Mayank Patwari
LinGuinE: Longitudinal Guidance Estimation for Volumetric Lung Tumour Segmentation
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Segmentation of lung gross tumour volumes is an important first step in radiotherapy and surgical intervention, and is starting to play a role in assessing chemotherapy response. Response to a drug is measured by tracking the tumour volumes over a series of CT scans over a time period i.e. a longitudinal study. However, there currently exist few solutions for automated or semi-automated longitudinal tumour segmentation. This paper introduces LinGuinE, an automated method to segment a longitudinal series of lung tumours. A radiologist must provide an initial input, indicating the location of the tumour in a CT scan at an arbitrary time point. LinGuinE samples points inside this tumour and propagates them to another time point using rigid registration. A click validity classifier selects points which still fall within the tumour; these are used to automatically create a segmentation in the new time point. We test LinGuinE on a dataset acquired from a phase 3 clinical trial for lung tumours and the publicly available 4-D lung CBCT dataset. We find that LinGuinE improves the Dice on both test sets by over 20% (p< 0.05) across 63 longitudinal studies. We show that any time point can be used as a starting point, conduct ablation experiments, and find that our LinGuinE setup yields the best results on both test datasets.
Trainable Joint Bilateral Filters for Enhanced Prediction Stability in Low-dose CT
Jul 15, 2022



Abstract:Low-dose computed tomography (CT) denoising algorithms aim to enable reduced patient dose in routine CT acquisitions while maintaining high image quality. Recently, deep learning~(DL)-based methods were introduced, outperforming conventional denoising algorithms on this task due to their high model capacity. However, for the transition of DL-based denoising to clinical practice, these data-driven approaches must generalize robustly beyond the seen training data. We, therefore, propose a hybrid denoising approach consisting of a set of trainable joint bilateral filters (JBFs) combined with a convolutional DL-based denoising network to predict the guidance image. Our proposed denoising pipeline combines the high model capacity enabled by DL-based feature extraction with the reliability of the conventional JBF. The pipeline's ability to generalize is demonstrated by training on abdomen CT scans without metal implants and testing on abdomen scans with metal implants as well as on head CT data. When embedding two well-established DL-based denoisers (RED-CNN/QAE) in our pipeline, the denoising performance is improved by $10\,\%$/$82\,\%$ (RMSE) and $3\,\%$/$81\,\%$ (PSNR) in regions containing metal and by $6\,\%$/$78\,\%$ (RMSE) and $2\,\%$/$4\,\%$ (PSNR) on head CT data, compared to the respective vanilla model. Concluding, the proposed trainable JBFs limit the error bound of deep neural networks to facilitate the applicability of DL-based denoisers in low-dose CT pipelines.
Limited Parameter Denoising for Low-dose X-ray Computed Tomography Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Apr 01, 2022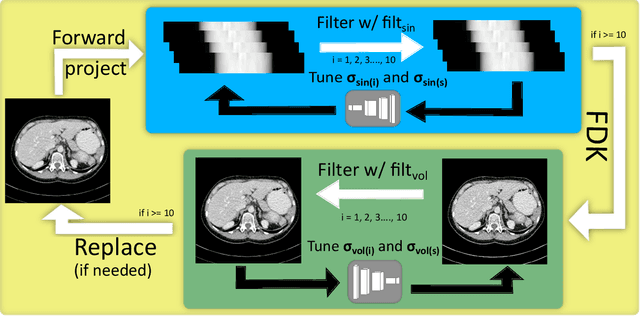
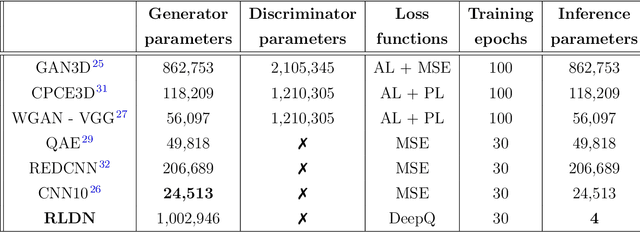
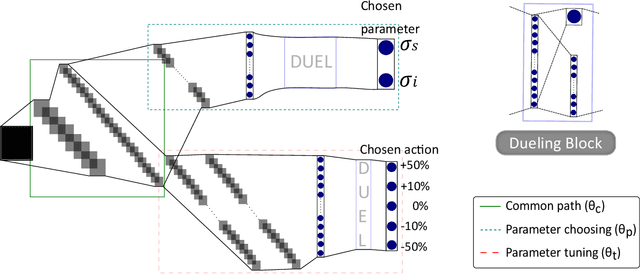
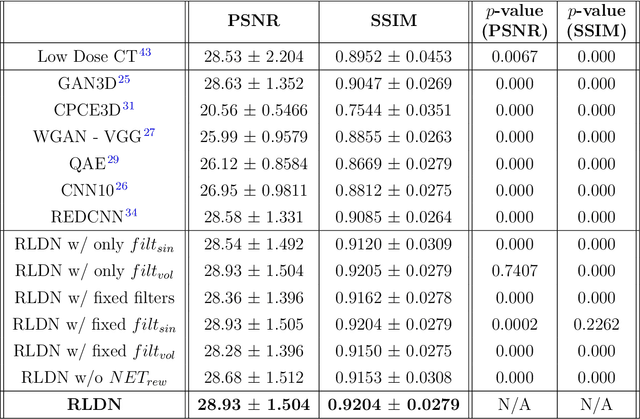
Abstract:The use of deep learning has successfully solved several problems in the field of medical imaging. Deep learning has been applied to the CT denoising problem successfully. However, the use of deep learning requires large amounts of data to train deep convolutional networks (CNNs). Moreover, due to large parameter count, such deep CNNs may cause unexpected results. In this study, we introduce a novel CT denoising framework, which has interpretable behaviour, and provides useful results with limited data. We employ bilateral filtering in both the projection and volume domains to remove noise. To account for non-stationary noise, we tune the $\sigma$ parameters of the volume for every projection view, and for every volume pixel. The tuning is carried out by two deep CNNs. Due to impracticality of labelling, the two deep CNNs are trained via a Deep-Q reinforcement learning task. The reward for the task is generated by using a custom reward function represented by a neural network. Our experiments were carried out on abdominal scans for the Mayo Clinic TCIA dataset, and the AAPM Low Dose CT Grand Challenge. Our denoising framework has excellent denoising performance increasing the PSNR from 28.53 to 28.93, and increasing the SSIM from 0.8952 to 0.9204. We outperform several state-of-the-art deep CNNs, which have several orders of magnitude higher number of parameters (p-value (PSNR) = 0.000, p-value (SSIM) = 0.000). Our method does not introduce any blurring, which is introduced by MSE loss based methods, or any deep learning artifacts, which are introduced by WGAN based models. Our ablation studies show that parameter tuning and using our reward network results in the best possible results.
Ultra Low-Parameter Denoising: Trainable Bilateral Filter Layers in Computed Tomography
Jan 25, 2022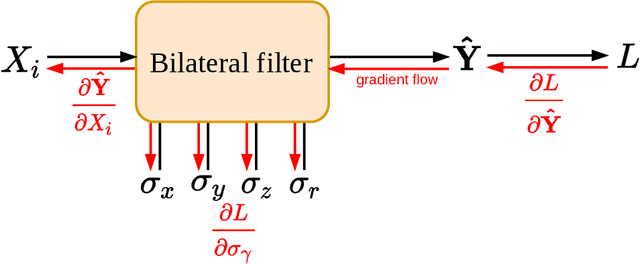
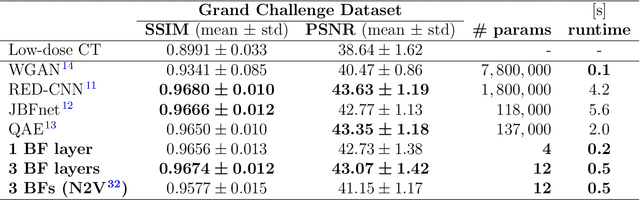
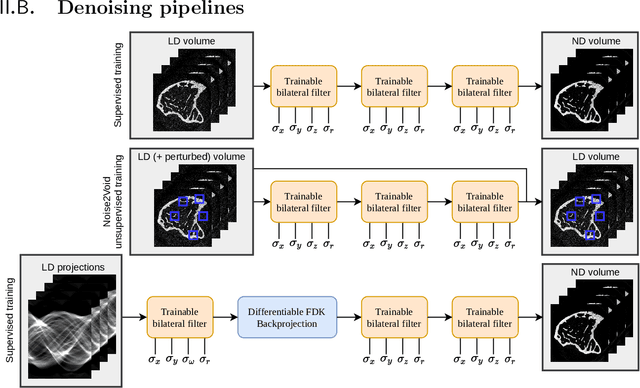
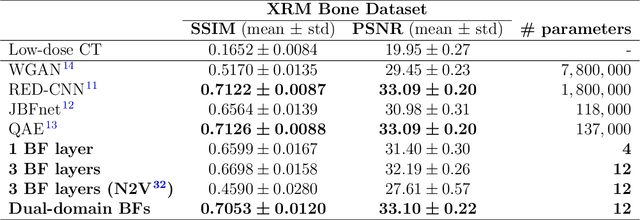
Abstract:Computed tomography is widely used as an imaging tool to visualize three-dimensional structures with expressive bone-soft tissue contrast. However, CT resolution and radiation dose are tightly entangled, highlighting the importance of low-dose CT combined with sophisticated denoising algorithms. Most data-driven denoising techniques are based on deep neural networks and, therefore, contain hundreds of thousands of trainable parameters, making them incomprehensible and prone to prediction failures. Developing understandable and robust denoising algorithms achieving state-of-the-art performance helps to minimize radiation dose while maintaining data integrity. This work presents an open-source CT denoising framework based on the idea of bilateral filtering. We propose a bilateral filter that can be incorporated into a deep learning pipeline and optimized in a purely data-driven way by calculating the gradient flow toward its hyperparameters and its input. Denoising in pure image-to-image pipelines and across different domains such as raw detector data and reconstructed volume, using a differentiable backprojection layer, is demonstrated. Although only using three spatial parameters and one range parameter per filter layer, the proposed denoising pipelines can compete with deep state-of-the-art denoising architectures with several hundred thousand parameters. Competitive denoising performance is achieved on x-ray microscope bone data (0.7053 and 33.10) and the 2016 Low Dose CT Grand Challenge dataset (0.9674 and 43.07) in terms of SSIM and PSNR. Due to the extremely low number of trainable parameters with well-defined effect, prediction reliance and data integrity is guaranteed at any time in the proposed pipelines, in contrast to most other deep learning-based denoising architectures.
Low Dose Helical CBCT denoising by using domain filtering with deep reinforcement learning
Apr 02, 2021



Abstract:Cone Beam Computed Tomography(CBCT) is a now known method to conduct CT imaging. Especially, The Low Dose CT imaging is one of possible options to protect organs of patients when conducting CT imaging. Therefore Low Dose CT imaging can be an alternative instead of Standard dose CT imaging. However Low Dose CT imaging has a fundamental issue with noises within results compared to Standard Dose CT imaging. Currently, there are lots of attempts to erase the noises. Most of methods with artificial intelligence have many parameters and unexplained layers or a kind of black-box methods. Therefore, our research has purposes related to these issues. Our approach has less parameters than usual methods by having Iterative learn-able bilateral filtering approach with Deep reinforcement learning. And we applied The Iterative learn-able filtering approach with deep reinforcement learning to sinograms and reconstructed volume domains. The method and the results of the method can be much more explainable than The other black box AI approaches. And we applied the method to Helical Cone Beam Computed Tomography(CBCT), which is the recent CBCT trend. We tested this method with on 2 abdominal scans(L004, L014) from Mayo Clinic TCIA dataset. The results and the performances of our approach overtake the results of the other previous methods.
Low Dose CT Denoising via Joint Bilateral Filtering and Intelligent Parameter Optimization
Jul 09, 2020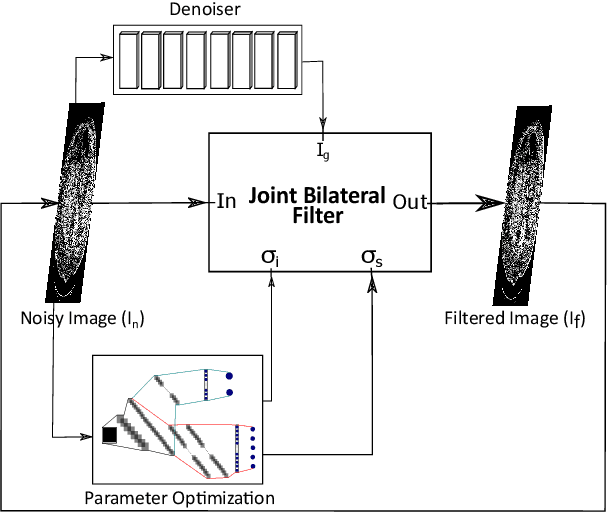
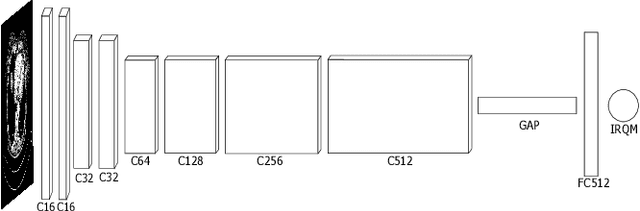
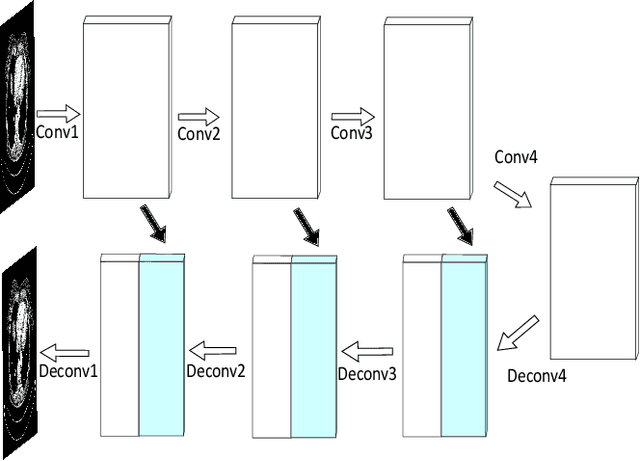
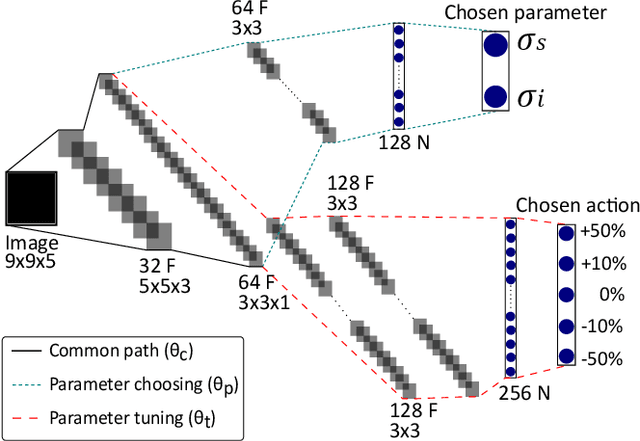
Abstract:Denoising of clinical CT images is an active area for deep learning research. Current clinically approved methods use iterative reconstruction methods to reduce the noise in CT images. Iterative reconstruction techniques require multiple forward and backward projections, which are time-consuming and computationally expensive. Recently, deep learning methods have been successfully used to denoise CT images. However, conventional deep learning methods suffer from the 'black box' problem. They have low accountability, which is necessary for use in clinical imaging situations. In this paper, we use a Joint Bilateral Filter (JBF) to denoise our CT images. The guidance image of the JBF is estimated using a deep residual convolutional neural network (CNN). The range smoothing and spatial smoothing parameters of the JBF are tuned by a deep reinforcement learning task. Our actor first chooses a parameter, and subsequently chooses an action to tune the value of the parameter. A reward network is designed to direct the reinforcement learning task. Our denoising method demonstrates good denoising performance, while retaining structural information. Our method significantly outperforms state of the art deep neural networks. Moreover, our method has only two parameters, which makes it significantly more interpretable and reduces the 'black box' problem. We experimentally measure the impact of our intelligent parameter optimization and our reward network. Our studies show that our current setup yields the best results in terms of structural preservation.
JBFnet -- Low Dose CT Denoising by Trainable Joint Bilateral Filtering
Jul 09, 2020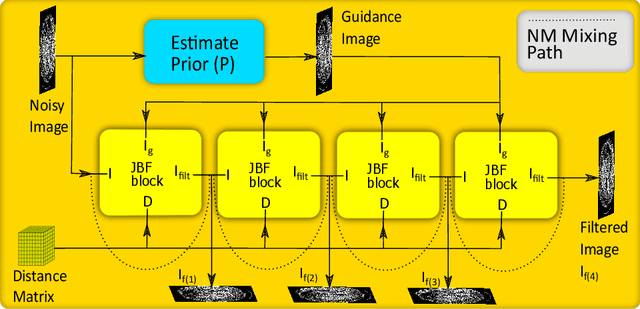
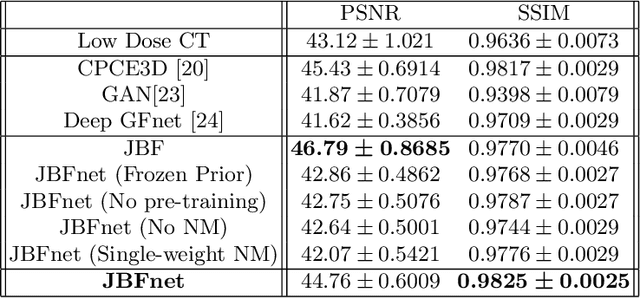
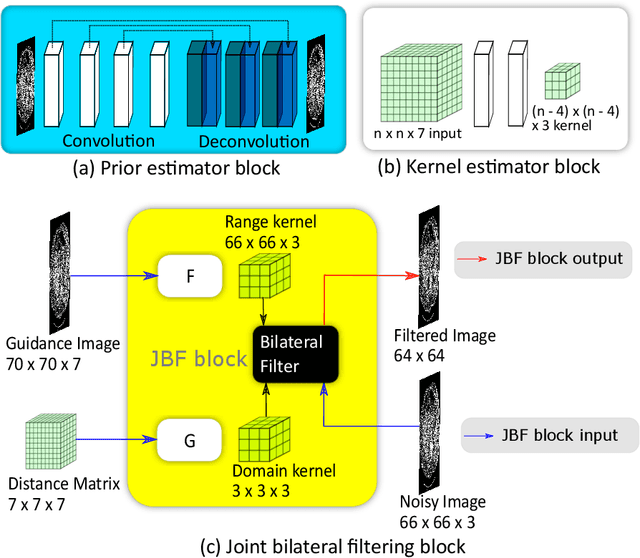
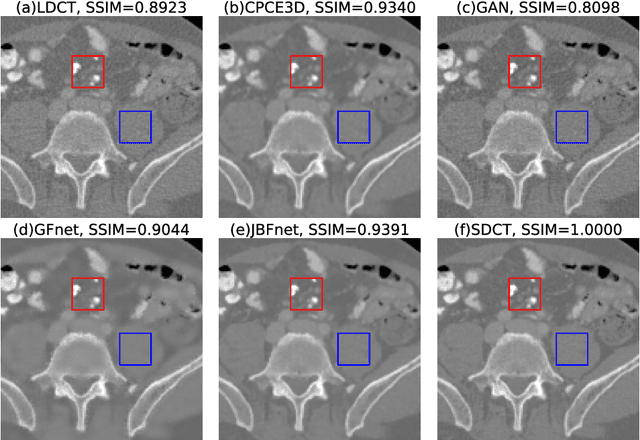
Abstract:Deep neural networks have shown great success in low dose CT denoising. However, most of these deep neural networks have several hundred thousand trainable parameters. This, combined with the inherent non-linearity of the neural network, makes the deep neural network diffcult to understand with low accountability. In this study we introduce JBFnet, a neural network for low dose CT denoising. The architecture of JBFnet implements iterative bilateral filtering. The filter functions of the Joint Bilateral Filter (JBF) are learned via shallow convolutional networks. The guidance image is estimated by a deep neural network. JBFnet is split into four filtering blocks, each of which performs Joint Bilateral Filtering. Each JBF block consists of 112 trainable parameters, making the noise removal process comprehendable. The Noise Map (NM) is added after filtering to preserve high level features. We train JBFnet with the data from the body scans of 10 patients, and test it on the AAPM low dose CT Grand Challenge dataset. We compare JBFnet with state-of-the-art deep learning networks. JBFnet outperforms CPCE3D, GAN and deep GFnet on the test dataset in terms of noise removal while preserving structures. We conduct several ablation studies to test the performance of our network architecture and training method. Our current setup achieves the best performance, while still maintaining behavioural accountability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge