Ryan Smith
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Visualization Tasks for Unlabelled Graphs
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:We investigate tasks that can be accomplished with unlabelled graphs, where nodes do not have persistent or semantically meaningful labels. New techniques to visualize these graphs have been proposed, but more understanding of unlabelled graph tasks is required before they can be adequately evaluated. Some tasks apply to both labelled and unlabelled graphs, but many do not translate between these contexts. We propose a taxonomy of unlabelled graph abstract tasks, organized according to the Scope of the data at play, the Action intended by the user, and the Target data under consideration. We show the descriptive power of this task abstraction by connecting to concrete examples from previous frameworks, and connect these abstractions to real-world problems. To showcase the evaluative power of the taxonomy, we perform a preliminary assessment of 6 visualizations for each task. For each combination of task and visual encoding, we consider the effort required from viewers, the likelihood of task success, and how both factors vary between small-scale and large-scale graphs.
Planning to Learn: A Novel Algorithm for Active Learning during Model-Based Planning
Aug 15, 2023Abstract:Active Inference is a recent framework for modeling planning under uncertainty. Empirical and theoretical work have now begun to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of this approach and how it might be improved. A recent extension - the sophisticated inference (SI) algorithm - improves performance on multi-step planning problems through recursive decision tree search. However, little work to date has been done to compare SI to other established planning algorithms. SI was also developed with a focus on inference as opposed to learning. The present paper has two aims. First, we compare performance of SI to Bayesian reinforcement learning (RL) schemes designed to solve similar problems. Second, we present an extension of SI - sophisticated learning (SL) - that more fully incorporates active learning during planning. SL maintains beliefs about how model parameters would change under the future observations expected under each policy. This allows a form of counterfactual retrospective inference in which the agent considers what could be learned from current or past observations given different future observations. To accomplish these aims, we make use of a novel, biologically inspired environment designed to highlight the problem structure for which SL offers a unique solution. Here, an agent must continually search for available (but changing) resources in the presence of competing affordances for information gain. Our simulations show that SL outperforms all other algorithms in this context - most notably, Bayes-adaptive RL and upper confidence bound algorithms, which aim to solve multi-step planning problems using similar principles (i.e., directed exploration and counterfactual reasoning). These results provide added support for the utility of Active Inference in solving this class of biologically-relevant problems and offer added tools for testing hypotheses about human cognition.
Shadows Aren't So Dangerous After All: A Fast and Robust Defense Against Shadow-Based Adversarial Attacks
Aug 18, 2022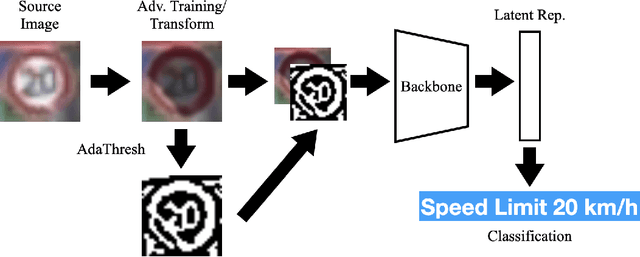


Abstract:Robust classification is essential in tasks like autonomous vehicle sign recognition, where the downsides of misclassification can be grave. Adversarial attacks threaten the robustness of neural network classifiers, causing them to consistently and confidently misidentify road signs. One such class of attack, shadow-based attacks, causes misidentifications by applying a natural-looking shadow to input images, resulting in road signs that appear natural to a human observer but confusing for these classifiers. Current defenses against such attacks use a simple adversarial training procedure to achieve a rather low 25\% and 40\% robustness on the GTSRB and LISA test sets, respectively. In this paper, we propose a robust, fast, and generalizable method, designed to defend against shadow attacks in the context of road sign recognition, that augments source images with binary adaptive threshold and edge maps. We empirically show its robustness against shadow attacks, and reformulate the problem to show its similarity $\varepsilon$ perturbation-based attacks. Experimental results show that our edge defense results in 78\% robustness while maintaining 98\% benign test accuracy on the GTSRB test set, with similar results from our threshold defense. Link to our code is in the paper.
AdaWCT: Adaptive Whitening and Coloring Style Injection
Aug 01, 2022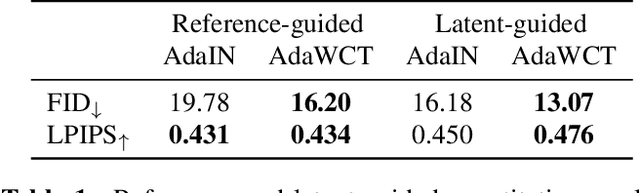
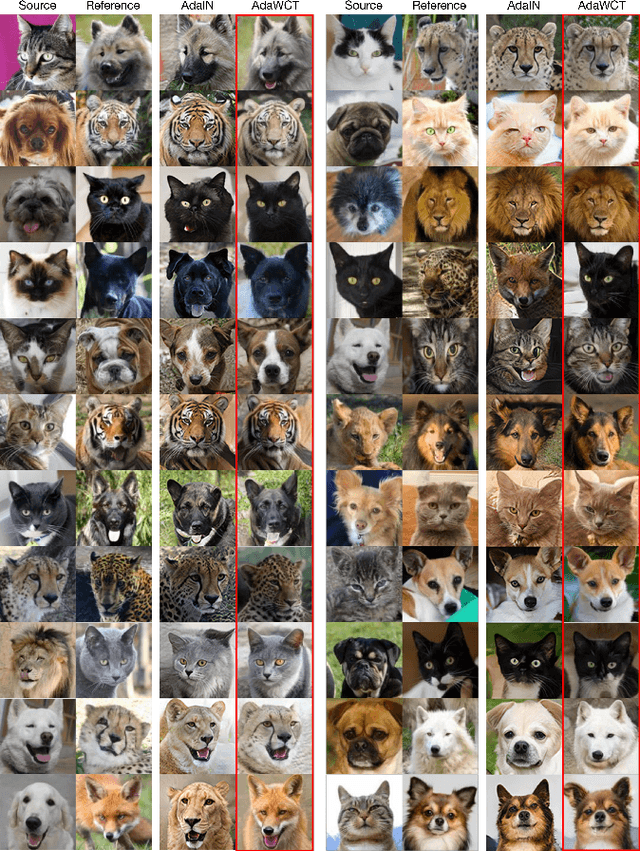

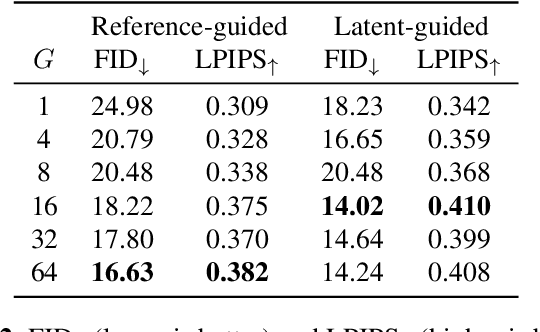

Abstract:Adaptive instance normalization (AdaIN) has become the standard method for style injection: by re-normalizing features through scale-and-shift operations, it has found widespread use in style transfer, image generation, and image-to-image translation. In this work, we present a generalization of AdaIN which relies on the whitening and coloring transformation (WCT) which we dub AdaWCT, that we apply for style injection in large GANs. We show, through experiments on the StarGANv2 architecture, that this generalization, albeit conceptually simple, results in significant improvements in the quality of the generated images.
Overparameterization Improves StyleGAN Inversion
May 12, 2022



Abstract:Deep generative models like StyleGAN hold the promise of semantic image editing: modifying images by their content, rather than their pixel values. Unfortunately, working with arbitrary images requires inverting the StyleGAN generator, which has remained challenging so far. Existing inversion approaches obtain promising yet imperfect results, having to trade-off between reconstruction quality and downstream editability. To improve quality, these approaches must resort to various techniques that extend the model latent space after training. Taking a step back, we observe that these methods essentially all propose, in one way or another, to increase the number of free parameters. This suggests that inversion might be difficult because it is underconstrained. In this work, we address this directly and dramatically overparameterize the latent space, before training, with simple changes to the original StyleGAN architecture. Our overparameterization increases the available degrees of freedom, which in turn facilitates inversion. We show that this allows us to obtain near-perfect image reconstruction without the need for encoders nor for altering the latent space after training. Our approach also retains editability, which we demonstrate by realistically interpolating between images.
Language Models in the Loop: Incorporating Prompting into Weak Supervision
May 04, 2022



Abstract:We propose a new strategy for applying large pre-trained language models to novel tasks when labeled training data is limited. Rather than apply the model in a typical zero-shot or few-shot fashion, we treat the model as the basis for labeling functions in a weak supervision framework. To create a classifier, we first prompt the model to answer multiple distinct queries about an example and define how the possible responses should be mapped to votes for labels and abstentions. We then denoise these noisy label sources using the Snorkel system and train an end classifier with the resulting training data. Our experimental evaluation shows that prompting large language models within a weak supervision framework can provide significant gains in accuracy. On the WRENCH weak supervision benchmark, this approach can significantly improve over zero-shot performance, an average 19.5% reduction in errors. We also find that this approach produces classifiers with comparable or superior accuracy to those trained from hand-engineered rules.
The relationship between dynamic programming and active inference: the discrete, finite-horizon case
Sep 22, 2020



Abstract:Active inference is a normative framework for generating behaviour based upon the free energy principle, a theory of self-organisation. This framework has been successfully used to solve reinforcement learning and stochastic control problems, yet, the formal relation between active inference and reward maximisation has not been fully explicated. In this paper, we consider the relation between active inference and dynamic programming under the Bellman equation, which underlies many approaches to reinforcement learning and control. We show that, on partially observable Markov decision processes, dynamic programming is a limiting case of active inference. In active inference, agents select actions to minimise expected free energy. In the absence of ambiguity about states, this reduces to matching expected states with a target distribution encoding the agent's preferences. When target states correspond to rewarding states, this maximises expected reward, as in reinforcement learning. When states are ambiguous, active inference agents will choose actions that simultaneously minimise ambiguity. This allows active inference agents to supplement their reward maximising (or exploitative) behaviour with novelty-seeking (or exploratory) behaviour. This clarifies the connection between active inference and reinforcement learning, and how both frameworks may benefit from each other.
In-Session Personalization for Talent Search
Sep 18, 2018
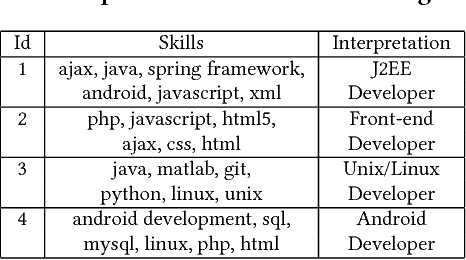

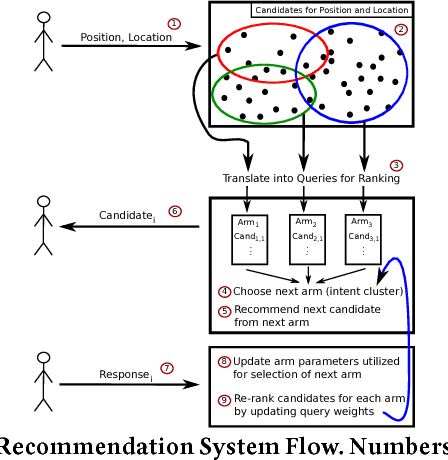
Abstract:Previous efforts in recommendation of candidates for talent search followed the general pattern of receiving an initial search criteria and generating a set of candidates utilizing a pre-trained model. Traditionally, the generated recommendations are final, that is, the list of potential candidates is not modified unless the user explicitly changes his/her search criteria. In this paper, we are proposing a candidate recommendation model which takes into account the immediate feedback of the user, and updates the candidate recommendations at each step. This setting also allows for very uninformative initial search queries, since we pinpoint the user's intent due to the feedback during the search session. To achieve our goal, we employ an intent clustering method based on topic modeling which separates the candidate space into meaningful, possibly overlapping, subsets (which we call intent clusters) for each position. On top of the candidate segments, we apply a multi-armed bandit approach to choose which intent cluster is more appropriate for the current session. We also present an online learning scheme which updates the intent clusters within the session, due to user feedback, to achieve further personalization. Our offline experiments as well as the results from the online deployment of our solution demonstrate the benefits of our proposed methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge