Ruba Priyadharshini
TamilEmo: Finegrained Emotion Detection Dataset for Tamil
Feb 09, 2022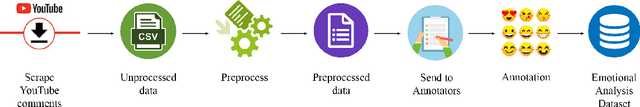

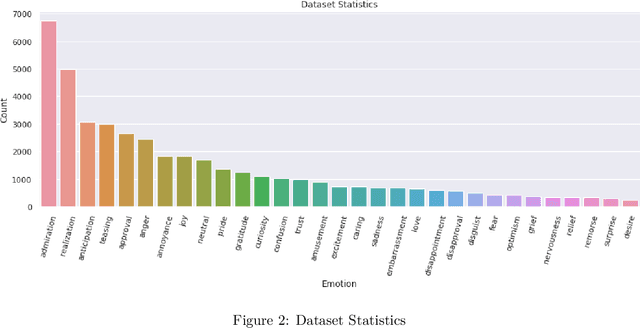
Abstract:Emotional Analysis from textual input has been considered both a challenging and interesting task in Natural Language Processing. However, due to the lack of datasets in low-resource languages (i.e. Tamil), it is difficult to conduct research of high standard in this area. Therefore we introduce this labelled dataset (a largest manually annotated dataset of more than 42k Tamil YouTube comments, labelled for 31 emotions including neutral) for emotion recognition. The goal of this dataset is to improve emotion detection in multiple downstream tasks in Tamil. We have also created three different groupings of our emotions (3-class, 7-class and 31-class) and evaluated the model's performance on each category of the grouping. Our MURIL-base model has achieved a 0.60 macro average F1-score across our 3-class group dataset. With 7-class and 31-class groups, the Random Forest model performed well with a macro average F1-scores of 0.42 and 0.29 respectively.
Hypers at ComMA@ICON: Modelling Aggressiveness, Gender Bias and Communal Bias Identification
Jan 13, 2022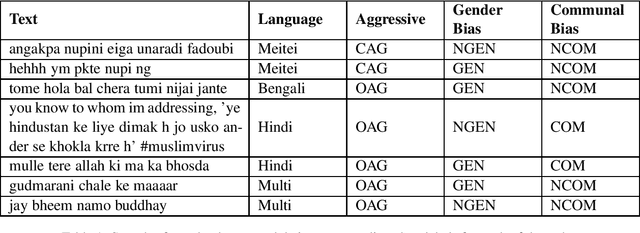
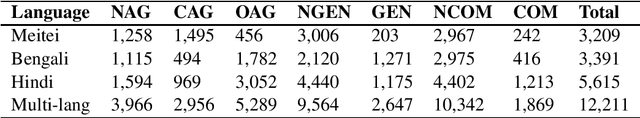
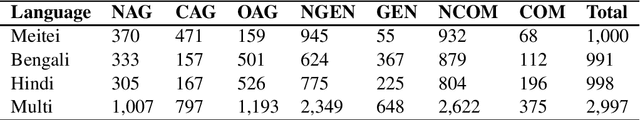
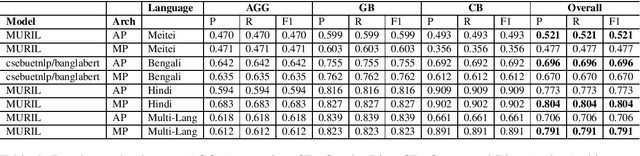
Abstract:Due to the exponentially increasing reach of social media, it is essential to focus on its negative aspects as it can potentially divide society and incite people into violence. In this paper, we present our system description of work on the shared task ComMA@ICON, where we have to classify how aggressive the sentence is and if the sentence is gender-biased or communal biased. These three could be the primary reasons to cause significant problems in society. As team Hypers we have proposed an approach that utilizes different pretrained models with Attention and mean pooling methods. We were able to get Rank 3 with 0.223 Instance F1 score on Bengali, Rank 2 with 0.322 Instance F1 score on Multi-lingual set, Rank 4 with 0.129 Instance F1 score on Meitei and Rank 5 with 0.336 Instance F1 score on Hindi. The source code and the pretrained models of this work can be found here.
Findings of the Sentiment Analysis of Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text
Nov 18, 2021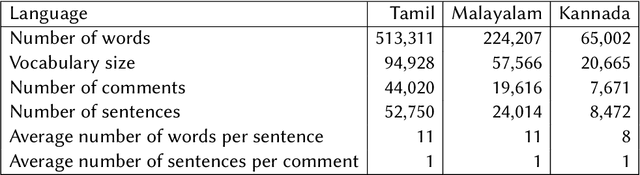
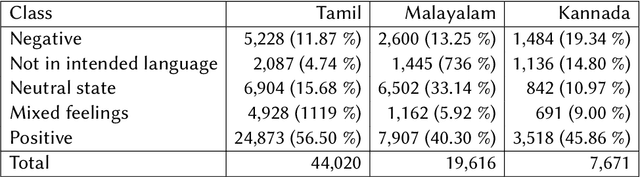
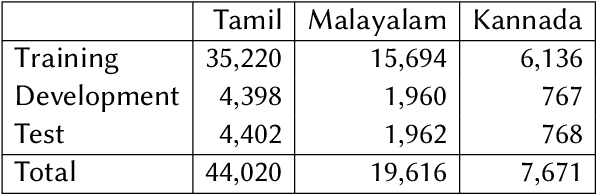
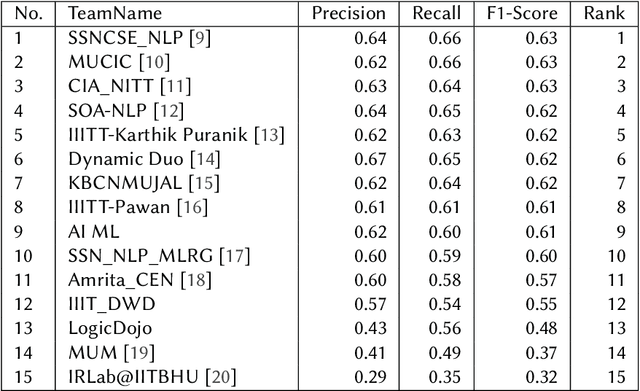
Abstract:We present the results of the Dravidian-CodeMix shared task held at FIRE 2021, a track on sentiment analysis for Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text. We describe the task, its organization, and the submitted systems. This shared task is the continuation of last year's Dravidian-CodeMix shared task held at FIRE 2020. This year's tasks included code-mixing at the intra-token and inter-token levels. Additionally, apart from Tamil and Malayalam, Kannada was also introduced. We received 22 systems for Tamil-English, 15 systems for Malayalam-English, and 15 for Kannada-English. The top system for Tamil-English, Malayalam-English and Kannada-English scored weighted average F1-score of 0.711, 0.804, and 0.630, respectively. In summary, the quality and quantity of the submission show that there is great interest in Dravidian languages in code-mixed setting and state of the art in this domain still needs more improvement.
Developing Successful Shared Tasks on Offensive Language Identification for Dravidian Languages
Nov 05, 2021
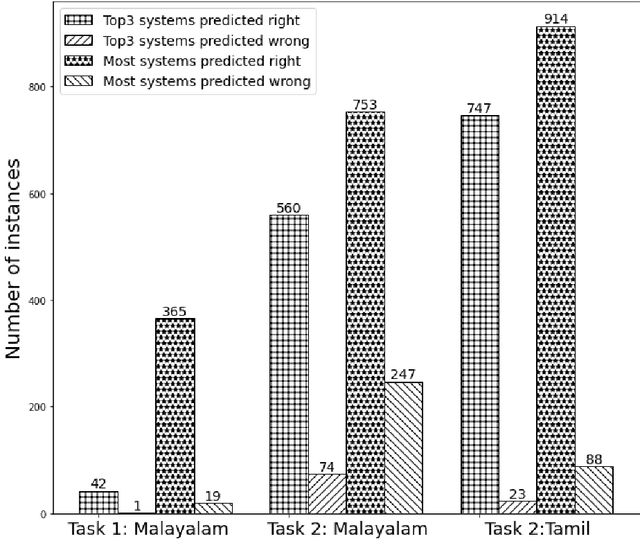

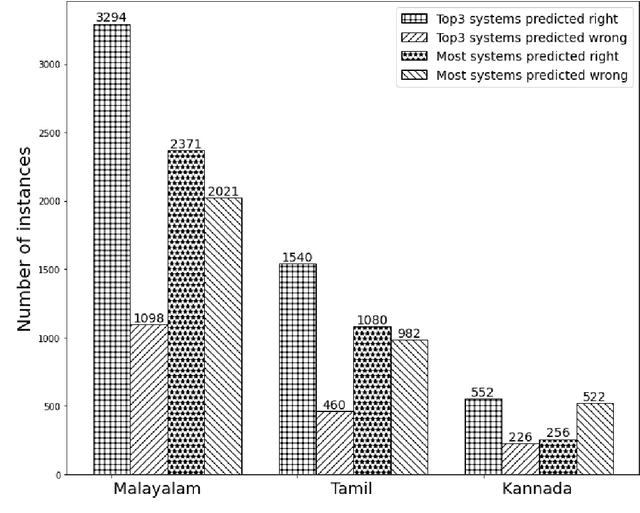
Abstract:With the fast growth of mobile computing and Web technologies, offensive language has become more prevalent on social networking platforms. Since offensive language identification in local languages is essential to moderate the social media content, in this paper we work with three Dravidian languages, namely Malayalam, Tamil, and Kannada, that are under-resourced. We present an evaluation task at FIRE 2020- HASOC-DravidianCodeMix and DravidianLangTech at EACL 2021, designed to provide a framework for comparing different approaches to this problem. This paper describes the data creation, defines the task, lists the participating systems, and discusses various methods.
Dataset for Identification of Homophobia and Transophobia in Multilingual YouTube Comments
Sep 01, 2021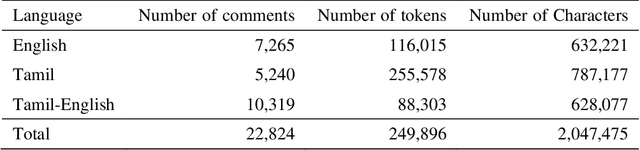
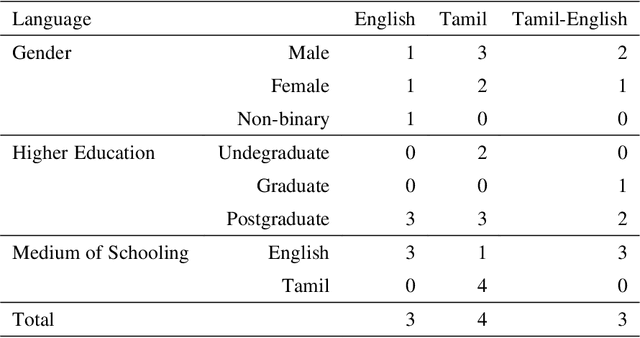
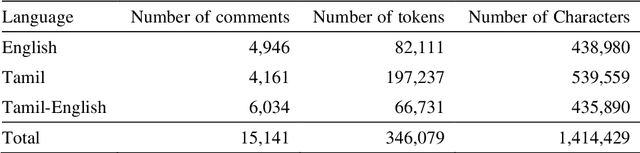
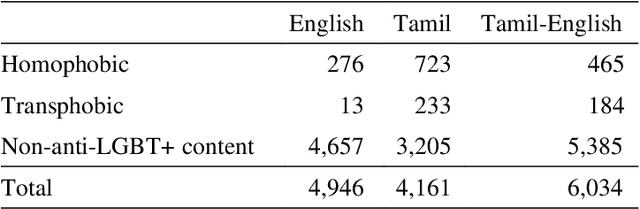
Abstract:The increased proliferation of abusive content on social media platforms has a negative impact on online users. The dread, dislike, discomfort, or mistrust of lesbian, gay, transgender or bisexual persons is defined as homophobia/transphobia. Homophobic/transphobic speech is a type of offensive language that may be summarized as hate speech directed toward LGBT+ people, and it has been a growing concern in recent years. Online homophobia/transphobia is a severe societal problem that can make online platforms poisonous and unwelcome to LGBT+ people while also attempting to eliminate equality, diversity, and inclusion. We provide a new hierarchical taxonomy for online homophobia and transphobia, as well as an expert-labelled dataset that will allow homophobic/transphobic content to be automatically identified. We educated annotators and supplied them with comprehensive annotation rules because this is a sensitive issue, and we previously discovered that untrained crowdsourcing annotators struggle with diagnosing homophobia due to cultural and other prejudices. The dataset comprises 15,141 annotated multilingual comments. This paper describes the process of building the dataset, qualitative analysis of data, and inter-annotator agreement. In addition, we create baseline models for the dataset. To the best of our knowledge, our dataset is the first such dataset created. Warning: This paper contains explicit statements of homophobia, transphobia, stereotypes which may be distressing to some readers.
Attentive fine-tuning of Transformers for Translation of low-resourced languages @LoResMT 2021
Aug 31, 2021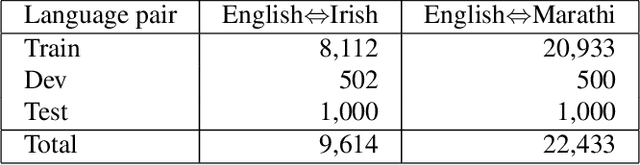


Abstract:This paper reports the Machine Translation (MT) systems submitted by the IIITT team for the English->Marathi and English->Irish language pairs LoResMT 2021 shared task. The task focuses on getting exceptional translations for rather low-resourced languages like Irish and Marathi. We fine-tune IndicTrans, a pretrained multilingual NMT model for English->Marathi, using external parallel corpus as input for additional training. We have used a pretrained Helsinki-NLP Opus MT English->Irish model for the latter language pair. Our approaches yield relatively promising results on the BLEU metrics. Under the team name IIITT, our systems ranked 1, 1, and 2 in English->Marathi, Irish->English, and English->Irish, respectively.
Offensive Language Identification in Low-resourced Code-mixed Dravidian languages using Pseudo-labeling
Aug 27, 2021



Abstract:Social media has effectively become the prime hub of communication and digital marketing. As these platforms enable the free manifestation of thoughts and facts in text, images and video, there is an extensive need to screen them to protect individuals and groups from offensive content targeted at them. Our work intends to classify codemixed social media comments/posts in the Dravidian languages of Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam. We intend to improve offensive language identification by generating pseudo-labels on the dataset. A custom dataset is constructed by transliterating all the code-mixed texts into the respective Dravidian language, either Kannada, Malayalam, or Tamil and then generating pseudo-labels for the transliterated dataset. The two datasets are combined using the generated pseudo-labels to create a custom dataset called CMTRA. As Dravidian languages are under-resourced, our approach increases the amount of training data for the language models. We fine-tune several recent pretrained language models on the newly constructed dataset. We extract the pretrained language embeddings and pass them onto recurrent neural networks. We observe that fine-tuning ULMFiT on the custom dataset yields the best results on the code-mixed test sets of all three languages. Our approach yields the best results among the benchmarked models on Tamil-English, achieving a weighted F1-Score of 0.7934 while scoring competitive weighted F1-Scores of 0.9624 and 0.7306 on the code-mixed test sets of Malayalam-English and Kannada-English, respectively.
Hope Speech detection in under-resourced Kannada language
Aug 10, 2021



Abstract:Numerous methods have been developed to monitor the spread of negativity in modern years by eliminating vulgar, offensive, and fierce comments from social media platforms. However, there are relatively lesser amounts of study that converges on embracing positivity, reinforcing supportive and reassuring content in online forums. Consequently, we propose creating an English-Kannada Hope speech dataset, KanHope and comparing several experiments to benchmark the dataset. The dataset consists of 6,176 user-generated comments in code mixed Kannada scraped from YouTube and manually annotated as bearing hope speech or Not-hope speech. In addition, we introduce DC-BERT4HOPE, a dual-channel model that uses the English translation of KanHope for additional training to promote hope speech detection. The approach achieves a weighted F1-score of 0.756, bettering other models. Henceforth, KanHope aims to instigate research in Kannada while broadly promoting researchers to take a pragmatic approach towards online content that encourages, positive, and supportive.
Do Images really do the Talking? Analysing the significance of Images in Tamil Troll meme classification
Aug 09, 2021



Abstract:A meme is an part of media created to share an opinion or emotion across the internet. Due to its popularity, memes have become the new forms of communication on social media. However, due to its nature, they are being used in harmful ways such as trolling and cyberbullying progressively. Various data modelling methods create different possibilities in feature extraction and turning them into beneficial information. The variety of modalities included in data plays a significant part in predicting the results. We try to explore the significance of visual features of images in classifying memes. Memes are a blend of both image and text, where the text is embedded into the image. We try to incorporate the memes as troll and non-trolling memes based on the images and the text on them. However, the images are to be analysed and combined with the text to increase performance. Our work illustrates different textual analysis methods and contrasting multimodal methods ranging from simple merging to cross attention to utilising both worlds' - best visual and textual features. The fine-tuned cross-lingual language model, XLM, performed the best in textual analysis, and the multimodal transformer performs the best in multimodal analysis.
DravidianCodeMix: Sentiment Analysis and Offensive Language Identification Dataset for Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text
Jun 17, 2021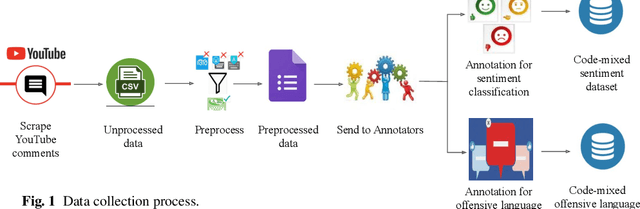
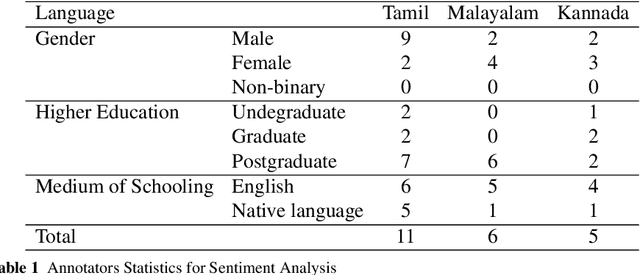
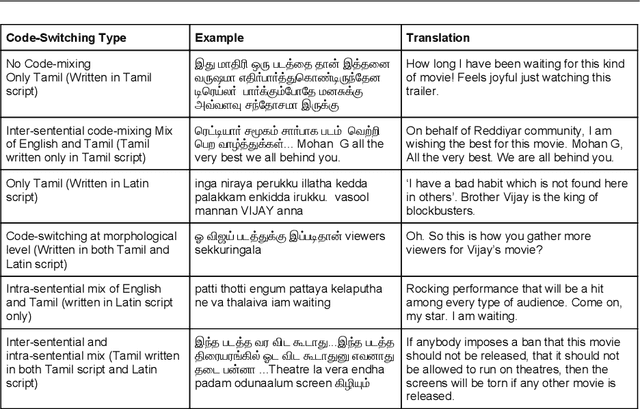
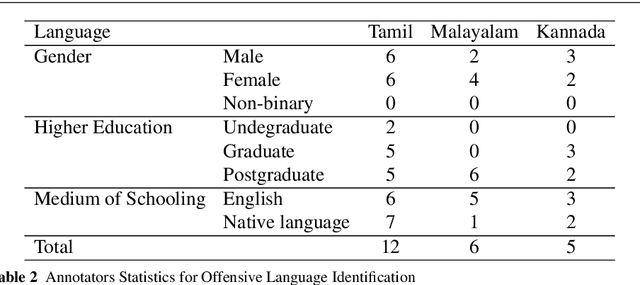
Abstract:This paper describes the development of a multilingual, manually annotated dataset for three under-resourced Dravidian languages generated from social media comments. The dataset was annotated for sentiment analysis and offensive language identification for a total of more than 60,000 YouTube comments. The dataset consists of around 44,000 comments in Tamil-English, around 7,000 comments in Kannada-English, and around 20,000 comments in Malayalam-English. The data was manually annotated by volunteer annotators and has a high inter-annotator agreement in Krippendorff's alpha. The dataset contains all types of code-mixing phenomena since it comprises user-generated content from a multilingual country. We also present baseline experiments to establish benchmarks on the dataset using machine learning methods. The dataset is available on Github (https://github.com/bharathichezhiyan/DravidianCodeMix-Dataset) and Zenodo (https://zenodo.org/record/4750858\#.YJtw0SYo\_0M).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge