Il-Chul Moon
Lookahead Sample Reward Guidance for Test-Time Scaling of Diffusion Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Diffusion models have demonstrated strong generative performance; however, generated samples often fail to fully align with human intent. This paper studies a test-time scaling method that enables sampling from regions with higher human-aligned reward values. Existing gradient guidance methods approximate the expected future reward (EFR) at an intermediate particle $\mathbf{x}_t$ using a Taylor approximation, but this approximation at each time step incurs high computational cost due to sequential neural backpropagation. We show that the EFR at any $\mathbf{x}_t$ can be computed using only marginal samples from a pre-trained diffusion model. The proposed EFR formulation detaches the neural dependency between $\mathbf{x}_t$ and the EFR, enabling closed-form guidance computation without neural backpropagation. To further improve efficiency, we introduce lookahead sampling to collect marginal samples. For final sample generation, we use an accurate solver that guides particles toward high-reward lookahead samples. We refer to this sampling scheme as LiDAR sampling. LiDAR achieves substantial performance improvements using only three samples with a 3-step lookahead solver, exhibiting steep performance gains as lookahead accuracy and sample count increase; notably, it reaches the same GenEval performance as the latest gradient guidance method for SDXL with a 9.5x speedup.
Semantic-aware Wasserstein Policy Regularization for Large Language Model Alignment
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are commonly aligned with human preferences using reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). In this method, LLM policies are generally optimized through reward maximization with Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence regularization of the reference policy. However, KL and its $f$-divergence variants only compare token probabilities at identical indices, failing to capture semantic similarity. We propose Wasserstein Policy Regularization (WPR), a semantic-aware regularization for the RLHF framework based on the entropy-regularized Wasserstein distance, which incorporates the geometry of the token space. The dual formulation of the distance expresses the regularization as penalty terms applied to the reward via optimal dual variables, which yield a tractable objective compatible with standard RL algorithms. Empirically, our method outperforms KL- and $f$-divergence-based baselines, demonstrating the benefits of semantic-aware policy distances for alignment. Our code is available at https://github.com/aailab-kaist/WPR.
Preference Optimization by Estimating the Ratio of the Data Distribution
May 26, 2025Abstract:Direct preference optimization (DPO) is widely used as a simple and stable method for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. This paper investigates a generalized DPO loss that enables a policy model to match the target policy from a likelihood ratio estimation perspective. The ratio of the target policy provides a unique identification of the policy distribution without relying on reward models or partition functions. This allows the generalized loss to retain both simplicity and theoretical guarantees, which prior work such as $f$-PO fails to achieve simultaneously. We propose Bregman preference optimization (BPO), a generalized framework for ratio matching that provides a family of objective functions achieving target policy optimality. BPO subsumes DPO as a special case and offers tractable forms for all instances, allowing implementation with a few lines of code. We further develop scaled Basu's power divergence (SBA), a gradient scaling method that can be used for BPO instances. The BPO framework complements other DPO variants and is applicable to target policies defined by these variants. In experiments, unlike other probabilistic loss extensions such as $f$-DPO or $f$-PO, which exhibit a trade-off between generation fidelity and diversity, instances of BPO improve both win rate and entropy compared with DPO. When applied to Llama-3-Instruct-8B, BPO achieves state-of-the-art performance among Llama-3-8B backbones, with a 55.9\% length-controlled win rate on AlpacaEval2.
Distilling Dataset into Neural Field
Mar 05, 2025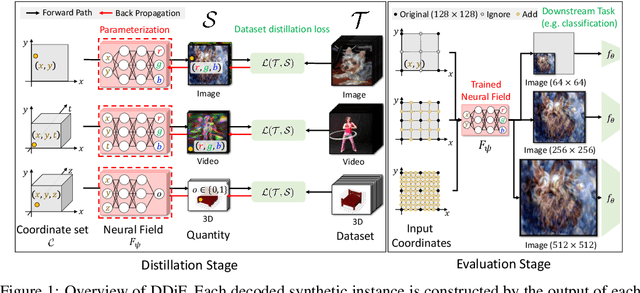
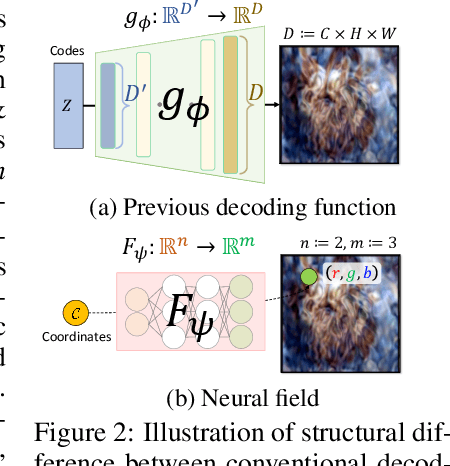

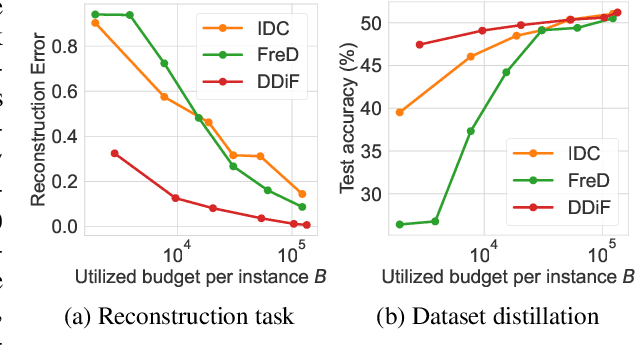
Abstract:Utilizing a large-scale dataset is essential for training high-performance deep learning models, but it also comes with substantial computation and storage costs. To overcome these challenges, dataset distillation has emerged as a promising solution by compressing the large-scale dataset into a smaller synthetic dataset that retains the essential information needed for training. This paper proposes a novel parameterization framework for dataset distillation, coined Distilling Dataset into Neural Field (DDiF), which leverages the neural field to store the necessary information of the large-scale dataset. Due to the unique nature of the neural field, which takes coordinates as input and output quantity, DDiF effectively preserves the information and easily generates various shapes of data. We theoretically confirm that DDiF exhibits greater expressiveness than some previous literature when the utilized budget for a single synthetic instance is the same. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that DDiF achieves superior performance on several benchmark datasets, extending beyond the image domain to include video, audio, and 3D voxel. We release the code at https://github.com/aailab-kaist/DDiF.
Trajectory-Class-Aware Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 03, 2025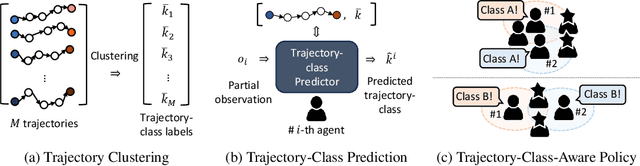


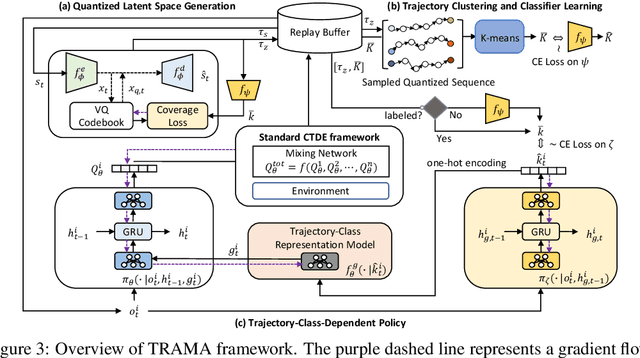
Abstract:In the context of multi-agent reinforcement learning, generalization is a challenge to solve various tasks that may require different joint policies or coordination without relying on policies specialized for each task. We refer to this type of problem as a multi-task, and we train agents to be versatile in this multi-task setting through a single training process. To address this challenge, we introduce TRajectory-class-Aware Multi-Agent reinforcement learning (TRAMA). In TRAMA, agents recognize a task type by identifying the class of trajectories they are experiencing through partial observations, and the agents use this trajectory awareness or prediction as additional information for action policy. To this end, we introduce three primary objectives in TRAMA: (a) constructing a quantized latent space to generate trajectory embeddings that reflect key similarities among them; (b) conducting trajectory clustering using these trajectory embeddings; and (c) building a trajectory-class-aware policy. Specifically for (c), we introduce a trajectory-class predictor that performs agent-wise predictions on the trajectory class; and we design a trajectory-class representation model for each trajectory class. Each agent takes actions based on this trajectory-class representation along with its partial observation for task-aware execution. The proposed method is evaluated on various tasks, including multi-task problems built upon StarCraft II. Empirical results show further performance improvements over state-of-the-art baselines.
Reward-based Input Construction for Cross-document Relation Extraction
May 31, 2024Abstract:Relation extraction (RE) is a fundamental task in natural language processing, aiming to identify relations between target entities in text. While many RE methods are designed for a single sentence or document, cross-document RE has emerged to address relations across multiple long documents. Given the nature of long documents in cross-document RE, extracting document embeddings is challenging due to the length constraints of pre-trained language models. Therefore, we propose REward-based Input Construction (REIC), the first learning-based sentence selector for cross-document RE. REIC extracts sentences based on relational evidence, enabling the RE module to effectively infer relations. Since supervision of evidence sentences is generally unavailable, we train REIC using reinforcement learning with RE prediction scores as rewards. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method over heuristic methods for different RE structures and backbones in cross-document RE. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/aailabkaist/REIC.
Diffusion Rejection Sampling
May 28, 2024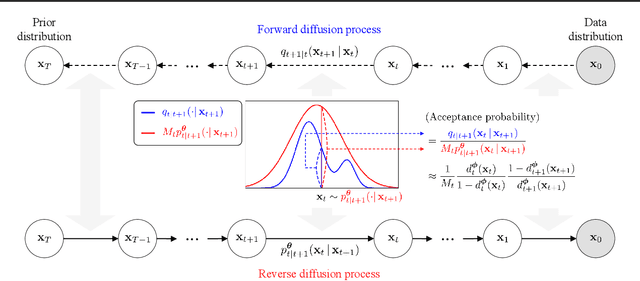
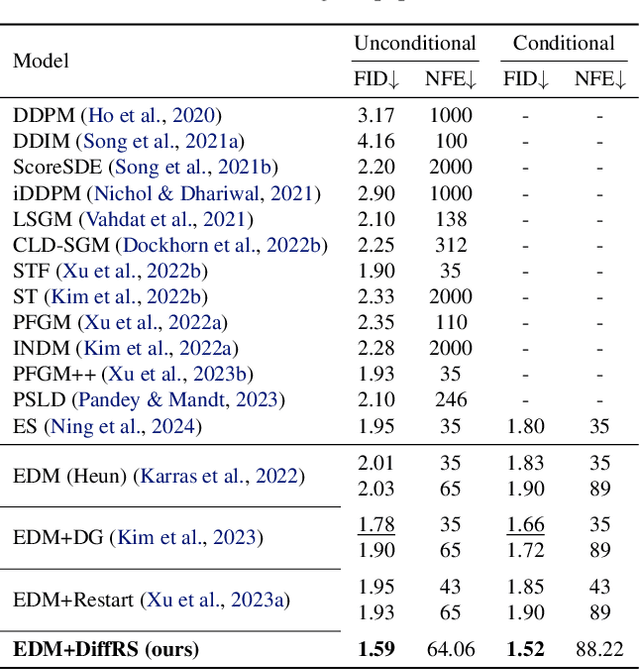
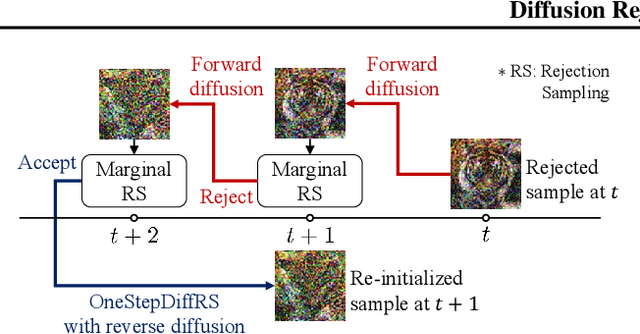
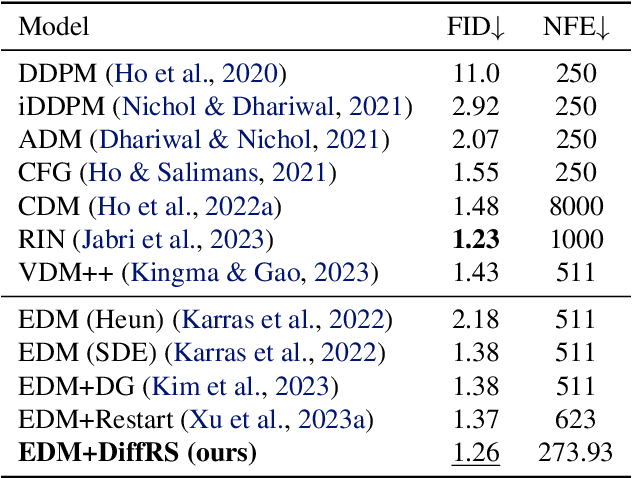
Abstract:Recent advances in powerful pre-trained diffusion models encourage the development of methods to improve the sampling performance under well-trained diffusion models. This paper introduces Diffusion Rejection Sampling (DiffRS), which uses a rejection sampling scheme that aligns the sampling transition kernels with the true ones at each timestep. The proposed method can be viewed as a mechanism that evaluates the quality of samples at each intermediate timestep and refines them with varying effort depending on the sample. Theoretical analysis shows that DiffRS can achieve a tighter bound on sampling error compared to pre-trained models. Empirical results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of DiffRS on the benchmark datasets and the effectiveness of DiffRS for fast diffusion samplers and large-scale text-to-image diffusion models. Our code is available at https://github.com/aailabkaist/DiffRS.
Diffusion Bridge AutoEncoders for Unsupervised Representation Learning
May 27, 2024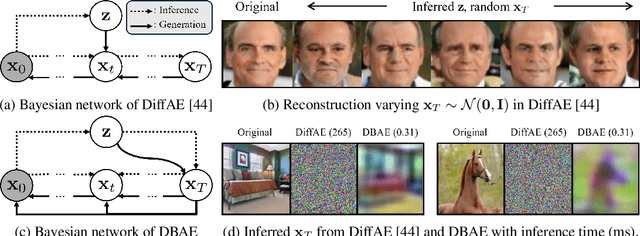
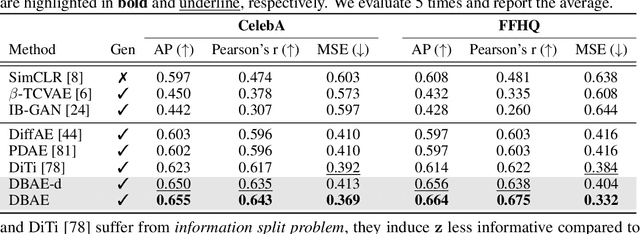
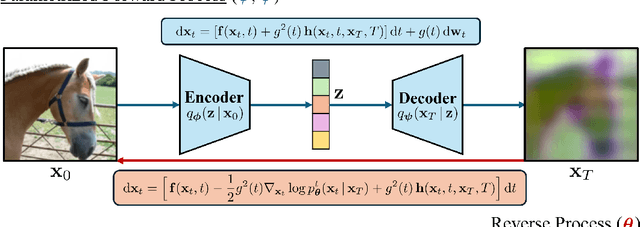
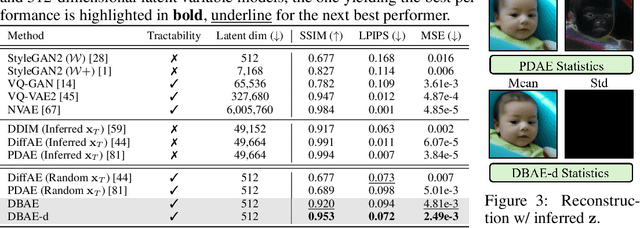
Abstract:Diffusion-based representation learning has achieved substantial attention due to its promising capabilities in latent representation and sample generation. Recent studies have employed an auxiliary encoder to identify a corresponding representation from a sample and to adjust the dimensionality of a latent variable z. Meanwhile, this auxiliary structure invokes information split problem because the diffusion and the auxiliary encoder would divide the information from the sample into two representations for each model. Particularly, the information modeled by the diffusion becomes over-regularized because of the static prior distribution on xT. To address this problem, we introduce Diffusion Bridge AuteEncoders (DBAE), which enable z-dependent endpoint xT inference through a feed-forward architecture. This structure creates an information bottleneck at z, so xT becomes dependent on z in its generation. This results in two consequences: 1) z holds the full information of samples, and 2) xT becomes a learnable distribution, not static any further. We propose an objective function for DBAE to enable both reconstruction and generative modeling, with their theoretical justification. Empirical evidence supports the effectiveness of the intended design in DBAE, which notably enhances downstream inference quality, reconstruction, and disentanglement. Additionally, DBAE generates high-fidelity samples in the unconditional generation.
Unknown Domain Inconsistency Minimization for Domain Generalization
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:The objective of domain generalization (DG) is to enhance the transferability of the model learned from a source domain to unobserved domains. To prevent overfitting to a specific domain, Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) reduces source domain's loss sharpness. Although SAM variants have delivered significant improvements in DG, we highlight that there's still potential for improvement in generalizing to unknown domains through the exploration on data space. This paper introduces an objective rooted in both parameter and data perturbed regions for domain generalization, coined Unknown Domain Inconsistency Minimization (UDIM). UDIM reduces the loss landscape inconsistency between source domain and unknown domains. As unknown domains are inaccessible, these domains are empirically crafted by perturbing instances from the source domain dataset. In particular, by aligning the loss landscape acquired in the source domain to the loss landscape of perturbed domains, we expect to achieve generalization grounded on these flat minima for the unknown domains. Theoretically, we validate that merging SAM optimization with the UDIM objective establishes an upper bound for the true objective of the DG task. In an empirical aspect, UDIM consistently outperforms SAM variants across multiple DG benchmark datasets. Notably, UDIM shows statistically significant improvements in scenarios with more restrictive domain information, underscoring UDIM's generalization capability in unseen domains. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/SJShin-AI/UDIM}.
Dirichlet-based Per-Sample Weighting by Transition Matrix for Noisy Label Learning
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:For learning with noisy labels, the transition matrix, which explicitly models the relation between noisy label distribution and clean label distribution, has been utilized to achieve the statistical consistency of either the classifier or the risk. Previous researches have focused more on how to estimate this transition matrix well, rather than how to utilize it. We propose good utilization of the transition matrix is crucial and suggest a new utilization method based on resampling, coined RENT. Specifically, we first demonstrate current utilizations can have potential limitations for implementation. As an extension to Reweighting, we suggest the Dirichlet distribution-based per-sample Weight Sampling (DWS) framework, and compare reweighting and resampling under DWS framework. With the analyses from DWS, we propose RENT, a REsampling method with Noise Transition matrix. Empirically, RENT consistently outperforms existing transition matrix utilization methods, which includes reweighting, on various benchmark datasets. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/BaeHeeSun/RENT}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge