Takenori Yoshimura
Embedding a Differentiable Mel-cepstral Synthesis Filter to a Neural Speech Synthesis System
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:This paper integrates a classic mel-cepstral synthesis filter into a modern neural speech synthesis system towards end-to-end controllable speech synthesis. Since the mel-cepstral synthesis filter is explicitly embedded in neural waveform models in the proposed system, both voice characteristics and the pitch of synthesized speech are highly controlled via a frequency warping parameter and fundamental frequency, respectively. We implement the mel-cepstral synthesis filter as a differentiable and GPU-friendly module to enable the acoustic and waveform models in the proposed system to be simultaneously optimized in an end-to-end manner. Experiments show that the proposed system improves speech quality from a baseline system maintaining controllability. The core PyTorch modules used in the experiments will be publicly available on GitHub.
ESPnet2-TTS: Extending the Edge of TTS Research
Oct 15, 2021



Abstract:This paper describes ESPnet2-TTS, an end-to-end text-to-speech (E2E-TTS) toolkit. ESPnet2-TTS extends our earlier version, ESPnet-TTS, by adding many new features, including: on-the-fly flexible pre-processing, joint training with neural vocoders, and state-of-the-art TTS models with extensions like full-band E2E text-to-waveform modeling, which simplify the training pipeline and further enhance TTS performance. The unified design of our recipes enables users to quickly reproduce state-of-the-art E2E-TTS results. We also provide many pre-trained models in a unified Python interface for inference, offering a quick means for users to generate baseline samples and build demos. Experimental evaluations with English and Japanese corpora demonstrate that our provided models synthesize utterances comparable to ground-truth ones, achieving state-of-the-art TTS performance. The toolkit is available online at https://github.com/espnet/espnet.
Neural Sequence-to-Sequence Speech Synthesis Using a Hidden Semi-Markov Model Based Structured Attention Mechanism
Aug 31, 2021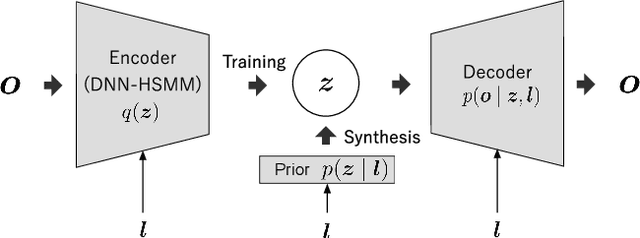
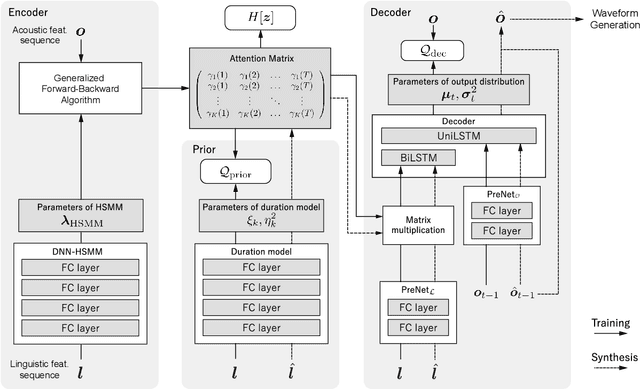
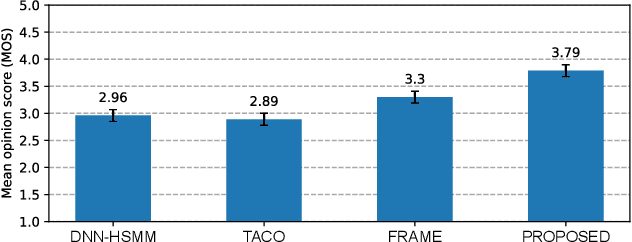
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) model integrating the structure of Hidden Semi-Markov Models (HSMMs) into its attention mechanism. In speech synthesis, it has been shown that methods based on Seq2Seq models using deep neural networks can synthesize high quality speech under the appropriate conditions. However, several essential problems still have remained, i.e., requiring large amounts of training data due to an excessive degree for freedom in alignment (mapping function between two sequences), and the difficulty in handling duration due to the lack of explicit duration modeling. The proposed method defines a generative models to realize the simultaneous optimization of alignments and model parameters based on the Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) framework, and provides monotonic alignments and explicit duration modeling based on the structure of HSMM. The proposed method can be regarded as an integration of Hidden Markov Model (HMM) based speech synthesis and deep learning based speech synthesis using Seq2Seq models, incorporating both the benefits. Subjective evaluation experiments showed that the proposed method obtained higher mean opinion scores than Tacotron 2 on relatively small amount of training data.
End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition Integrated With CTC-Based Voice Activity Detection
Feb 14, 2020



Abstract:This paper integrates a voice activity detection (VAD) function with end-to-end automatic speech recognition toward an online speech interface and transcribing very long audio recordings. We focus on connectionist temporal classification (CTC) and its extension of CTC/attention architectures. As opposed to an attention-based architecture, input-synchronous label prediction can be performed based on a greedy search with the CTC (pre-)softmax output. This prediction includes consecutive long blank labels, which can be regarded as a non-speech region. We use the labels as a cue for detecting speech segments with simple thresholding. The threshold value is directly related to the length of a non-speech region, which is more intuitive and easier to control than conventional VAD hyperparameters. Experimental results on unsegmented data show that the proposed method outperformed the baseline methods using the conventional energy-based and neural-network-based VAD methods and achieved an RTF less than 0.2. The proposed method is publicly available.
ESPnet-TTS: Unified, Reproducible, and Integratable Open Source End-to-End Text-to-Speech Toolkit
Oct 24, 2019



Abstract:This paper introduces a new end-to-end text-to-speech (E2E-TTS) toolkit named ESPnet-TTS, which is an extension of the open-source speech processing toolkit ESPnet. The toolkit supports state-of-the-art E2E-TTS models, including Tacotron~2, Transformer TTS, and FastSpeech, and also provides recipes inspired by the Kaldi automatic speech recognition (ASR) toolkit. The recipes are based on the design unified with the ESPnet ASR recipe, providing high reproducibility. The toolkit also provides pre-trained models and samples of all of the recipes so that users can use it as a baseline. Furthermore, the unified design enables the integration of ASR functions with TTS, e.g., ASR-based objective evaluation and semi-supervised learning with both ASR and TTS models. This paper describes the design of the toolkit and experimental evaluation in comparison with other toolkits. The experimental results show that our best model outperforms other toolkits, resulting in a mean opinion score (MOS) of 4.25 on the LJSpeech dataset. The toolkit is available on GitHub.
A Comparative Study on Transformer vs RNN in Speech Applications
Sep 28, 2019



Abstract:Sequence-to-sequence models have been widely used in end-to-end speech processing, for example, automatic speech recognition (ASR), speech translation (ST), and text-to-speech (TTS). This paper focuses on an emergent sequence-to-sequence model called Transformer, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in neural machine translation and other natural language processing applications. We undertook intensive studies in which we experimentally compared and analyzed Transformer and conventional recurrent neural networks (RNN) in a total of 15 ASR, one multilingual ASR, one ST, and two TTS benchmarks. Our experiments revealed various training tips and significant performance benefits obtained with Transformer for each task including the surprising superiority of Transformer in 13/15 ASR benchmarks in comparison with RNN. We are preparing to release Kaldi-style reproducible recipes using open source and publicly available datasets for all the ASR, ST, and TTS tasks for the community to succeed our exciting outcomes.
* Accepted at ASRU 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge