Sirou Zhu
Scaling In-Context Online Learning Capability of LLMs via Cross-Episode Meta-RL
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve strong performance when all task-relevant information is available upfront, as in static prediction and instruction-following problems. However, many real-world decision-making tasks are inherently online: crucial information must be acquired through interaction, feedback is delayed, and effective behavior requires balancing information collection and exploitation over time. While in-context learning enables adaptation without weight updates, existing LLMs often struggle to reliably leverage in-context interaction experience in such settings. In this work, we show that this limitation can be addressed through training. We introduce ORBIT, a multi-task, multi-episode meta-reinforcement learning framework that trains LLMs to learn from interaction in context. After meta-training, a relatively small open-source model (Qwen3-14B) demonstrates substantially improved in-context online learning on entirely unseen environments, matching the performance of GPT-5.2 and outperforming standard RL fine-tuning by a large margin. Scaling experiments further reveal consistent gains with model size, suggesting significant headroom for learn-at-inference-time decision-making agents. Code reproducing the results in the paper can be found at https://github.com/XiaofengLin7/ORBIT.
Efficient AI in Practice: Training and Deployment of Efficient LLMs for Industry Applications
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance across a wide range of industrial applications, from search and recommendations to generative tasks. Although scaling laws indicate that larger models generally yield better generalization and performance, their substantial computational requirements often render them impractical for many real-world scenarios at scale. In this paper, we present methods and insights for training small language models (SLMs) that deliver high performance and efficiency in deployment. We focus on two key techniques: (1) knowledge distillation and (2) model compression via quantization and pruning. These approaches enable SLMs to retain much of the quality of their larger counterparts while significantly reducing training, serving costs, and latency. We detail the impact of these techniques on a variety of use cases at a large professional social network platform and share deployment lessons - including hardware optimization strategies that enhance speed and throughput for both predictive and reasoning-based applications.
AlphaPO -- Reward shape matters for LLM alignment
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) and its variants have made huge strides toward the effective alignment of large language models (LLMs) to follow instructions and reflect human values. More recently, Direct Alignment Algorithms (DAAs) have emerged in which the reward modeling stage of RLHF is skipped by characterizing the reward directly as a function of the policy being learned. Examples include Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Simple Preference Optimization (SimPO). These methods often suffer from likelihood displacement, a phenomenon by which the probabilities of preferred responses are often reduced undesirably. In this paper, we argue that, for DAAs the reward (function) shape matters. We introduce AlphaPO, a new DAA method that leverages an $\alpha$-parameter to help change the shape of the reward function beyond the standard log reward. AlphaPO helps maintain fine-grained control over likelihood displacement and over-optimization. Compared to SimPO, one of the best performing DAAs, AlphaPO leads to about 7\% to 10\% relative improvement in alignment performance for the instruct versions of Mistral-7B and Llama3-8B. The analysis and results presented highlight the importance of the reward shape, and how one can systematically change it to affect training dynamics, as well as improve alignment performance.
LiGNN: Graph Neural Networks at LinkedIn
Feb 17, 2024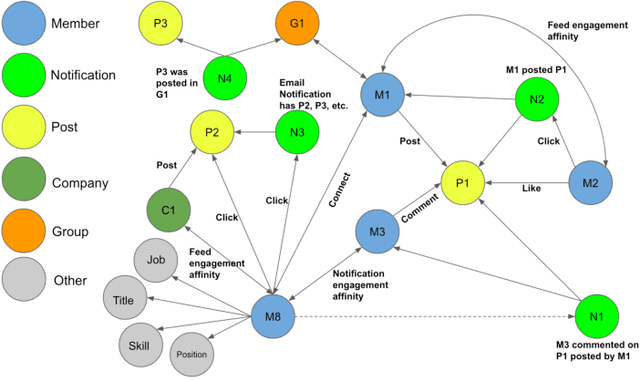

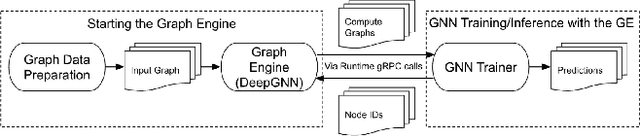

Abstract:In this paper, we present LiGNN, a deployed large-scale Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) Framework. We share our insight on developing and deployment of GNNs at large scale at LinkedIn. We present a set of algorithmic improvements to the quality of GNN representation learning including temporal graph architectures with long term losses, effective cold start solutions via graph densification, ID embeddings and multi-hop neighbor sampling. We explain how we built and sped up by 7x our large-scale training on LinkedIn graphs with adaptive sampling of neighbors, grouping and slicing of training data batches, specialized shared-memory queue and local gradient optimization. We summarize our deployment lessons and learnings gathered from A/B test experiments. The techniques presented in this work have contributed to an approximate relative improvements of 1% of Job application hearing back rate, 2% Ads CTR lift, 0.5% of Feed engaged daily active users, 0.2% session lift and 0.1% weekly active user lift from people recommendation. We believe that this work can provide practical solutions and insights for engineers who are interested in applying Graph neural networks at large scale.
LiRank: Industrial Large Scale Ranking Models at LinkedIn
Feb 10, 2024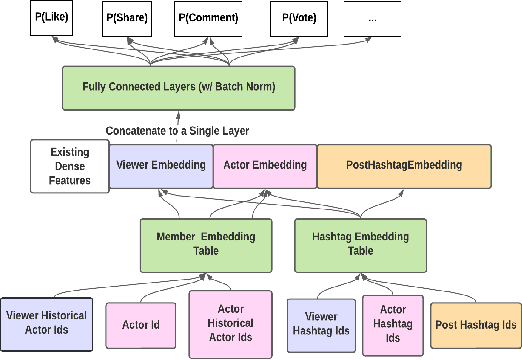
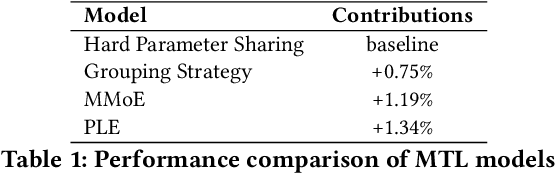
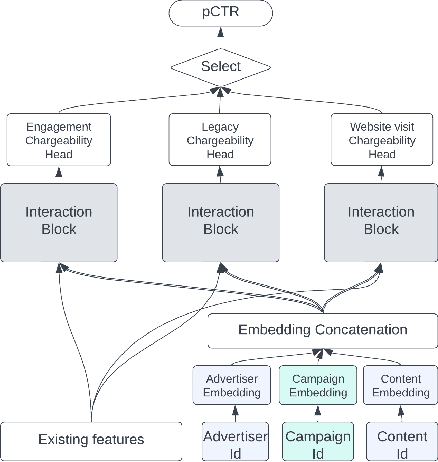

Abstract:We present LiRank, a large-scale ranking framework at LinkedIn that brings to production state-of-the-art modeling architectures and optimization methods. We unveil several modeling improvements, including Residual DCN, which adds attention and residual connections to the famous DCNv2 architecture. We share insights into combining and tuning SOTA architectures to create a unified model, including Dense Gating, Transformers and Residual DCN. We also propose novel techniques for calibration and describe how we productionalized deep learning based explore/exploit methods. To enable effective, production-grade serving of large ranking models, we detail how to train and compress models using quantization and vocabulary compression. We provide details about the deployment setup for large-scale use cases of Feed ranking, Jobs Recommendations, and Ads click-through rate (CTR) prediction. We summarize our learnings from various A/B tests by elucidating the most effective technical approaches. These ideas have contributed to relative metrics improvements across the board at LinkedIn: +0.5% member sessions in the Feed, +1.76% qualified job applications for Jobs search and recommendations, and +4.3% for Ads CTR. We hope this work can provide practical insights and solutions for practitioners interested in leveraging large-scale deep ranking systems.
SALIENCE: An Unsupervised User Adaptation Model for Multiple Wearable Sensors Based Human Activity Recognition
Aug 17, 2021



Abstract:Unsupervised user adaptation aligns the feature distributions of the data from training users and the new user, so a well-trained wearable human activity recognition (WHAR) model can be well adapted to the new user. With the development of wearable sensors, multiple wearable sensors based WHAR is gaining more and more attention. In order to address the challenge that the transferabilities of different sensors are different, we propose SALIENCE (unsupervised user adaptation model for multiple wearable sensors based human activity recognition) model. It aligns the data of each sensor separately to achieve local alignment, while uniformly aligning the data of all sensors to ensure global alignment. In addition, an attention mechanism is proposed to focus the activity classifier of SALIENCE on the sensors with strong feature discrimination and well distribution alignment. Experiments are conducted on two public WHAR datasets, and the experimental results show that our model can yield a competitive performance.
Knowledge Graph Completion with Text-aided Regularization
Jan 22, 2021

Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion is a task of expanding the knowledge graph/base through estimating possible entities, or proper nouns, that can be connected using a set of predefined relations, or verb/predicates describing interconnections of two things. Generally, we describe this problem as adding new edges to a current network of vertices and edges. Traditional approaches mainly focus on using the existing graphical information that is intrinsic of the graph and train the corresponding embeddings to describe the information; however, we think that the corpus that are related to the entities should also contain information that can positively influence the embeddings to better make predictions. In our project, we try numerous ways of using extracted or raw textual information to help existing KG embedding frameworks reach better prediction results, in the means of adding a similarity function to the regularization part in the loss function. Results have shown that we have made decent improvements over baseline KG embedding methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge