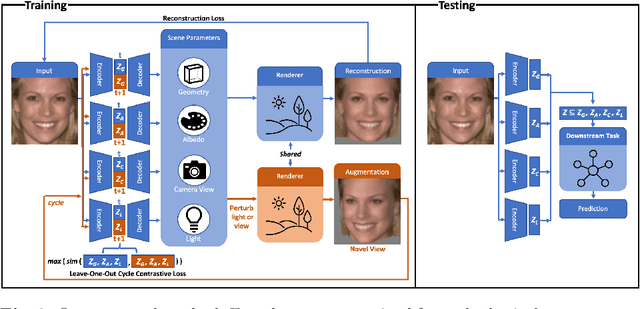

Abstract:State-of-the-art methods in generative representation learning yield semantic disentanglement, but typically do not consider physical scene parameters, such as geometry, albedo, lighting, or camera. We posit that inverse rendering, a way to reverse the rendering process to recover scene parameters from an image, can also be used to learn physically disentangled representations of scenes without supervision. In this paper, we show the utility of inverse rendering in learning representations that yield improved accuracy on downstream clustering, linear classification, and segmentation tasks with the help of our novel Leave-One-Out, Cycle Contrastive loss (LOOCC), which improves disentanglement of scene parameters and robustness to out-of-distribution lighting and viewpoints. We perform a comparison of our method with other generative representation learning methods across a variety of downstream tasks, including face attribute classification, emotion recognition, identification, face segmentation, and car classification. Our physically disentangled representations yield higher accuracy than semantically disentangled alternatives across all tasks and by as much as 18%. We hope that this work will motivate future research in applying advances in inverse rendering and 3D understanding to representation learning.
Towards Learning Neural Representations from Shadows
Mar 29, 2022
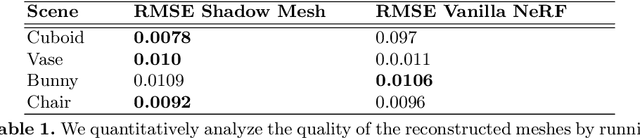
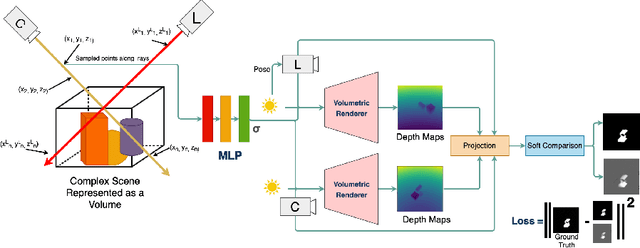

Abstract:We present a method that learns neural scene representations from only shadows present in the scene. While traditional shape-from-shadow (SfS) algorithms reconstruct geometry from shadows, they assume a fixed scanning setup and fail to generalize to complex scenes. Neural rendering algorithms, on the other hand, rely on photometric consistency between RGB images but largely ignore physical cues such as shadows, which have been shown to provide valuable information about the scene. We observe that shadows are a powerful cue that can constrain neural scene representations to learn SfS, and even outperform NeRF to reconstruct otherwise hidden geometry. We propose a graphics-inspired differentiable approach to render accurate shadows with volumetric rendering, predicting a shadow map that can be compared to the ground truth shadow. Even with just binary shadow maps, we show that neural rendering can localize the object and estimate coarse geometry. Our approach reveals that sparse cues in images can be used to estimate geometry using differentiable volumetric rendering. Moreover, our framework is highly generalizable and can work alongside existing 3D reconstruction techniques that otherwise only use photometric consistency. Our code is made available in our supplementary materials.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge