Sanoojan Baliah
A Culturally-diverse Multilingual Multimodal Video Benchmark & Model
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have recently gained attention due to their effectiveness to understand and generate descriptions of visual content. Most existing LMMs are in English language. While few recent works explore multilingual image LMMs, to the best of our knowledge, moving beyond the English language for cultural and linguistic inclusivity is yet to be investigated in the context of video LMMs. In pursuit of more inclusive video LMMs, we introduce a multilingual Video LMM benchmark, named ViMUL-Bench, to evaluate Video LMMs across 14 languages, including both low- and high-resource languages: English, Chinese, Spanish, French, German, Hindi, Arabic, Russian, Bengali, Urdu, Sinhala, Tamil, Swedish, and Japanese. Our ViMUL-Bench is designed to rigorously test video LMMs across 15 categories including eight culturally diverse categories, ranging from lifestyles and festivals to foods and rituals and from local landmarks to prominent cultural personalities. ViMUL-Bench comprises both open-ended (short and long-form) and multiple-choice questions spanning various video durations (short, medium, and long) with 8k samples that are manually verified by native language speakers. In addition, we also introduce a machine translated multilingual video training set comprising 1.2 million samples and develop a simple multilingual video LMM, named ViMUL, that is shown to provide a better tradeoff between high-and low-resource languages for video understanding. We hope our ViMUL-Bench and multilingual video LMM along with a large-scale multilingual video training set will help ease future research in developing cultural and linguistic inclusive multilingual video LMMs. Our proposed benchmark, video LMM and training data will be publicly released at https://mbzuai-oryx.github.io/ViMUL/.
O-TPT: Orthogonality Constraints for Calibrating Test-time Prompt Tuning in Vision-Language Models
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Test-time prompt tuning for vision-language models (VLMs) is getting attention because of their ability to learn with unlabeled data without fine-tuning. Although test-time prompt tuning methods for VLMs can boost accuracy, the resulting models tend to demonstrate poor calibration, which casts doubts on the reliability and trustworthiness of these models. Notably, more attention needs to be devoted to calibrating the test-time prompt tuning in vision-language models. To this end, we propose a new approach, called O-TPT that introduces orthogonality constraints on the textual features corresponding to the learnable prompts for calibrating test-time prompt tuning in VLMs. Towards introducing orthogonality constraints, we make the following contributions. First, we uncover new insights behind the suboptimal calibration performance of existing methods relying on textual feature dispersion. Second, we show that imposing a simple orthogonalization of textual features is a more effective approach towards obtaining textual dispersion. We conduct extensive experiments on various datasets with different backbones and baselines. The results indicate that our method consistently outperforms the prior state of the art in significantly reducing the overall average calibration error. Also, our method surpasses the zero-shot calibration performance on fine-grained classification tasks.
All Languages Matter: Evaluating LMMs on Culturally Diverse 100 Languages
Nov 25, 2024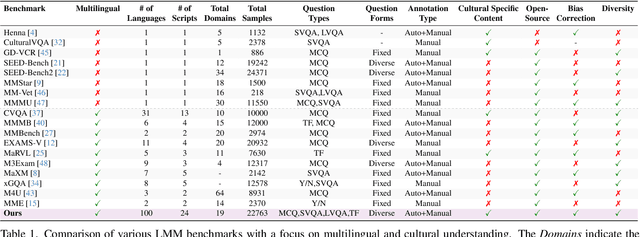
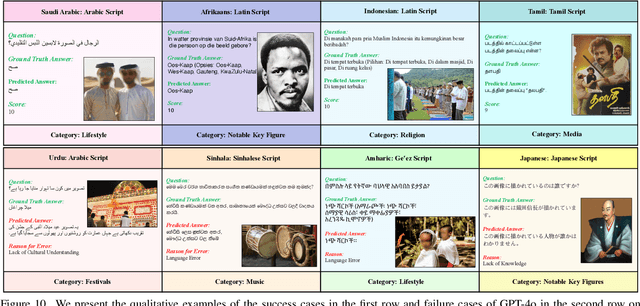
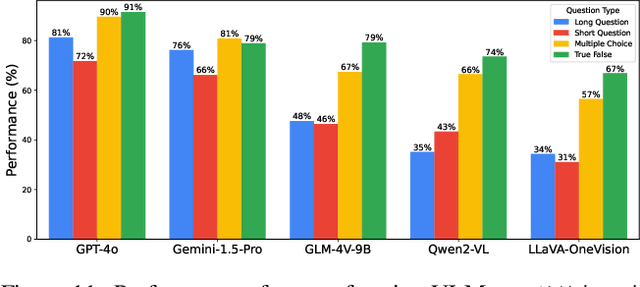
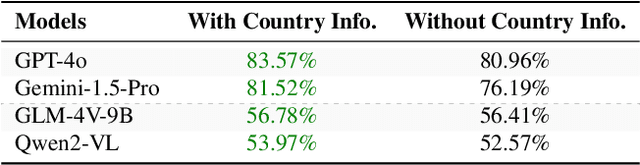
Abstract:Existing Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) generally focus on only a few regions and languages. As LMMs continue to improve, it is increasingly important to ensure they understand cultural contexts, respect local sensitivities, and support low-resource languages, all while effectively integrating corresponding visual cues. In pursuit of culturally diverse global multimodal models, our proposed All Languages Matter Benchmark (ALM-bench) represents the largest and most comprehensive effort to date for evaluating LMMs across 100 languages. ALM-bench challenges existing models by testing their ability to understand and reason about culturally diverse images paired with text in various languages, including many low-resource languages traditionally underrepresented in LMM research. The benchmark offers a robust and nuanced evaluation framework featuring various question formats, including true/false, multiple choice, and open-ended questions, which are further divided into short and long-answer categories. ALM-bench design ensures a comprehensive assessment of a model's ability to handle varied levels of difficulty in visual and linguistic reasoning. To capture the rich tapestry of global cultures, ALM-bench carefully curates content from 13 distinct cultural aspects, ranging from traditions and rituals to famous personalities and celebrations. Through this, ALM-bench not only provides a rigorous testing ground for state-of-the-art open and closed-source LMMs but also highlights the importance of cultural and linguistic inclusivity, encouraging the development of models that can serve diverse global populations effectively. Our benchmark is publicly available.
Realistic and Efficient Face Swapping: A Unified Approach with Diffusion Models
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:Despite promising progress in face swapping task, realistic swapped images remain elusive, often marred by artifacts, particularly in scenarios involving high pose variation, color differences, and occlusion. To address these issues, we propose a novel approach that better harnesses diffusion models for face-swapping by making following core contributions. (a) We propose to re-frame the face-swapping task as a self-supervised, train-time inpainting problem, enhancing the identity transfer while blending with the target image. (b) We introduce a multi-step Denoising Diffusion Implicit Model (DDIM) sampling during training, reinforcing identity and perceptual similarities. (c) Third, we introduce CLIP feature disentanglement to extract pose, expression, and lighting information from the target image, improving fidelity. (d) Further, we introduce a mask shuffling technique during inpainting training, which allows us to create a so-called universal model for swapping, with an additional feature of head swapping. Ours can swap hair and even accessories, beyond traditional face swapping. Unlike prior works reliant on multiple off-the-shelf models, ours is a relatively unified approach and so it is resilient to errors in other off-the-shelf models. Extensive experiments on FFHQ and CelebA datasets validate the efficacy and robustness of our approach, showcasing high-fidelity, realistic face-swapping with minimal inference time. Our code is available at https://github.com/Sanoojan/REFace.
Towards Generalizing to Unseen Domains with Few Labels
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:We approach the challenge of addressing semi-supervised domain generalization (SSDG). Specifically, our aim is to obtain a model that learns domain-generalizable features by leveraging a limited subset of labelled data alongside a substantially larger pool of unlabeled data. Existing domain generalization (DG) methods which are unable to exploit unlabeled data perform poorly compared to semi-supervised learning (SSL) methods under SSDG setting. Nevertheless, SSL methods have considerable room for performance improvement when compared to fully-supervised DG training. To tackle this underexplored, yet highly practical problem of SSDG, we make the following core contributions. First, we propose a feature-based conformity technique that matches the posterior distributions from the feature space with the pseudo-label from the model's output space. Second, we develop a semantics alignment loss to learn semantically-compatible representations by regularizing the semantic structure in the feature space. Our method is plug-and-play and can be readily integrated with different SSL-based SSDG baselines without introducing any additional parameters. Extensive experimental results across five challenging DG benchmarks with four strong SSL baselines suggest that our method provides consistent and notable gains in two different SSDG settings.
Unsupervised Landmark Discovery Using Consistency Guided Bottleneck
Sep 19, 2023


Abstract:We study a challenging problem of unsupervised discovery of object landmarks. Many recent methods rely on bottlenecks to generate 2D Gaussian heatmaps however, these are limited in generating informed heatmaps while training, presumably due to the lack of effective structural cues. Also, it is assumed that all predicted landmarks are semantically relevant despite having no ground truth supervision. In the current work, we introduce a consistency-guided bottleneck in an image reconstruction-based pipeline that leverages landmark consistency, a measure of compatibility score with the pseudo-ground truth to generate adaptive heatmaps. We propose obtaining pseudo-supervision via forming landmark correspondence across images. The consistency then modulates the uncertainty of the discovered landmarks in the generation of adaptive heatmaps which rank consistent landmarks above their noisy counterparts, providing effective structural information for improved robustness. Evaluations on five diverse datasets including MAFL, AFLW, LS3D, Cats, and Shoes demonstrate excellent performance of the proposed approach compared to the existing state-of-the-art methods. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/MamonaAwan/CGB_ULD.
Exploring the Transfer Learning Capabilities of CLIP in Domain Generalization for Diabetic Retinopathy
Aug 27, 2023



Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy (DR), a leading cause of vision impairment, requires early detection and treatment. Developing robust AI models for DR classification holds substantial potential, but a key challenge is ensuring their generalization in unfamiliar domains with varying data distributions. To address this, our paper investigates cross-domain generalization, also known as domain generalization (DG), within the context of DR classification. DG, a challenging problem in the medical domain, is complicated by the difficulty of gathering labeled data across different domains, such as patient demographics and disease stages. Some recent studies have shown the effectiveness of using CLIP to handle the DG problem in natural images. In this study, we investigate CLIP's transfer learning capabilities and its potential for cross-domain generalization in diabetic retinopathy (DR) classification. We carry out comprehensive experiments to assess the efficacy and potential of CLIP in addressing DG for DR classification. Further, we introduce a multi-modal fine-tuning strategy named Context Optimization with Learnable Visual Tokens (CoOpLVT), which enhances context optimization by conditioning on visual features. Our findings demonstrate that the proposed method increases the F1-score by 1.8% over the baseline, thus underlining its promise for effective DG in DR classification. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Sanoojan/CLIP-DRDG.
Dynamic Template Initialization for Part-Aware Person Re-ID
Aug 24, 2022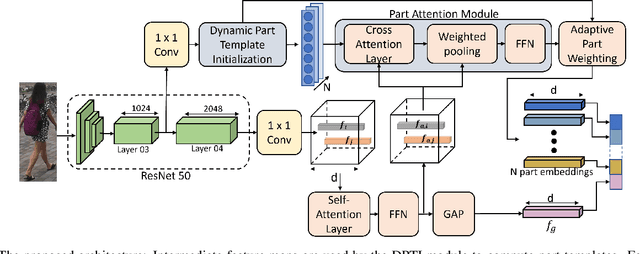
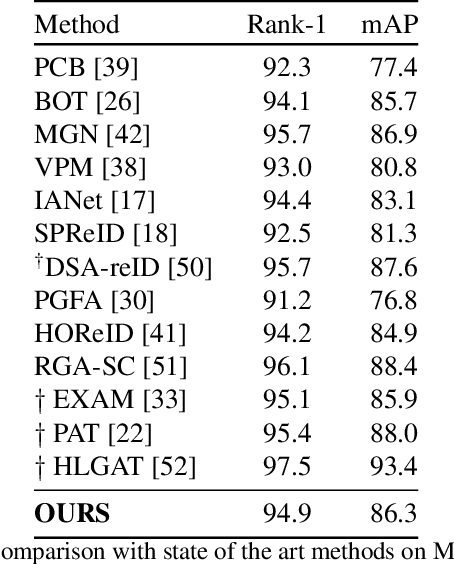
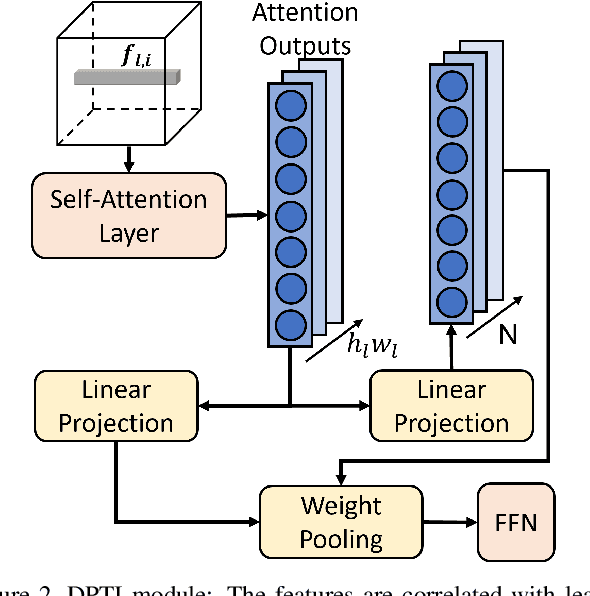
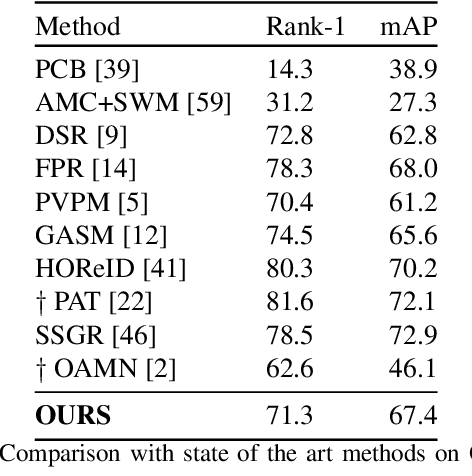
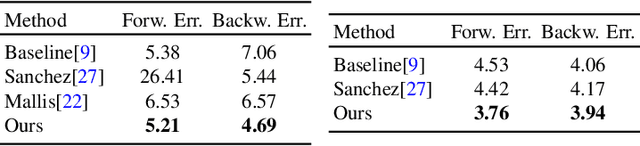
Abstract:Many of the existing Person Re-identification (Re-ID) approaches depend on feature maps which are either partitioned to localize parts of a person or reduced to create a global representation. While part localization has shown significant success, it uses either na{\i}ve position-based partitions or static feature templates. These, however, hypothesize the pre-existence of the parts in a given image or their positions, ignoring the input image-specific information which limits their usability in challenging scenarios such as Re-ID with partial occlusions and partial probe images. In this paper, we introduce a spatial attention-based Dynamic Part Template Initialization module that dynamically generates part-templates using mid-level semantic features at the earlier layers of the backbone. Following a self-attention layer, human part-level features of the backbone are used to extract the templates of diverse human body parts using a simplified cross-attention scheme which will then be used to identify and collate representations of various human parts from semantically rich features, increasing the discriminative ability of the entire model. We further explore adaptive weighting of part descriptors to quantify the absence or occlusion of local attributes and suppress the contribution of the corresponding part descriptors to the matching criteria. Extensive experiments on holistic, occluded, and partial Re-ID task benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed architecture is able to achieve competitive performance. Codes will be included in the supplementary material and will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge