Charangan Vasantharajan
TamilEmo: Finegrained Emotion Detection Dataset for Tamil
Feb 09, 2022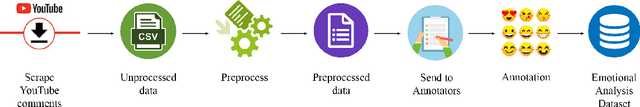
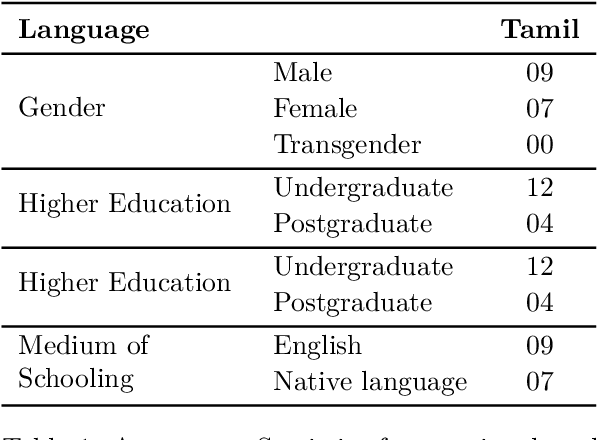

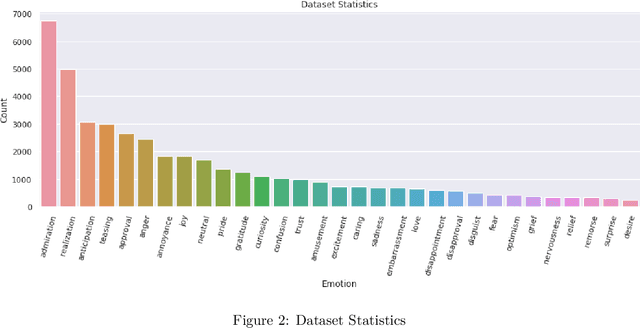
Abstract:Emotional Analysis from textual input has been considered both a challenging and interesting task in Natural Language Processing. However, due to the lack of datasets in low-resource languages (i.e. Tamil), it is difficult to conduct research of high standard in this area. Therefore we introduce this labelled dataset (a largest manually annotated dataset of more than 42k Tamil YouTube comments, labelled for 31 emotions including neutral) for emotion recognition. The goal of this dataset is to improve emotion detection in multiple downstream tasks in Tamil. We have also created three different groupings of our emotions (3-class, 7-class and 31-class) and evaluated the model's performance on each category of the grouping. Our MURIL-base model has achieved a 0.60 macro average F1-score across our 3-class group dataset. With 7-class and 31-class groups, the Random Forest model performed well with a macro average F1-scores of 0.42 and 0.29 respectively.
Findings of the Sentiment Analysis of Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text
Nov 18, 2021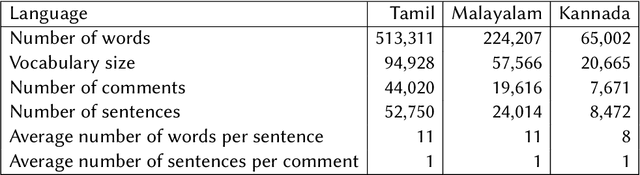
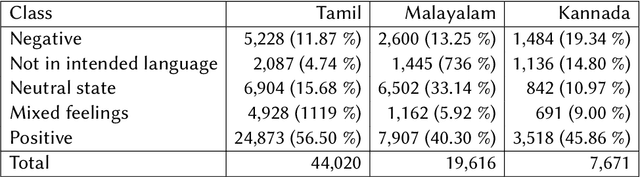
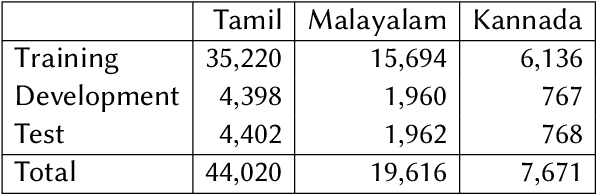
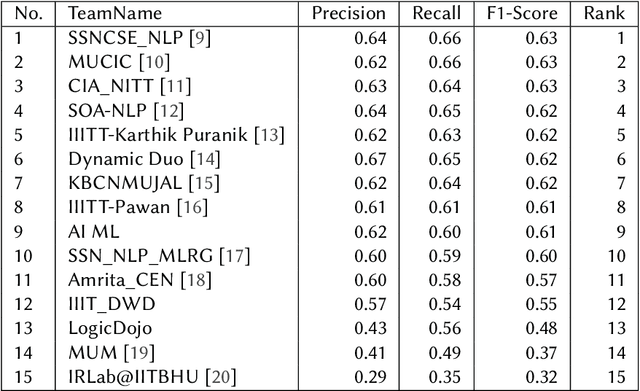
Abstract:We present the results of the Dravidian-CodeMix shared task held at FIRE 2021, a track on sentiment analysis for Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text. We describe the task, its organization, and the submitted systems. This shared task is the continuation of last year's Dravidian-CodeMix shared task held at FIRE 2020. This year's tasks included code-mixing at the intra-token and inter-token levels. Additionally, apart from Tamil and Malayalam, Kannada was also introduced. We received 22 systems for Tamil-English, 15 systems for Malayalam-English, and 15 for Kannada-English. The top system for Tamil-English, Malayalam-English and Kannada-English scored weighted average F1-score of 0.711, 0.804, and 0.630, respectively. In summary, the quality and quantity of the submission show that there is great interest in Dravidian languages in code-mixed setting and state of the art in this domain still needs more improvement.
Tamizhi-Net OCR: Creating A Quality Large Scale Tamil-Sinhala-English Parallel Corpus Using Deep Learning Based Printed Character Recognition
Sep 13, 2021



Abstract:Most of the low resource languages do not have the necessary resources to create even a substantial monolingual corpus. These languages may often be found in government proceedings but mostly in the form of Portable Document Formats (PDFs) that contains legacy fonts. Extracting text from these documents to create a monolingual corpus is challenging due to legacy font usage and printer-friendly encoding which are not optimized for text extraction. Therefore, we propose a simple, automatic, and novel idea that can scale for Tamil, Sinhala, and English languages and many documents. For this purpose, we enhanced the performance of Tesseract 4.1.1 by employing LSTM-based training on many legacy fonts to recognize printed characters in the above languages. Especially, our model detects code-mix text, numbers, and special characters from the printed document. It is shown that this approach can boost the character-level accuracy of Tesseract 4.1.1 from 85.5 to 98.2 for Tamil (+12.9% relative change) and 91.8 to 94.8 for Sinhala (+3.26% relative change) on a dataset that is considered as challenging by its authors.
Towards Offensive Language Identification for Tamil Code-Mixed YouTube Comments and Posts
Aug 26, 2021



Abstract:Offensive Language detection in social media platforms has been an active field of research over the past years. In non-native English spoken countries, social media users mostly use a code-mixed form of text in their posts/comments. This poses several challenges in the offensive content identification tasks, and considering the low resources available for Tamil, the task becomes much harder. The current study presents extensive experiments using multiple deep learning, and transfer learning models to detect offensive content on YouTube. We propose a novel and flexible approach of selective translation and transliteration techniques to reap better results from fine-tuning and ensembling multilingual transformer networks like BERT, Distil- BERT, and XLM-RoBERTa. The experimental results showed that ULMFiT is the best model for this task. The best performing models were ULMFiT and mBERTBiLSTM for this Tamil code-mix dataset instead of more popular transfer learning models such as Distil- BERT and XLM-RoBERTa and hybrid deep learning models. The proposed model ULMFiT and mBERTBiLSTM yielded good results and are promising for effective offensive speech identification in low-resourced languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge