Yichuan Cheng
Log Neural Controlled Differential Equations: The Lie Brackets Make a Difference
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:The vector field of a controlled differential equation (CDE) describes the relationship between a control path and the evolution of a solution path. Neural CDEs (NCDEs) treat time series data as observations from a control path, parameterise a CDE's vector field using a neural network, and use the solution path as a continuously evolving hidden state. As their formulation makes them robust to irregular sampling rates, NCDEs are a powerful approach for modelling real-world data. Building on neural rough differential equations (NRDEs), we introduce Log-NCDEs, a novel and effective method for training NCDEs. The core component of Log-NCDEs is the Log-ODE method, a tool from the study of rough paths for approximating a CDE's solution. On a range of multivariate time series classification benchmarks, Log-NCDEs are shown to achieve a higher average test set accuracy than NCDEs, NRDEs, and two state-of-the-art models, S5 and the linear recurrent unit.
SRFormer: Empowering Regression-Based Text Detection Transformer with Segmentation
Aug 21, 2023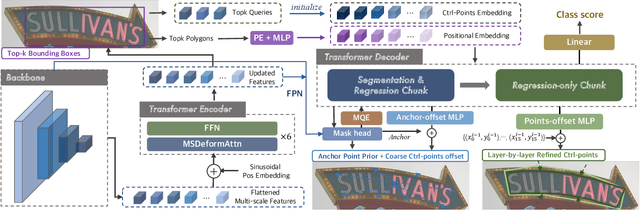
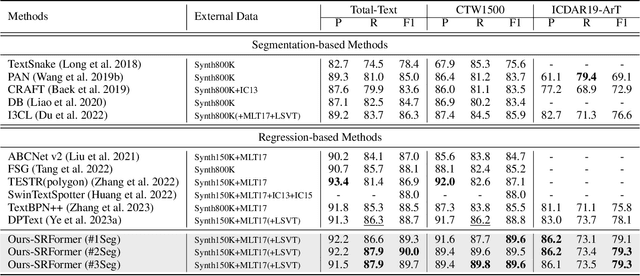
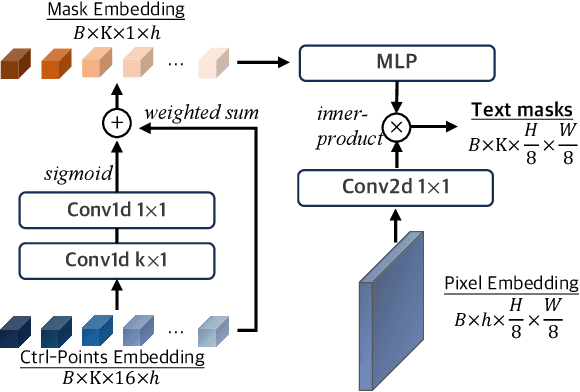
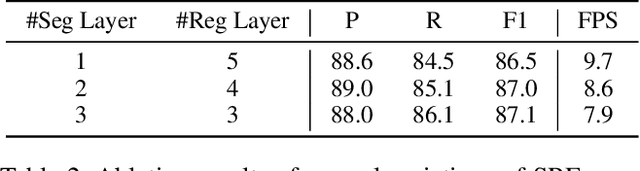
Abstract:Existing techniques for text detection can be broadly classified into two primary groups: segmentation-based methods and regression-based methods. Segmentation models offer enhanced robustness to font variations but require intricate post-processing, leading to high computational overhead. Regression-based methods undertake instance-aware prediction but face limitations in robustness and data efficiency due to their reliance on high-level representations. In our academic pursuit, we propose SRFormer, a unified DETR-based model with amalgamated Segmentation and Regression, aiming at the synergistic harnessing of the inherent robustness in segmentation representations, along with the straightforward post-processing of instance-level regression. Our empirical analysis indicates that favorable segmentation predictions can be obtained at the initial decoder layers. In light of this, we constrain the incorporation of segmentation branches to the first few decoder layers and employ progressive regression refinement in subsequent layers, achieving performance gains while minimizing additional computational load from the mask. Furthermore, we propose a Mask-informed Query Enhancement module. We take the segmentation result as a natural soft-ROI to pool and extract robust pixel representations, which are then employed to enhance and diversify instance queries. Extensive experimentation across multiple benchmarks has yielded compelling findings, highlighting our method's exceptional robustness, superior training and data efficiency, as well as its state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge