Kazuhiro Nakamura
Embedding a Differentiable Mel-cepstral Synthesis Filter to a Neural Speech Synthesis System
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:This paper integrates a classic mel-cepstral synthesis filter into a modern neural speech synthesis system towards end-to-end controllable speech synthesis. Since the mel-cepstral synthesis filter is explicitly embedded in neural waveform models in the proposed system, both voice characteristics and the pitch of synthesized speech are highly controlled via a frequency warping parameter and fundamental frequency, respectively. We implement the mel-cepstral synthesis filter as a differentiable and GPU-friendly module to enable the acoustic and waveform models in the proposed system to be simultaneously optimized in an end-to-end manner. Experiments show that the proposed system improves speech quality from a baseline system maintaining controllability. The core PyTorch modules used in the experiments will be publicly available on GitHub.
Fast and High-Quality Singing Voice Synthesis System based on Convolutional Neural Networks
Oct 24, 2019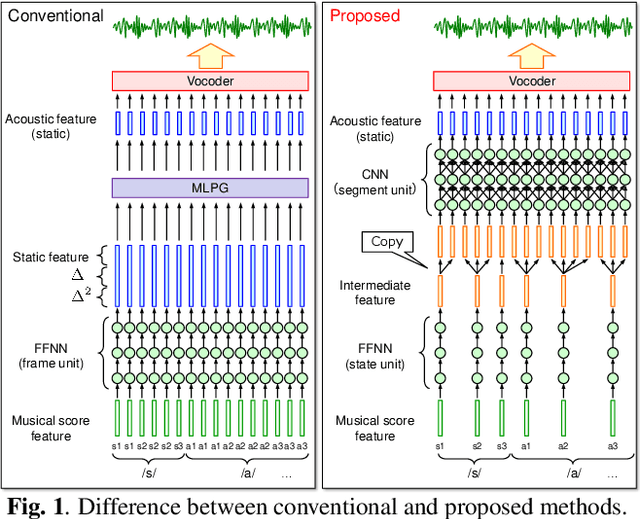
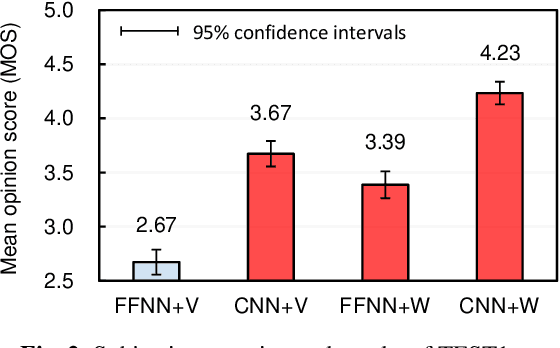
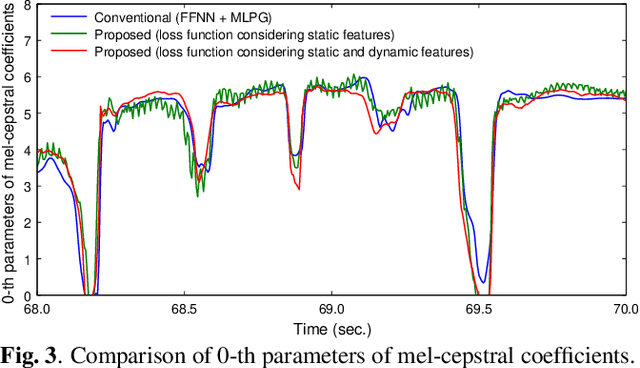
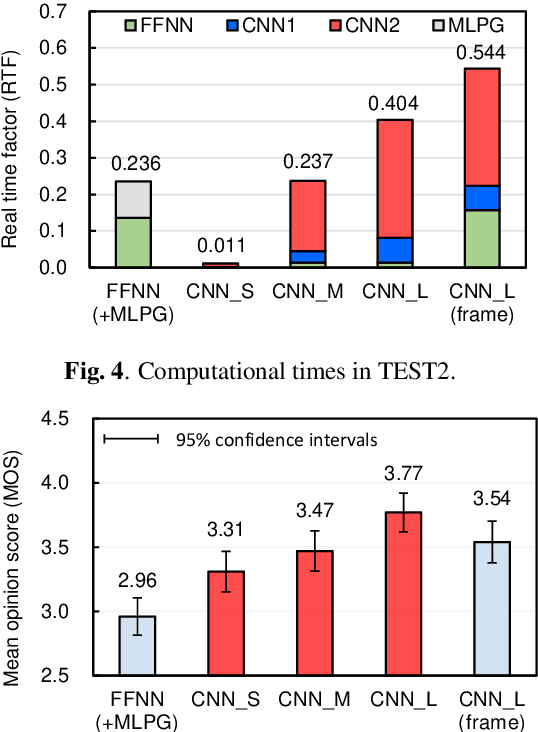
Abstract:The present paper describes singing voice synthesis based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Singing voice synthesis systems based on deep neural networks (DNNs) are currently being proposed and are improving the naturalness of synthesized singing voices. As singing voices represent a rich form of expression, a powerful technique to model them accurately is required. In the proposed technique, long-term dependencies of singing voices are modeled by CNNs. An acoustic feature sequence is generated for each segment that consists of long-term frames, and a natural trajectory is obtained without the parameter generation algorithm. Furthermore, a computational complexity reduction technique, which drives the DNNs in different time units depending on type of musical score features, is proposed. Experimental results show that the proposed method can synthesize natural sounding singing voices much faster than the conventional method.
Singing voice synthesis based on convolutional neural networks
Apr 15, 2019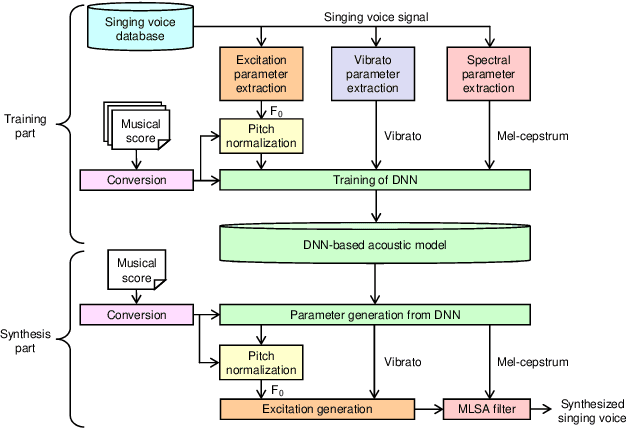
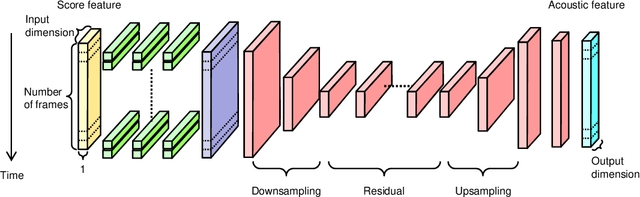
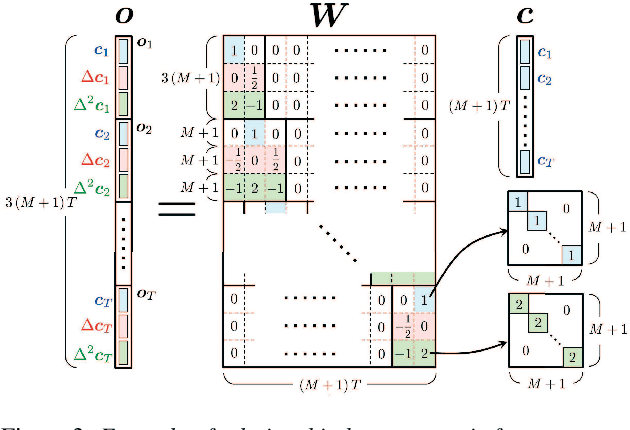
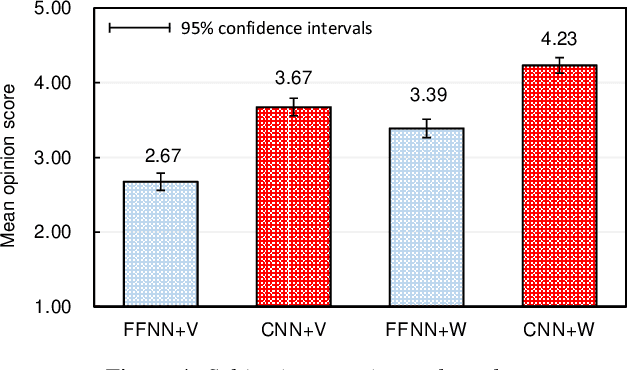
Abstract:The present paper describes a singing voice synthesis based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Singing voice synthesis systems based on deep neural networks (DNNs) are currently being proposed and are improving the naturalness of synthesized singing voices. In these systems, the relationship between musical score feature sequences and acoustic feature sequences extracted from singing voices is modeled by DNNs. Then, an acoustic feature sequence of an arbitrary musical score is output in units of frames by the trained DNNs, and a natural trajectory of a singing voice is obtained by using a parameter generation algorithm. As singing voices contain rich expression, a powerful technique to model them accurately is required. In the proposed technique, long-term dependencies of singing voices are modeled by CNNs. An acoustic feature sequence is generated in units of segments that consist of long-term frames, and a natural trajectory is obtained without the parameter generation algorithm. Experimental results in a subjective listening test show that the proposed architecture can synthesize natural sounding singing voices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge