Mingi Ji
LayerMerge: Neural Network Depth Compression through Layer Pruning and Merging
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Recent works show that reducing the number of layers in a convolutional neural network can enhance efficiency while maintaining the performance of the network. Existing depth compression methods remove redundant non-linear activation functions and merge the consecutive convolution layers into a single layer. However, these methods suffer from a critical drawback; the kernel size of the merged layers becomes larger, significantly undermining the latency reduction gained from reducing the depth of the network. We show that this problem can be addressed by jointly pruning convolution layers and activation functions. To this end, we propose LayerMerge, a novel depth compression method that selects which activation layers and convolution layers to remove, to achieve a desired inference speed-up while minimizing performance loss. Since the corresponding selection problem involves an exponential search space, we formulate a novel surrogate optimization problem and efficiently solve it via dynamic programming. Empirical results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing depth compression and layer pruning methods on various network architectures, both on image classification and generation tasks. We release the code at https://github.com/snu-mllab/LayerMerge.
Unknown-Aware Domain Adversarial Learning for Open-Set Domain Adaptation
Jun 15, 2022
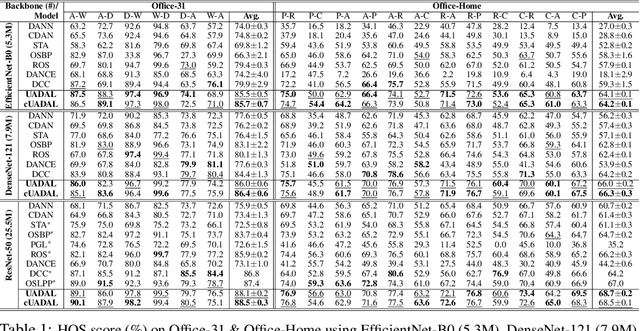
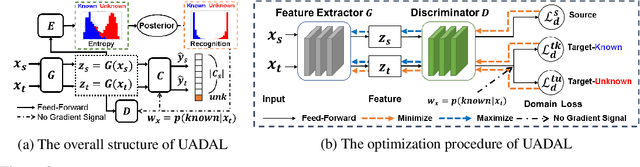
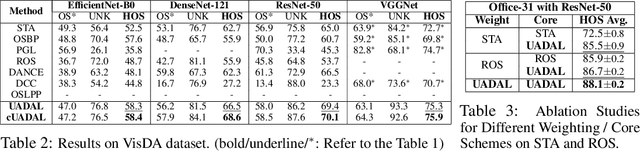
Abstract:Open-Set Domain Adaptation (OSDA) assumes that a target domain contains unknown classes, which are not discovered in a source domain. Existing domain adversarial learning methods are not suitable for OSDA because distribution matching with \textit{unknown} classes leads to the negative transfer. Previous OSDA methods have focused on matching the source and the target distribution by only utilizing \textit{known} classes. However, this \textit{known}-only matching may fail to learn the target-\textit{unknown} feature space. Therefore, we propose Unknown-Aware Domain Adversarial Learning (UADAL), which \textit{aligns} the source and the targe-\textit{known} distribution while simultaneously \textit{segregating} the target-\textit{unknown} distribution in the feature alignment procedure. We provide theoretical analyses on the optimized state of the proposed \textit{unknown-aware} feature alignment, so we can guarantee both \textit{alignment} and \textit{segregation} theoretically. Empirically, we evaluate UADAL on the benchmark datasets, which shows that UADAL outperforms other methods with better feature alignments by reporting the state-of-the-art performances.
BROS: A Pre-trained Language Model Focusing on Text and Layout for Better Key Information Extraction from Documents
Sep 10, 2021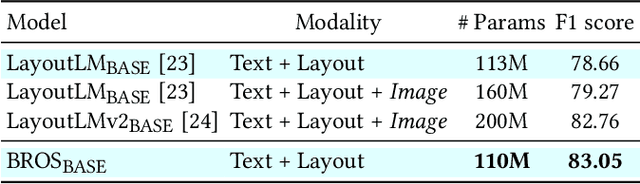
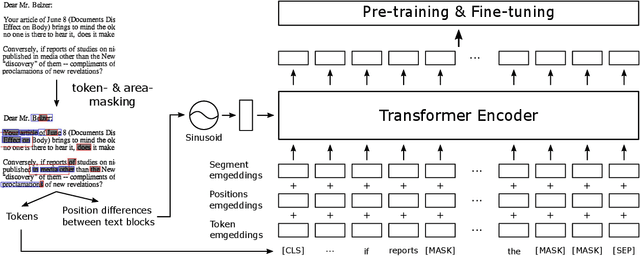

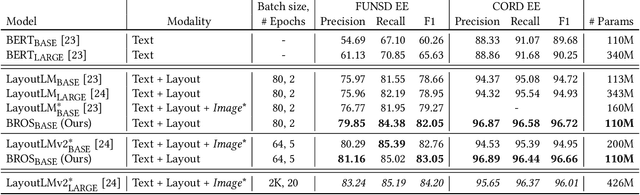
Abstract:Key information extraction (KIE) from document images requires understanding the contextual and spatial semantics of texts in two-dimensional (2D) space. Many recent studies try to solve the task by developing pre-training language models focusing on combining visual features from document images with texts and their layout. On the other hand, this paper tackles the problem by going back to the basic: effective combination of text and layout. Specifically, we propose a pre-trained language model, named BROS (BERT Relying On Spatiality), that encodes relative positions of texts in 2D space and learns from unlabeled documents with area-masking strategy. With this optimized training scheme for understanding texts in 2D space, BROS shows comparable or better performance compared to previous methods on four KIE benchmarks (FUNSD, SROIE*, CORD, and SciTSR) without relying on visual features. This paper also reveals two real-world challenges in KIE tasks--(1) minimizing the error from incorrect text ordering and (2) efficient learning from fewer downstream examples--and demonstrates the superiority of BROS over previous methods. Our code will be open to the public.
Refine Myself by Teaching Myself: Feature Refinement via Self-Knowledge Distillation
Mar 15, 2021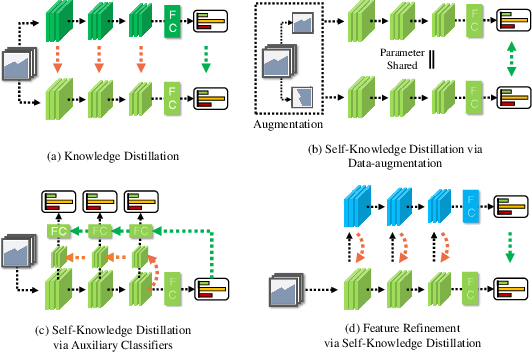
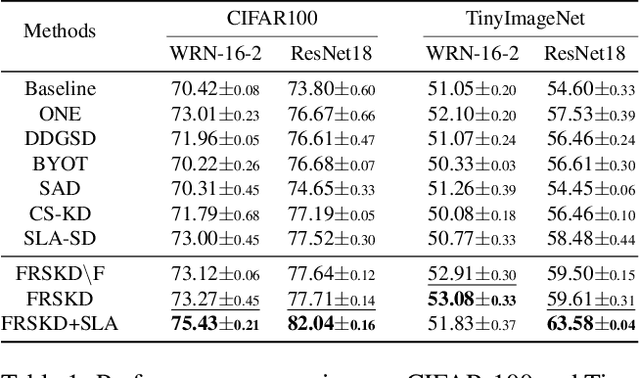
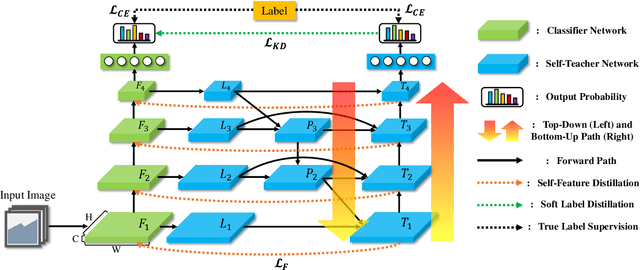
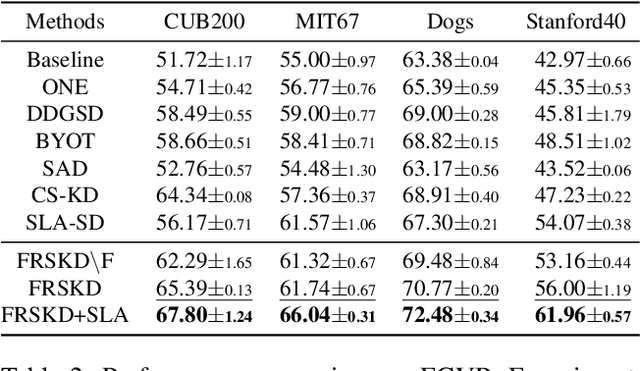
Abstract:Knowledge distillation is a method of transferring the knowledge from a pretrained complex teacher model to a student model, so a smaller network can replace a large teacher network at the deployment stage. To reduce the necessity of training a large teacher model, the recent literatures introduced a self-knowledge distillation, which trains a student network progressively to distill its own knowledge without a pretrained teacher network. While Self-knowledge distillation is largely divided into a data augmentation based approach and an auxiliary network based approach, the data augmentation approach looses its local information in the augmentation process, which hinders its applicability to diverse vision tasks, such as semantic segmentation. Moreover, these knowledge distillation approaches do not receive the refined feature maps, which are prevalent in the object detection and semantic segmentation community. This paper proposes a novel self-knowledge distillation method, Feature Refinement via Self-Knowledge Distillation (FRSKD), which utilizes an auxiliary self-teacher network to transfer a refined knowledge for the classifier network. Our proposed method, FRSKD, can utilize both soft label and feature-map distillations for the self-knowledge distillation. Therefore, FRSKD can be applied to classification, and semantic segmentation, which emphasize preserving the local information. We demonstrate the effectiveness of FRSKD by enumerating its performance improvements in diverse tasks and benchmark datasets. The implemented code is available at https://github.com/MingiJi/FRSKD.
Show, Attend and Distill:Knowledge Distillation via Attention-based Feature Matching
Feb 05, 2021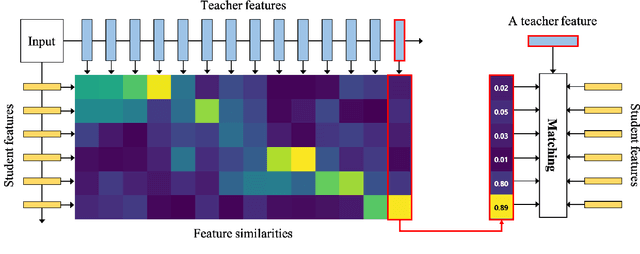
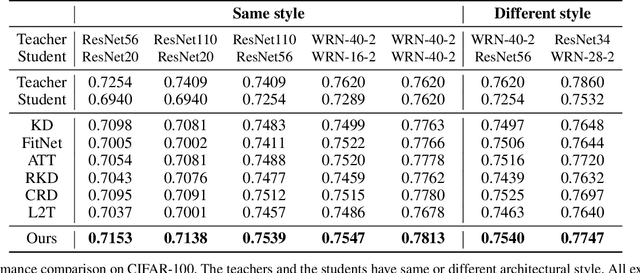
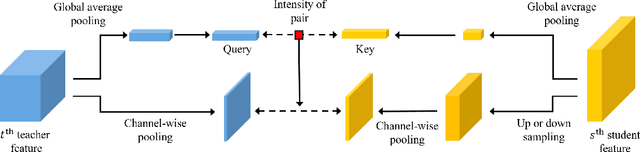
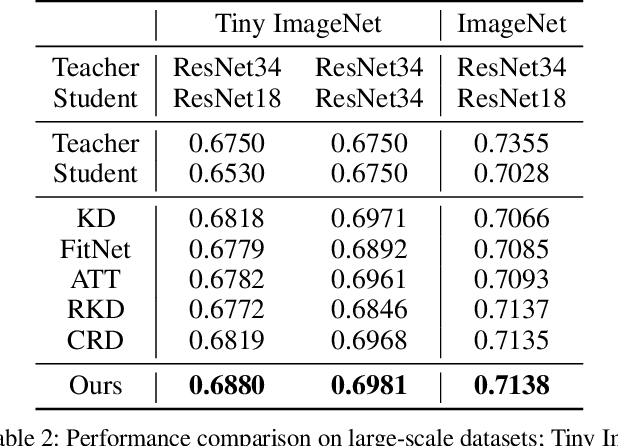
Abstract:Knowledge distillation extracts general knowledge from a pre-trained teacher network and provides guidance to a target student network. Most studies manually tie intermediate features of the teacher and student, and transfer knowledge through pre-defined links. However, manual selection often constructs ineffective links that limit the improvement from the distillation. There has been an attempt to address the problem, but it is still challenging to identify effective links under practical scenarios. In this paper, we introduce an effective and efficient feature distillation method utilizing all the feature levels of the teacher without manually selecting the links. Specifically, our method utilizes an attention-based meta-network that learns relative similarities between features, and applies identified similarities to control distillation intensities of all possible pairs. As a result, our method determines competent links more efficiently than the previous approach and provides better performance on model compression and transfer learning tasks. Further qualitative analyses and ablative studies describe how our method contributes to better distillation. The implementation code is available at github.com/clovaai/attention-feature-distillation.
Sequential Recommendation with Relation-Aware Kernelized Self-Attention
Nov 15, 2019
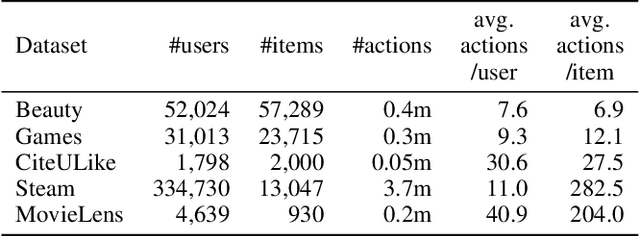

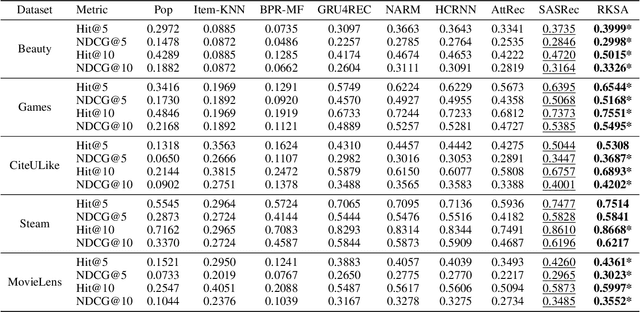
Abstract:Recent studies identified that sequential Recommendation is improved by the attention mechanism. By following this development, we propose Relation-Aware Kernelized Self-Attention (RKSA) adopting a self-attention mechanism of the Transformer with augmentation of a probabilistic model. The original self-attention of Transformer is a deterministic measure without relation-awareness. Therefore, we introduce a latent space to the self-attention, and the latent space models the recommendation context from relation as a multivariate skew-normal distribution with a kernelized covariance matrix from co-occurrences, item characteristics, and user information. This work merges the self-attention of the Transformer and the sequential recommendation by adding a probabilistic model of the recommendation task specifics. We experimented RKSA over the benchmark datasets, and RKSA shows significant improvements compared to the recent baseline models. Also, RKSA were able to produce a latent space model that answers the reasons for recommendation.
* 8 pages, 5 figures, AAAI
Hierarchical Context enabled Recurrent Neural Network for Recommendation
Apr 26, 2019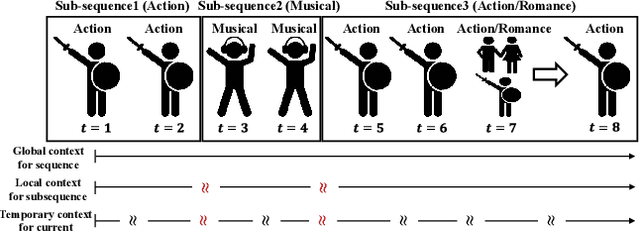



Abstract:A long user history inevitably reflects the transitions of personal interests over time. The analyses on the user history require the robust sequential model to anticipate the transitions and the decays of user interests. The user history is often modeled by various RNN structures, but the RNN structures in the recommendation system still suffer from the long-term dependency and the interest drifts. To resolve these challenges, we suggest HCRNN with three hierarchical contexts of the global, the local, and the temporary interests. This structure is designed to withhold the global long-term interest of users, to reflect the local sub-sequence interests, and to attend the temporary interests of each transition. Besides, we propose a hierarchical context-based gate structure to incorporate our \textit{interest drift assumption}. As we suggest a new RNN structure, we support HCRNN with a complementary \textit{bi-channel attention} structure to utilize hierarchical context. We experimented the suggested structure on the sequential recommendation tasks with CiteULike, MovieLens, and LastFM, and our model showed the best performances in the sequential recommendations.
Adversarial Dropout for Recurrent Neural Networks
Apr 22, 2019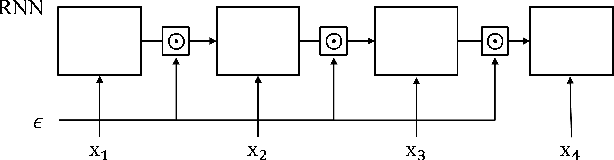

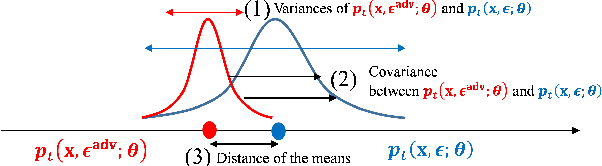

Abstract:Successful application processing sequential data, such as text and speech, requires an improved generalization performance of recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Dropout techniques for RNNs were introduced to respond to these demands, but we conjecture that the dropout on RNNs could have been improved by adopting the adversarial concept. This paper investigates ways to improve the dropout for RNNs by utilizing intentionally generated dropout masks. Specifically, the guided dropout used in this research is called as adversarial dropout, which adversarially disconnects neurons that are dominantly used to predict correct targets over time. Our analysis showed that our regularizer, which consists of a gap between the original and the reconfigured RNNs, was the upper bound of the gap between the training and the inference phases of the random dropout. We demonstrated that minimizing our regularizer improved the effectiveness of the dropout for RNNs on sequential MNIST tasks, semi-supervised text classification tasks, and language modeling tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge