Sungrae Park
User-Oriented Multi-Turn Dialogue Generation with Tool Use at scale
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The recent paradigm shift toward large reasoning models (LRMs) as autonomous agents has intensified the demand for sophisticated, multi-turn tool-use capabilities. Yet, existing datasets and data-generation approaches are limited by static, predefined toolsets that cannot scale to the complexity of open-ended human-agent collaboration. To address this, we initially developed a framework for automated task-oriented multi-turn dialogue generation at scale, utilizing an LRM-based simulator to dynamically generate high-value, domain-specific tools to solve specified tasks. However, we observe that a purely task-oriented design often results in "solely task-solving" trajectories, where the agent completes the objective with minimal interaction, failing to generate the high turn-count conversations seen in realistic scenarios. To bridge this gap, we shift toward a user-oriented simulation paradigm. By decoupling task generation from a dedicated user simulator that mimics human behavioral rules - such as incremental request-making and turn-by-turn feedback - we facilitate more authentic, extended multi-turn dialogues that reflect the iterative nature of real-world problem solving. Our generation pipeline operates as a versatile, plug-and-play module capable of initiating generation from any state, ensuring high scalability in producing extended tool-use data. Furthermore, by facilitating multiple task completions within a single trajectory, it yields a high-density dataset that reflects the multifaceted demands of real-world human-agent interaction.
Solar Open Technical Report
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Solar Open, a 102B-parameter bilingual Mixture-of-Experts language model for underserved languages. Solar Open demonstrates a systematic methodology for building competitive LLMs by addressing three interconnected challenges. First, to train effectively despite data scarcity for underserved languages, we synthesize 4.5T tokens of high-quality, domain-specific, and RL-oriented data. Second, we coordinate this data through a progressive curriculum jointly optimizing composition, quality thresholds, and domain coverage across 20 trillion tokens. Third, to enable reasoning capabilities through scalable RL, we apply our proposed framework SnapPO for efficient optimization. Across benchmarks in English and Korean, Solar Open achieves competitive performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of this methodology for underserved language AI development.
MIDUS: Memory-Infused Depth Up-Scaling
Dec 15, 2025



Abstract:Scaling large language models (LLMs) demands approaches that increase capacity without incurring excessive parameter growth or inference cost. Depth Up-Scaling (DUS) has emerged as a promising strategy by duplicating layers and applying Continual Pre-training (CPT), but its reliance on feed-forward networks (FFNs) limits efficiency and attainable gains. We introduce Memory-Infused Depth Up-Scaling (MIDUS), which replaces FFNs in duplicated blocks with a head-wise memory (HML) layer. Motivated by observations that attention heads have distinct roles both across and within layers, MIDUS assigns an independent memory bank to each head, enabling head-wise retrieval and injecting information into subsequent layers while preserving head-wise functional structure. This design combines sparse memory access with head-wise representations and incorporates an efficient per-head value factorization module, thereby relaxing the usual efficiency-performance trade-off. Across our CPT experiments, MIDUS exhibits robust performance improvements over strong DUS baselines while maintaining a highly efficient parameter footprint. Our findings establish MIDUS as a compelling and resource-efficient alternative to conventional FFN replication for depth up-scaling by leveraging its head-wise memory design.
KIEval: Evaluation Metric for Document Key Information Extraction
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Document Key Information Extraction (KIE) is a technology that transforms valuable information in document images into structured data, and it has become an essential function in industrial settings. However, current evaluation metrics of this technology do not accurately reflect the critical attributes of its industrial applications. In this paper, we present KIEval, a novel application-centric evaluation metric for Document KIE models. Unlike prior metrics, KIEval assesses Document KIE models not just on the extraction of individual information (entity) but also of the structured information (grouping). Evaluation of structured information provides assessment of Document KIE models that are more reflective of extracting grouped information from documents in industrial settings. Designed with industrial application in mind, we believe that KIEval can become a standard evaluation metric for developing or applying Document KIE models in practice. The code will be publicly available.
SRFormer: Empowering Regression-Based Text Detection Transformer with Segmentation
Aug 21, 2023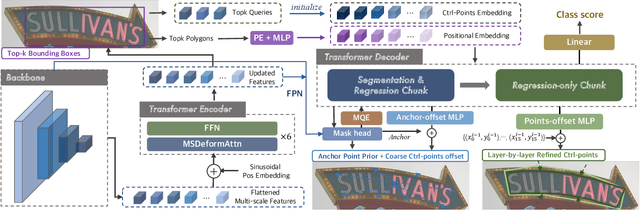
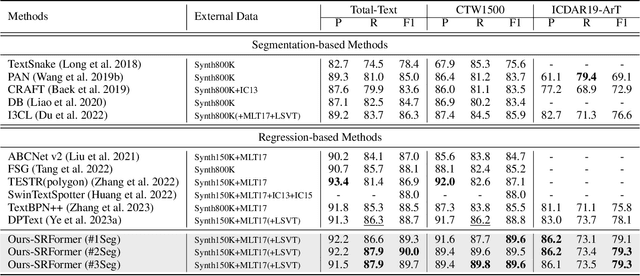
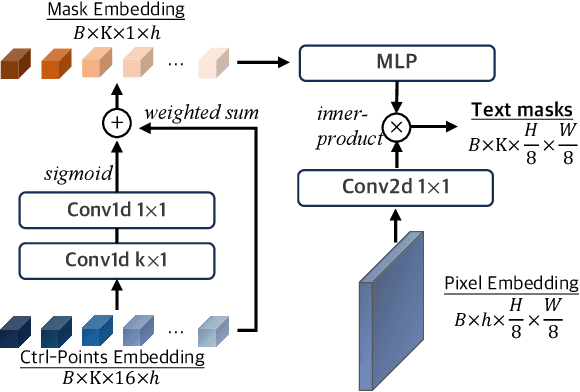
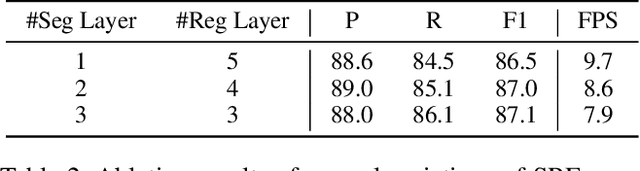
Abstract:Existing techniques for text detection can be broadly classified into two primary groups: segmentation-based methods and regression-based methods. Segmentation models offer enhanced robustness to font variations but require intricate post-processing, leading to high computational overhead. Regression-based methods undertake instance-aware prediction but face limitations in robustness and data efficiency due to their reliance on high-level representations. In our academic pursuit, we propose SRFormer, a unified DETR-based model with amalgamated Segmentation and Regression, aiming at the synergistic harnessing of the inherent robustness in segmentation representations, along with the straightforward post-processing of instance-level regression. Our empirical analysis indicates that favorable segmentation predictions can be obtained at the initial decoder layers. In light of this, we constrain the incorporation of segmentation branches to the first few decoder layers and employ progressive regression refinement in subsequent layers, achieving performance gains while minimizing additional computational load from the mask. Furthermore, we propose a Mask-informed Query Enhancement module. We take the segmentation result as a natural soft-ROI to pool and extract robust pixel representations, which are then employed to enhance and diversify instance queries. Extensive experimentation across multiple benchmarks has yielded compelling findings, highlighting our method's exceptional robustness, superior training and data efficiency, as well as its state-of-the-art performance.
Domain Generalization by Mutual-Information Regularization with Pre-trained Models
Mar 21, 2022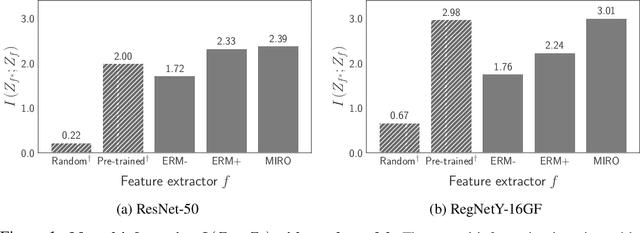
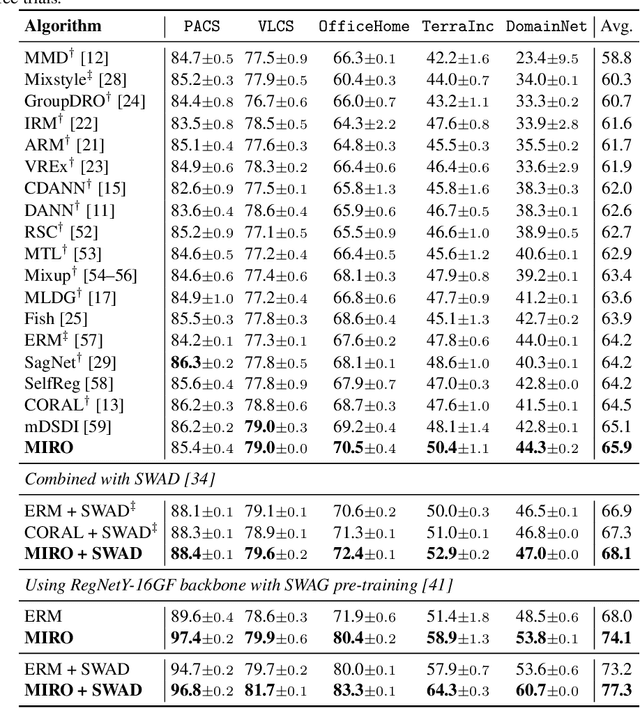
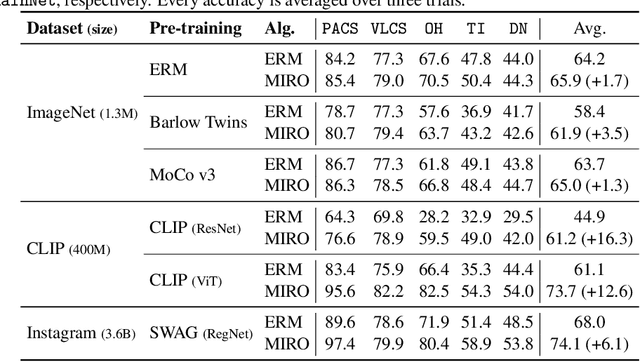
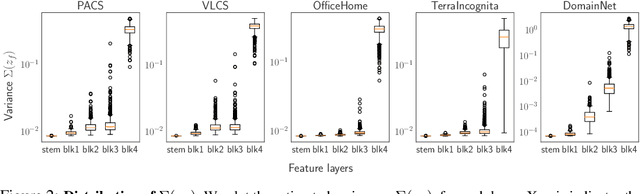
Abstract:Domain generalization (DG) aims to learn a generalized model to an unseen target domain using only limited source domains. Previous attempts to DG fail to learn domain-invariant representations only from the source domains due to the significant domain shifts between training and test domains. Instead, we re-formulate the DG objective using mutual information with the oracle model, a model generalized to any possible domain. We derive a tractable variational lower bound via approximating the oracle model by a pre-trained model, called Mutual Information Regularization with Oracle (MIRO). Our extensive experiments show that MIRO significantly improves the out-of-distribution performance. Furthermore, our scaling experiments show that the larger the scale of the pre-trained model, the greater the performance improvement of MIRO. Source code is available at https://github.com/kakaobrain/miro.
Multi-modal Text Recognition Networks: Interactive Enhancements between Visual and Semantic Features
Nov 30, 2021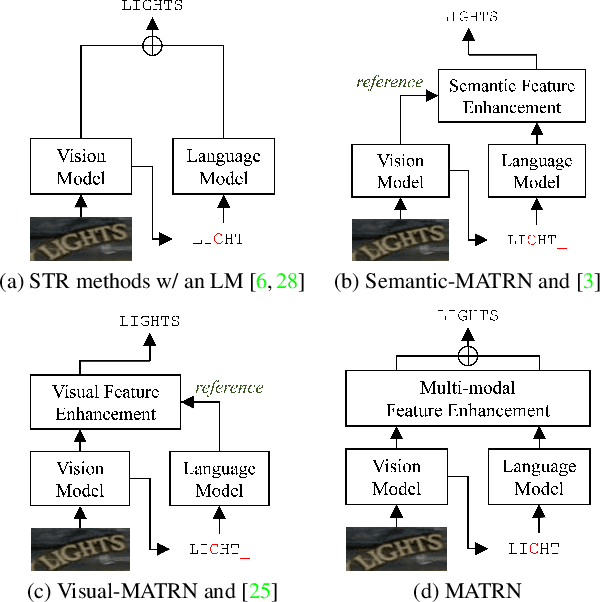
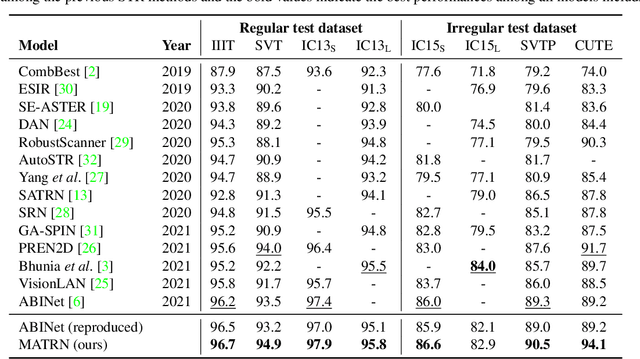
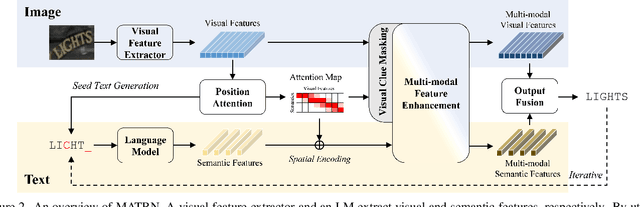
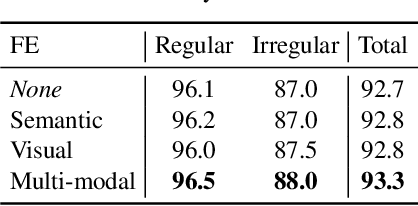
Abstract:Linguistic knowledge has brought great benefits to scene text recognition by providing semantics to refine character sequences. However, since linguistic knowledge has been applied individually on the output sequence, previous methods have not fully utilized the semantics to understand visual clues for text recognition. This paper introduces a novel method, called Multi-modAl Text Recognition Network (MATRN), that enables interactions between visual and semantic features for better recognition performances. Specifically, MATRN identifies visual and semantic feature pairs and encodes spatial information into semantic features. Based on the spatial encoding, visual and semantic features are enhanced by referring to related features in the other modality. Furthermore, MATRN stimulates combining semantic features into visual features by hiding visual clues related to the character in the training phase. Our experiments demonstrate that MATRN achieves state-of-the-art performances on seven benchmarks with large margins, while naive combinations of two modalities show marginal improvements. Further ablative studies prove the effectiveness of our proposed components. Our implementation will be publicly available.
BROS: A Pre-trained Language Model Focusing on Text and Layout for Better Key Information Extraction from Documents
Sep 10, 2021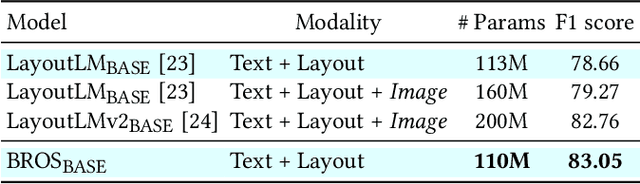
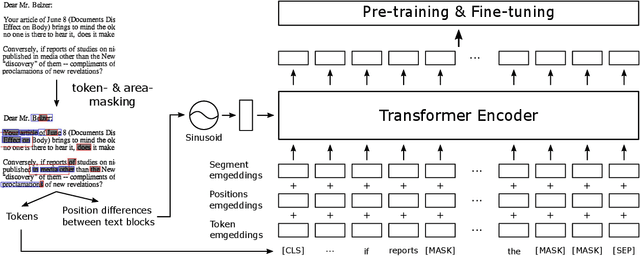

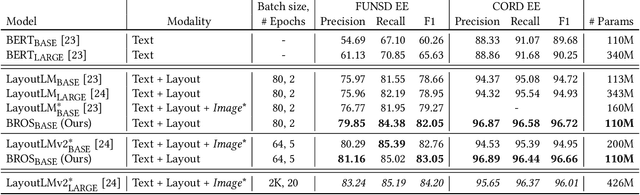
Abstract:Key information extraction (KIE) from document images requires understanding the contextual and spatial semantics of texts in two-dimensional (2D) space. Many recent studies try to solve the task by developing pre-training language models focusing on combining visual features from document images with texts and their layout. On the other hand, this paper tackles the problem by going back to the basic: effective combination of text and layout. Specifically, we propose a pre-trained language model, named BROS (BERT Relying On Spatiality), that encodes relative positions of texts in 2D space and learns from unlabeled documents with area-masking strategy. With this optimized training scheme for understanding texts in 2D space, BROS shows comparable or better performance compared to previous methods on four KIE benchmarks (FUNSD, SROIE*, CORD, and SciTSR) without relying on visual features. This paper also reveals two real-world challenges in KIE tasks--(1) minimizing the error from incorrect text ordering and (2) efficient learning from fewer downstream examples--and demonstrates the superiority of BROS over previous methods. Our code will be open to the public.
RewriteNet: Realistic Scene Text Image Generation via Editing Text in Real-world Image
Jul 23, 2021
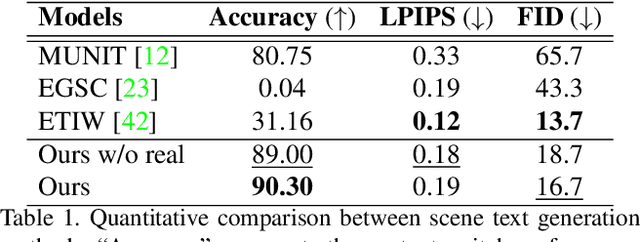
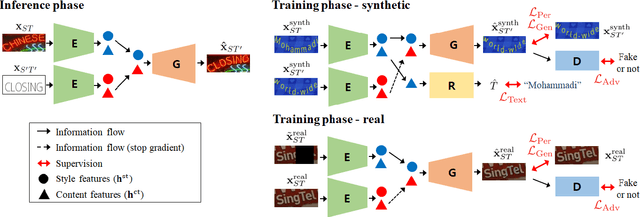
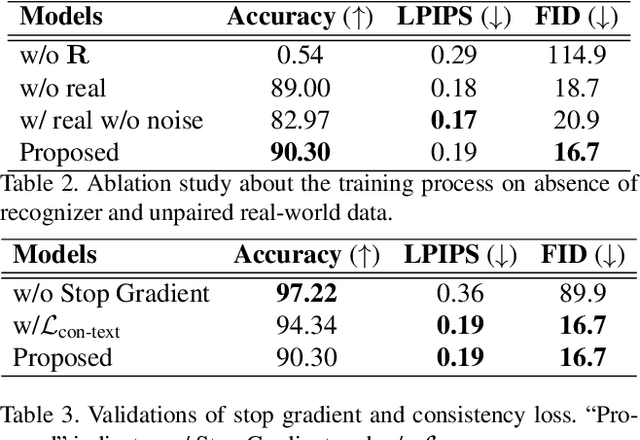
Abstract:Scene text editing (STE), which converts a text in a scene image into the desired text while preserving an original style, is a challenging task due to a complex intervention between text and style. To address this challenge, we propose a novel representational learning-based STE model, referred to as RewriteNet that employs textual information as well as visual information. We assume that the scene text image can be decomposed into content and style features where the former represents the text information and style represents scene text characteristics such as font, alignment, and background. Under this assumption, we propose a method to separately encode content and style features of the input image by introducing the scene text recognizer that is trained by text information. Then, a text-edited image is generated by combining the style feature from the original image and the content feature from the target text. Unlike previous works that are only able to use synthetic images in the training phase, we also exploit real-world images by proposing a self-supervised training scheme, which bridges the domain gap between synthetic and real data. Our experiments demonstrate that RewriteNet achieves better quantitative and qualitative performance than other comparisons. Moreover, we validate that the use of text information and the self-supervised training scheme improves text switching performance. The implementation and dataset will be publicly available.
SynthTIGER: Synthetic Text Image GEneratoR Towards Better Text Recognition Models
Jul 20, 2021
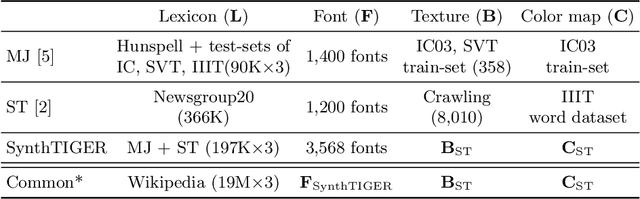
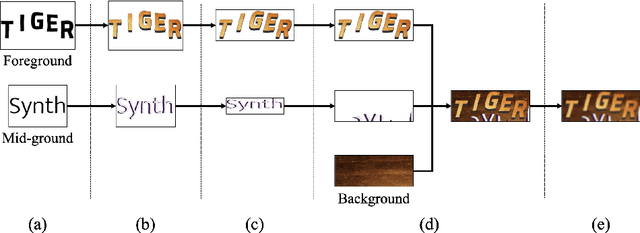
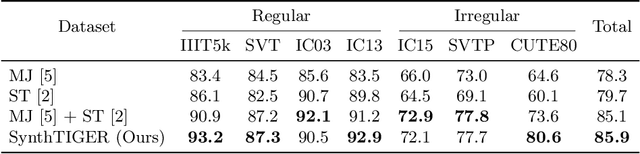
Abstract:For successful scene text recognition (STR) models, synthetic text image generators have alleviated the lack of annotated text images from the real world. Specifically, they generate multiple text images with diverse backgrounds, font styles, and text shapes and enable STR models to learn visual patterns that might not be accessible from manually annotated data. In this paper, we introduce a new synthetic text image generator, SynthTIGER, by analyzing techniques used for text image synthesis and integrating effective ones under a single algorithm. Moreover, we propose two techniques that alleviate the long-tail problem in length and character distributions of training data. In our experiments, SynthTIGER achieves better STR performance than the combination of synthetic datasets, MJSynth (MJ) and SynthText (ST). Our ablation study demonstrates the benefits of using sub-components of SynthTIGER and the guideline on generating synthetic text images for STR models. Our implementation is publicly available at https://github.com/clovaai/synthtiger.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge