Julian Hitschler
Sparse Stochastic Zeroth-Order Optimization with an Application to Bandit Structured Prediction
Jul 31, 2018
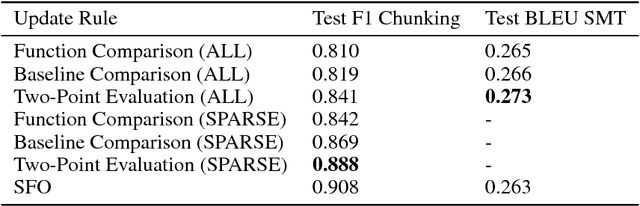

Abstract:Stochastic zeroth-order (SZO), or gradient-free, optimization allows to optimize arbitrary functions by relying only on function evaluations under parameter perturbations, however, the iteration complexity of SZO methods suffers a factor proportional to the dimensionality of the perturbed function. We show that in scenarios with natural sparsity patterns as in structured prediction applications, this factor can be reduced to the expected number of active features over input-output pairs. We give a general proof that applies sparse SZO optimization to Lipschitz-continuous, nonconvex, stochastic objectives, and present an experimental evaluation on linear bandit structured prediction tasks with sparse word-based feature representations that confirm our theoretical results.
Nematus: a Toolkit for Neural Machine Translation
Mar 13, 2017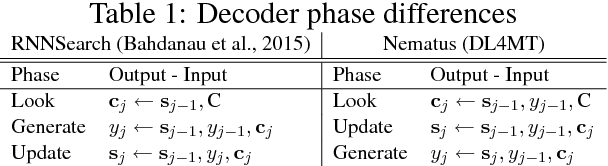
Abstract:We present Nematus, a toolkit for Neural Machine Translation. The toolkit prioritizes high translation accuracy, usability, and extensibility. Nematus has been used to build top-performing submissions to shared translation tasks at WMT and IWSLT, and has been used to train systems for production environments.
Multimodal Pivots for Image Caption Translation
Jun 13, 2016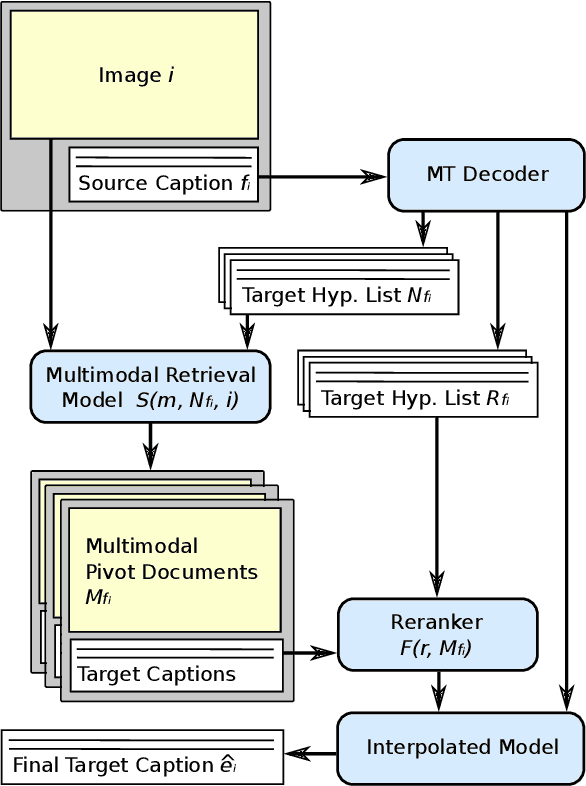
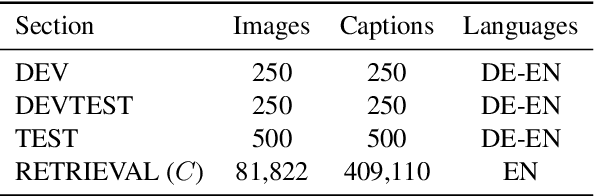
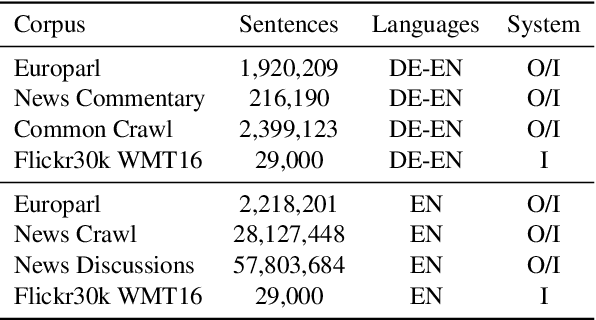
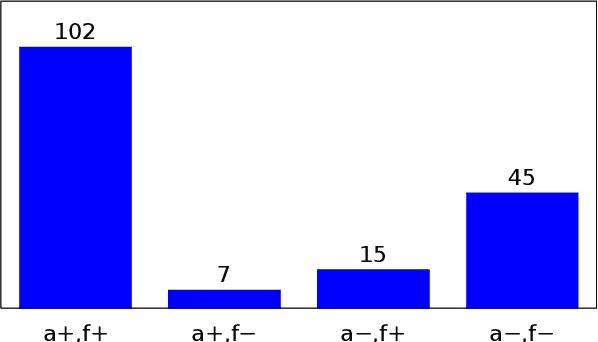
Abstract:We present an approach to improve statistical machine translation of image descriptions by multimodal pivots defined in visual space. The key idea is to perform image retrieval over a database of images that are captioned in the target language, and use the captions of the most similar images for crosslingual reranking of translation outputs. Our approach does not depend on the availability of large amounts of in-domain parallel data, but only relies on available large datasets of monolingually captioned images, and on state-of-the-art convolutional neural networks to compute image similarities. Our experimental evaluation shows improvements of 1 BLEU point over strong baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge