Stanislas Lauly
MT-GenEval: A Counterfactual and Contextual Dataset for Evaluating Gender Accuracy in Machine Translation
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:As generic machine translation (MT) quality has improved, the need for targeted benchmarks that explore fine-grained aspects of quality has increased. In particular, gender accuracy in translation can have implications in terms of output fluency, translation accuracy, and ethics. In this paper, we introduce MT-GenEval, a benchmark for evaluating gender accuracy in translation from English into eight widely-spoken languages. MT-GenEval complements existing benchmarks by providing realistic, gender-balanced, counterfactual data in eight language pairs where the gender of individuals is unambiguous in the input segment, including multi-sentence segments requiring inter-sentential gender agreement. Our data and code is publicly available under a CC BY SA 3.0 license.
Joint translation and unit conversion for end-to-end localization
Apr 10, 2020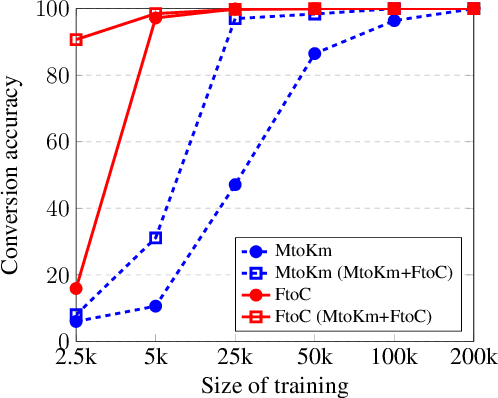

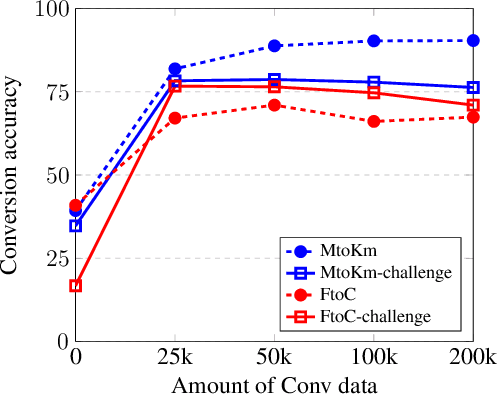
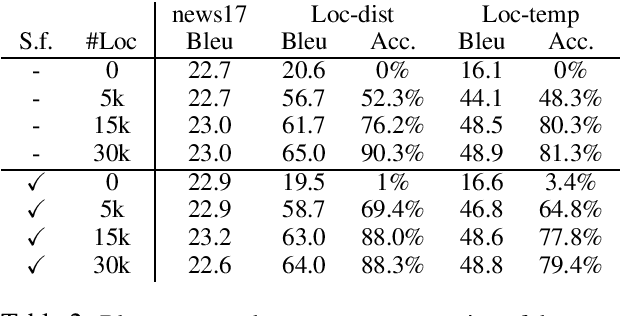
Abstract:A variety of natural language tasks require processing of textual data which contains a mix of natural language and formal languages such as mathematical expressions. In this paper, we take unit conversions as an example and propose a data augmentation technique which leads to models learning both translation and conversion tasks as well as how to adequately switch between them for end-to-end localization.
Does Neural Machine Translation Benefit from Larger Context?
Apr 17, 2017


Abstract:We propose a neural machine translation architecture that models the surrounding text in addition to the source sentence. These models lead to better performance, both in terms of general translation quality and pronoun prediction, when trained on small corpora, although this improvement largely disappears when trained with a larger corpus. We also discover that attention-based neural machine translation is well suited for pronoun prediction and compares favorably with other approaches that were specifically designed for this task.
Document Neural Autoregressive Distribution Estimation
Mar 18, 2016



Abstract:We present an approach based on feed-forward neural networks for learning the distribution of textual documents. This approach is inspired by the Neural Autoregressive Distribution Estimator(NADE) model, which has been shown to be a good estimator of the distribution of discrete-valued igh-dimensional vectors. In this paper, we present how NADE can successfully be adapted to the case of textual data, retaining from NADE the property that sampling or computing the probability of observations can be done exactly and efficiently. The approach can also be used to learn deep representations of documents that are competitive to those learned by the alternative topic modeling approaches. Finally, we describe how the approach can be combined with a regular neural network N-gram model and substantially improve its performance, by making its learned representation sensitive to the larger, document-specific context.
An Autoencoder Approach to Learning Bilingual Word Representations
Feb 06, 2014
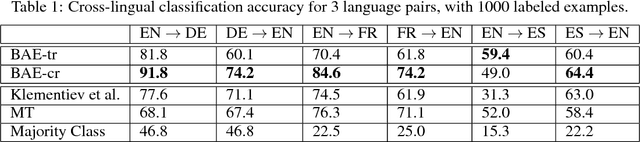
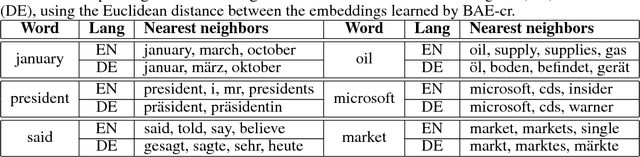

Abstract:Cross-language learning allows us to use training data from one language to build models for a different language. Many approaches to bilingual learning require that we have word-level alignment of sentences from parallel corpora. In this work we explore the use of autoencoder-based methods for cross-language learning of vectorial word representations that are aligned between two languages, while not relying on word-level alignments. We show that by simply learning to reconstruct the bag-of-words representations of aligned sentences, within and between languages, we can in fact learn high-quality representations and do without word alignments. Since training autoencoders on word observations presents certain computational issues, we propose and compare different variations adapted to this setting. We also propose an explicit correlation maximizing regularizer that leads to significant improvement in the performance. We empirically investigate the success of our approach on the problem of cross-language test classification, where a classifier trained on a given language (e.g., English) must learn to generalize to a different language (e.g., German). These experiments demonstrate that our approaches are competitive with the state-of-the-art, achieving up to 10-14 percentage point improvements over the best reported results on this task.
Learning Multilingual Word Representations using a Bag-of-Words Autoencoder
Jan 08, 2014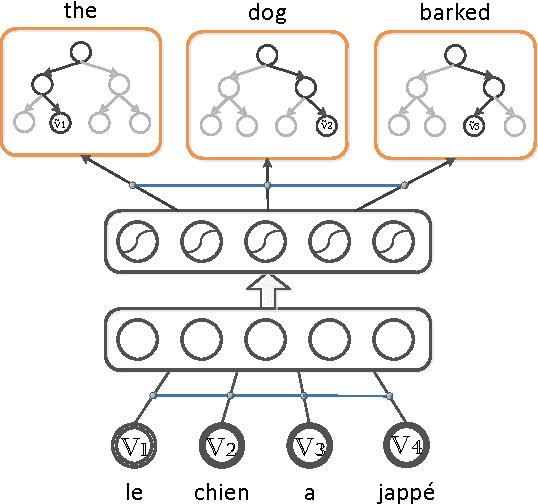
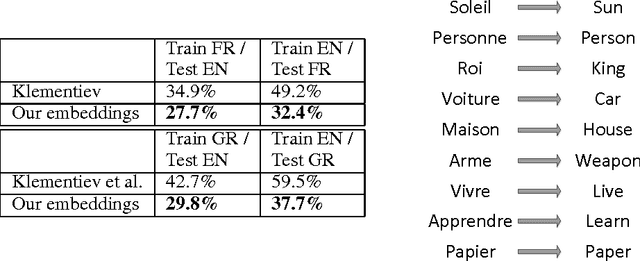

Abstract:Recent work on learning multilingual word representations usually relies on the use of word-level alignements (e.g. infered with the help of GIZA++) between translated sentences, in order to align the word embeddings in different languages. In this workshop paper, we investigate an autoencoder model for learning multilingual word representations that does without such word-level alignements. The autoencoder is trained to reconstruct the bag-of-word representation of given sentence from an encoded representation extracted from its translation. We evaluate our approach on a multilingual document classification task, where labeled data is available only for one language (e.g. English) while classification must be performed in a different language (e.g. French). In our experiments, we observe that our method compares favorably with a previously proposed method that exploits word-level alignments to learn word representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge