Maria Nădejde
Pseudo-Label Training and Model Inertia in Neural Machine Translation
May 19, 2023Abstract:Like many other machine learning applications, neural machine translation (NMT) benefits from over-parameterized deep neural models. However, these models have been observed to be brittle: NMT model predictions are sensitive to small input changes and can show significant variation across re-training or incremental model updates. This work studies a frequently used method in NMT, pseudo-label training (PLT), which is common to the related techniques of forward-translation (or self-training) and sequence-level knowledge distillation. While the effect of PLT on quality is well-documented, we highlight a lesser-known effect: PLT can enhance a model's stability to model updates and input perturbations, a set of properties we call model inertia. We study inertia effects under different training settings and we identify distribution simplification as a mechanism behind the observed results.
MT-GenEval: A Counterfactual and Contextual Dataset for Evaluating Gender Accuracy in Machine Translation
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:As generic machine translation (MT) quality has improved, the need for targeted benchmarks that explore fine-grained aspects of quality has increased. In particular, gender accuracy in translation can have implications in terms of output fluency, translation accuracy, and ethics. In this paper, we introduce MT-GenEval, a benchmark for evaluating gender accuracy in translation from English into eight widely-spoken languages. MT-GenEval complements existing benchmarks by providing realistic, gender-balanced, counterfactual data in eight language pairs where the gender of individuals is unambiguous in the input segment, including multi-sentence segments requiring inter-sentential gender agreement. Our data and code is publicly available under a CC BY SA 3.0 license.
CoCoA-MT: A Dataset and Benchmark for Contrastive Controlled MT with Application to Formality
May 09, 2022
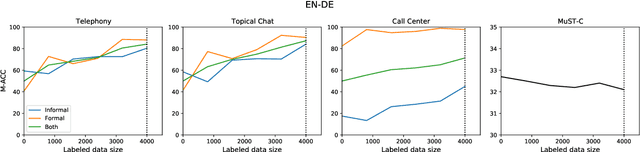
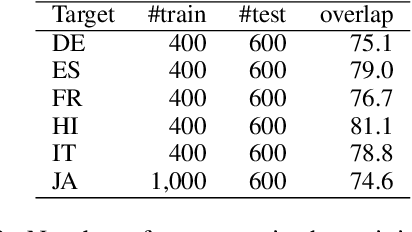
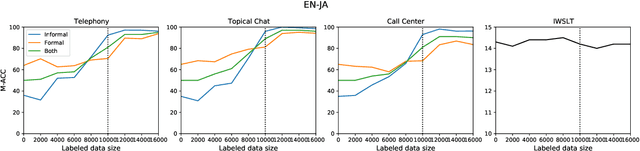
Abstract:The machine translation (MT) task is typically formulated as that of returning a single translation for an input segment. However, in many cases, multiple different translations are valid and the appropriate translation may depend on the intended target audience, characteristics of the speaker, or even the relationship between speakers. Specific problems arise when dealing with honorifics, particularly translating from English into languages with formality markers. For example, the sentence "Are you sure?" can be translated in German as "Sind Sie sich sicher?" (formal register) or "Bist du dir sicher?" (informal). Using wrong or inconsistent tone may be perceived as inappropriate or jarring for users of certain cultures and demographics. This work addresses the problem of learning to control target language attributes, in this case formality, from a small amount of labeled contrastive data. We introduce an annotated dataset (CoCoA-MT) and an associated evaluation metric for training and evaluating formality-controlled MT models for six diverse target languages. We show that we can train formality-controlled models by fine-tuning on labeled contrastive data, achieving high accuracy (82% in-domain and 73% out-of-domain) while maintaining overall quality.
Nematus: a Toolkit for Neural Machine Translation
Mar 13, 2017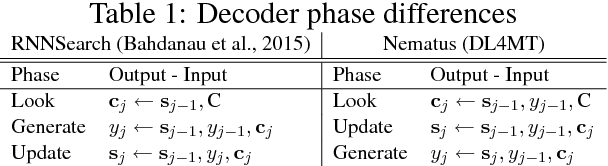
Abstract:We present Nematus, a toolkit for Neural Machine Translation. The toolkit prioritizes high translation accuracy, usability, and extensibility. Nematus has been used to build top-performing submissions to shared translation tasks at WMT and IWSLT, and has been used to train systems for production environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge