Stefan Ploner
A Spatiotemporal Illumination Model for 3D Image Fusion in Optical Coherence Tomography
Feb 19, 2024Abstract:Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive, micrometer-scale imaging modality that has become a clinical standard in ophthalmology. By raster-scanning the retina, sequential cross-sectional image slices are acquired to generate volumetric data. In-vivo imaging suffers from discontinuities between slices that show up as motion and illumination artifacts. We present a new illumination model that exploits continuity in orthogonally raster-scanned volume data. Our novel spatiotemporal parametrization adheres to illumination continuity both temporally, along the imaged slices, as well as spatially, in the transverse directions. Yet, our formulation does not make inter-slice assumptions, which could have discontinuities. This is the first optimization of a 3D inverse model in an image reconstruction context in OCT. Evaluation in 68 volumes from eyes with pathology showed reduction of illumination artifacts in 88\% of the data, and only 6\% showed moderate residual illumination artifacts. The method enables the use of forward-warped motion corrected data, which is more accurate, and enables supersampling and advanced 3D image reconstruction in OCT.
Unsupervised detection of small hyperreflective features in ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography
Mar 26, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in optical coherence tomography such as the development of high speed ultrahigh resolution scanners and corresponding signal processing techniques may reveal new potential biomarkers in retinal diseases. Newly visible features are, for example, small hyperreflective specks in age-related macular degeneration. Identifying these new markers is crucial to investigate potential association with disease progression and treatment outcomes. Therefore, it is necessary to reliably detect these features in 3D volumetric scans. Because manual labeling of entire volumes is infeasible a need for automatic detection arises. Labeled datasets are often not publicly available and there are usually large variations in scan protocols and scanner types. Thus, this work focuses on an unsupervised approach that is based on local peak-detection and random walker segmentation to detect small features on each B-scan of the volume.
A Spatiotemporal Model for Precise and Efficient Fully-automatic 3D Motion Correction in OCT
Sep 15, 2022Abstract:Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a micrometer-scale, volumetric imaging modality that has become a clinical standard in ophthalmology. OCT instruments image by raster-scanning a focused light spot across the retina, acquiring sequential cross-sectional images to generate volumetric data. Patient eye motion during the acquisition poses unique challenges: Non-rigid, discontinuous distortions can occur, leading to gaps in data and distorted topographic measurements. We present a new distortion model and a corresponding fully-automatic, reference-free optimization strategy for computational motion correction in orthogonally raster-scanned, retinal OCT volumes. Using a novel, domain-specific spatiotemporal parametrization of forward-warping displacements, eye motion can be corrected continuously for the first time. Parameter estimation with temporal regularization improves robustness and accuracy over previous spatial approaches. We correct each A-scan individually in 3D in a single mapping, including repeated acquisitions used in OCT angiography protocols. Specialized 3D forward image warping reduces median runtime to < 9 s, fast enough for clinical use. We present a quantitative evaluation on 18 subjects with ocular pathology and demonstrate accurate correction during microsaccades. Transverse correction is limited only by ocular tremor, whereas submicron repeatability is achieved axially (0.51 um median of medians), representing a dramatic improvement over previous work. This allows assessing longitudinal changes in focal retinal pathologies as a marker of disease progression or treatment response, and promises to enable multiple new capabilities such as supersampled/super-resolution volume reconstruction and analysis of pathological eye motion occuring in neurological diseases.
Trainable Joint Bilateral Filters for Enhanced Prediction Stability in Low-dose CT
Jul 15, 2022



Abstract:Low-dose computed tomography (CT) denoising algorithms aim to enable reduced patient dose in routine CT acquisitions while maintaining high image quality. Recently, deep learning~(DL)-based methods were introduced, outperforming conventional denoising algorithms on this task due to their high model capacity. However, for the transition of DL-based denoising to clinical practice, these data-driven approaches must generalize robustly beyond the seen training data. We, therefore, propose a hybrid denoising approach consisting of a set of trainable joint bilateral filters (JBFs) combined with a convolutional DL-based denoising network to predict the guidance image. Our proposed denoising pipeline combines the high model capacity enabled by DL-based feature extraction with the reliability of the conventional JBF. The pipeline's ability to generalize is demonstrated by training on abdomen CT scans without metal implants and testing on abdomen scans with metal implants as well as on head CT data. When embedding two well-established DL-based denoisers (RED-CNN/QAE) in our pipeline, the denoising performance is improved by $10\,\%$/$82\,\%$ (RMSE) and $3\,\%$/$81\,\%$ (PSNR) in regions containing metal and by $6\,\%$/$78\,\%$ (RMSE) and $2\,\%$/$4\,\%$ (PSNR) on head CT data, compared to the respective vanilla model. Concluding, the proposed trainable JBFs limit the error bound of deep neural networks to facilitate the applicability of DL-based denoisers in low-dose CT pipelines.
Ultra Low-Parameter Denoising: Trainable Bilateral Filter Layers in Computed Tomography
Jan 25, 2022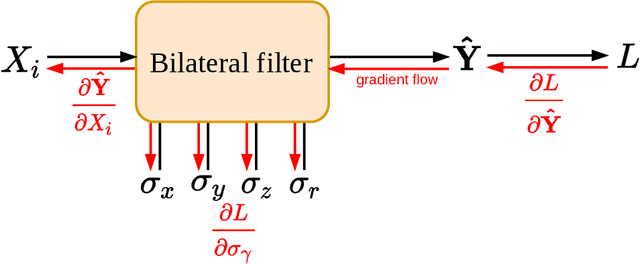
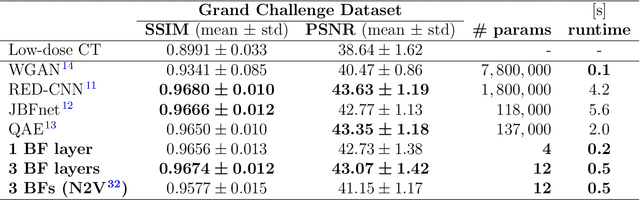
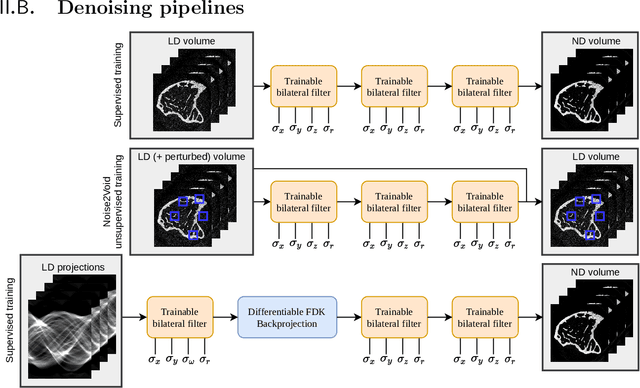
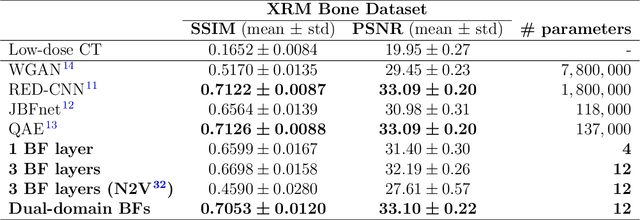
Abstract:Computed tomography is widely used as an imaging tool to visualize three-dimensional structures with expressive bone-soft tissue contrast. However, CT resolution and radiation dose are tightly entangled, highlighting the importance of low-dose CT combined with sophisticated denoising algorithms. Most data-driven denoising techniques are based on deep neural networks and, therefore, contain hundreds of thousands of trainable parameters, making them incomprehensible and prone to prediction failures. Developing understandable and robust denoising algorithms achieving state-of-the-art performance helps to minimize radiation dose while maintaining data integrity. This work presents an open-source CT denoising framework based on the idea of bilateral filtering. We propose a bilateral filter that can be incorporated into a deep learning pipeline and optimized in a purely data-driven way by calculating the gradient flow toward its hyperparameters and its input. Denoising in pure image-to-image pipelines and across different domains such as raw detector data and reconstructed volume, using a differentiable backprojection layer, is demonstrated. Although only using three spatial parameters and one range parameter per filter layer, the proposed denoising pipelines can compete with deep state-of-the-art denoising architectures with several hundred thousand parameters. Competitive denoising performance is achieved on x-ray microscope bone data (0.7053 and 33.10) and the 2016 Low Dose CT Grand Challenge dataset (0.9674 and 43.07) in terms of SSIM and PSNR. Due to the extremely low number of trainable parameters with well-defined effect, prediction reliance and data integrity is guaranteed at any time in the proposed pipelines, in contrast to most other deep learning-based denoising architectures.
PYRO-NN: Python Reconstruction Operators in Neural Networks
Apr 30, 2019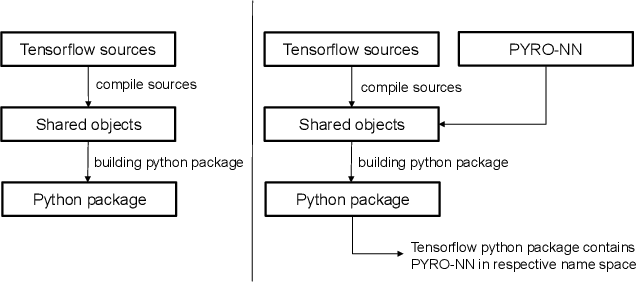
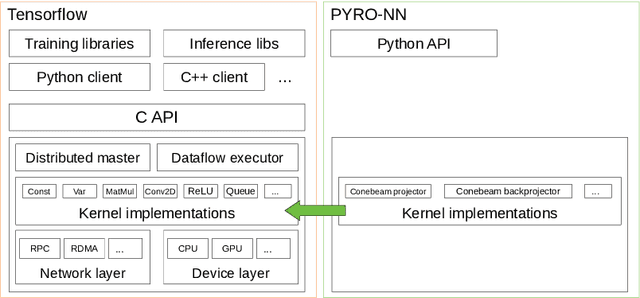
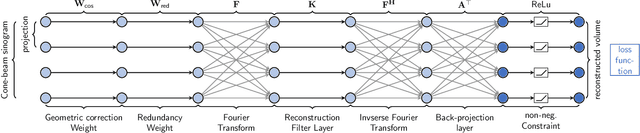
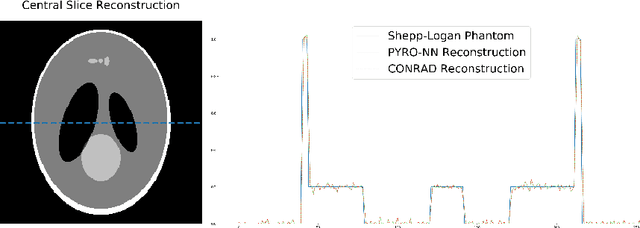
Abstract:Purpose: Recently, several attempts were conducted to transfer deep learning to medical image reconstruction. An increasingly number of publications follow the concept of embedding the CT reconstruction as a known operator into a neural network. However, most of the approaches presented lack an efficient CT reconstruction framework fully integrated into deep learning environments. As a result, many approaches are forced to use workarounds for mathematically unambiguously solvable problems. Methods: PYRO-NN is a generalized framework to embed known operators into the prevalent deep learning framework Tensorflow. The current status includes state-of-the-art parallel-, fan- and cone-beam projectors and back-projectors accelerated with CUDA provided as Tensorflow layers. On top, the framework provides a high level Python API to conduct FBP and iterative reconstruction experiments with data from real CT systems. Results: The framework provides all necessary algorithms and tools to design end-to-end neural network pipelines with integrated CT reconstruction algorithms. The high level Python API allows a simple use of the layers as known from Tensorflow. To demonstrate the capabilities of the layers, the framework comes with three baseline experiments showing a cone-beam short scan FDK reconstruction, a CT reconstruction filter learning setup, and a TV regularized iterative reconstruction. All algorithms and tools are referenced to a scientific publication and are compared to existing non deep learning reconstruction frameworks. The framework is available as open-source software at \url{https://github.com/csyben/PYRO-NN}. Conclusions: PYRO-NN comes with the prevalent deep learning framework Tensorflow and allows to setup end-to-end trainable neural networks in the medical image reconstruction context. We believe that the framework will be a step towards reproducible research
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge