John P. McCrae
When retrieval outperforms generation: Dense evidence retrieval for scalable fake news detection
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of misinformation necessitates robust yet computationally efficient fact verification systems. While current state-of-the-art approaches leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) for generating explanatory rationales, these methods face significant computational barriers and hallucination risks in real-world deployments. We present DeReC (Dense Retrieval Classification), a lightweight framework that demonstrates how general-purpose text embeddings can effectively replace autoregressive LLM-based approaches in fact verification tasks. By combining dense retrieval with specialized classification, our system achieves better accuracy while being significantly more efficient. DeReC outperforms explanation-generating LLMs in efficiency, reducing runtime by 95% on RAWFC (23 minutes 36 seconds compared to 454 minutes 12 seconds) and by 92% on LIAR-RAW (134 minutes 14 seconds compared to 1692 minutes 23 seconds), showcasing its effectiveness across varying dataset sizes. On the RAWFC dataset, DeReC achieves an F1 score of 65.58%, surpassing the state-of-the-art method L-Defense (61.20%). Our results demonstrate that carefully engineered retrieval-based systems can match or exceed LLM performance in specialized tasks while being significantly more practical for real-world deployment.
Inferring Adjective Hypernyms with Language Models to Increase the Connectivity of Open English Wordnet
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Open English Wordnet is a key resource published in OntoLex-lemon as part of the linguistic linked open data cloud. There are, however, many links missing in the resource, and in this paper, we look at how we can establish hypernymy between adjectives. We present a theoretical discussion of the hypernymy relation and how it differs for adjectives in contrast to nouns and verbs. We develop a new resource for adjective hypernymy and fine-tune large language models to predict adjective hypernymy, showing that the methodology of TaxoLLaMa can be adapted to this task.
Evaluating Text Style Transfer Evaluation: Are There Any Reliable Metrics?
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Text Style Transfer (TST) is the task of transforming a text to reflect a particular style while preserving its original content. Evaluating TST outputs is a multidimensional challenge, requiring the assessment of style transfer accuracy, content preservation, and naturalness. Using human evaluation is ideal but costly, same as in other natural language processing (NLP) tasks, however, automatic metrics for TST have not received as much attention as metrics for, e.g., machine translation or summarization. In this paper, we examine both set of existing and novel metrics from broader NLP tasks for TST evaluation, focusing on two popular subtasks-sentiment transfer and detoxification-in a multilingual context comprising English, Hindi, and Bengali. By conducting meta-evaluation through correlation with human judgments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of these metrics when used individually and in ensembles. Additionally, we investigate the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) as tools for TST evaluation. Our findings highlight that certain advanced NLP metrics and experimental-hybrid-techniques, provide better insights than existing TST metrics for delivering more accurate, consistent, and reproducible TST evaluations.
Multilingual Text Style Transfer: Datasets & Models for Indian Languages
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Text style transfer (TST) involves altering the linguistic style of a text while preserving its core content. This paper focuses on sentiment transfer, a vital TST subtask (Mukherjee et al., 2022a), across a spectrum of Indian languages: Hindi, Magahi, Malayalam, Marathi, Punjabi, Odia, Telugu, and Urdu, expanding upon previous work on English-Bangla sentiment transfer (Mukherjee et al., 2023). We introduce dedicated datasets of 1,000 positive and 1,000 negative style-parallel sentences for each of these eight languages. We then evaluate the performance of various benchmark models categorized into parallel, non-parallel, cross-lingual, and shared learning approaches, including the Llama2 and GPT-3.5 large language models (LLMs). Our experiments highlight the significance of parallel data in TST and demonstrate the effectiveness of the Masked Style Filling (MSF) approach (Mukherjee et al., 2023) in non-parallel techniques. Moreover, cross-lingual and joint multilingual learning methods show promise, offering insights into selecting optimal models tailored to the specific language and task requirements. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first comprehensive exploration of the TST task as sentiment transfer across a diverse set of languages.
MaCmS: Magahi Code-mixed Dataset for Sentiment Analysis
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:The present paper introduces new sentiment data, MaCMS, for Magahi-Hindi-English (MHE) code-mixed language, where Magahi is a less-resourced minority language. This dataset is the first Magahi-Hindi-English code-mixed dataset for sentiment analysis tasks. Further, we also provide a linguistics analysis of the dataset to understand the structure of code-mixing and a statistical study to understand the language preferences of speakers with different polarities. With these analyses, we also train baseline models to evaluate the dataset's quality.
Text Detoxification as Style Transfer in English and Hindi
Feb 12, 2024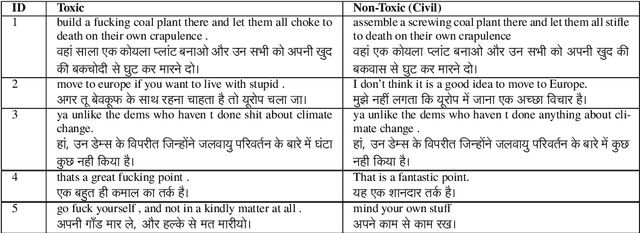
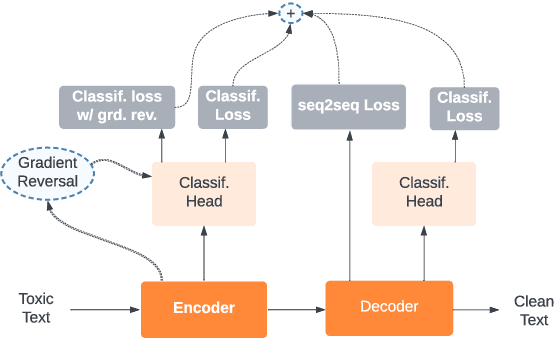

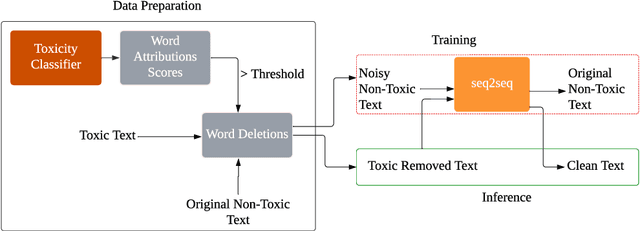
Abstract:This paper focuses on text detoxification, i.e., automatically converting toxic text into non-toxic text. This task contributes to safer and more respectful online communication and can be considered a Text Style Transfer (TST) task, where the text style changes while its content is preserved. We present three approaches: knowledge transfer from a similar task, multi-task learning approach, combining sequence-to-sequence modeling with various toxicity classification tasks, and, delete and reconstruct approach. To support our research, we utilize a dataset provided by Dementieva et al.(2021), which contains multiple versions of detoxified texts corresponding to toxic texts. In our experiments, we selected the best variants through expert human annotators, creating a dataset where each toxic sentence is paired with a single, appropriate detoxified version. Additionally, we introduced a small Hindi parallel dataset, aligning with a part of the English dataset, suitable for evaluation purposes. Our results demonstrate that our approach effectively balances text detoxication while preserving the actual content and maintaining fluency.
Weakly-supervised Deep Cognate Detection Framework for Low-Resourced Languages Using Morphological Knowledge of Closely-Related Languages
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:Exploiting cognates for transfer learning in under-resourced languages is an exciting opportunity for language understanding tasks, including unsupervised machine translation, named entity recognition and information retrieval. Previous approaches mainly focused on supervised cognate detection tasks based on orthographic, phonetic or state-of-the-art contextual language models, which under-perform for most under-resourced languages. This paper proposes a novel language-agnostic weakly-supervised deep cognate detection framework for under-resourced languages using morphological knowledge from closely related languages. We train an encoder to gain morphological knowledge of a language and transfer the knowledge to perform unsupervised and weakly-supervised cognate detection tasks with and without the pivot language for the closely-related languages. While unsupervised, it overcomes the need for hand-crafted annotation of cognates. We performed experiments on different published cognate detection datasets across language families and observed not only significant improvement over the state-of-the-art but also our method outperformed the state-of-the-art supervised and unsupervised methods. Our model can be extended to a wide range of languages from any language family as it overcomes the requirement of the annotation of the cognate pairs for training. The code and dataset building scripts can be found at https://github.com/koustavagoswami/Weakly_supervised-Cognate_Detection
Empowering recommender systems using automatically generated Knowledge Graphs and Reinforcement Learning
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:Personalized recommendations have a growing importance in direct marketing, which motivates research to enhance customer experiences by knowledge graph (KG) applications. For example, in financial services, companies may benefit from providing relevant financial articles to their customers to cultivate relationships, foster client engagement and promote informed financial decisions. While several approaches center on KG-based recommender systems for improved content, in this study we focus on interpretable KG-based recommender systems for decision making.To this end, we present two knowledge graph-based approaches for personalized article recommendations for a set of customers of a large multinational financial services company. The first approach employs Reinforcement Learning and the second approach uses the XGBoost algorithm for recommending articles to the customers. Both approaches make use of a KG generated from both structured (tabular data) and unstructured data (a large body of text data).Using the Reinforcement Learning-based recommender system we could leverage the graph traversal path leading to the recommendation as a way to generate interpretations (Path Directed Reasoning (PDR)). In the XGBoost-based approach, one can also provide explainable results using post-hoc methods such as SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) and ELI5 (Explain Like I am Five).Importantly, our approach offers explainable results, promoting better decision-making. This study underscores the potential of combining advanced machine learning techniques with KG-driven insights to bolster experience in customer relationship management.
Findings of the Sentiment Analysis of Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text
Nov 18, 2021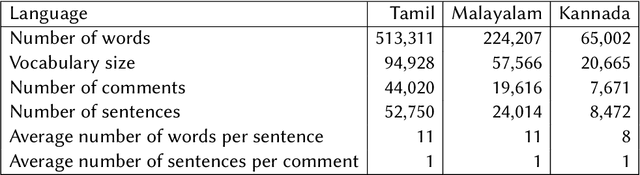
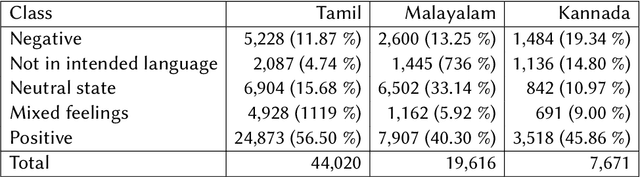
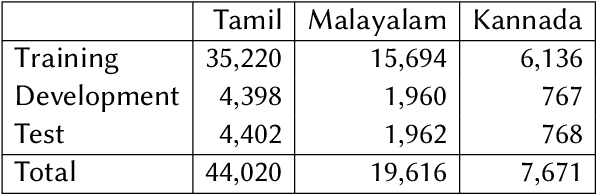
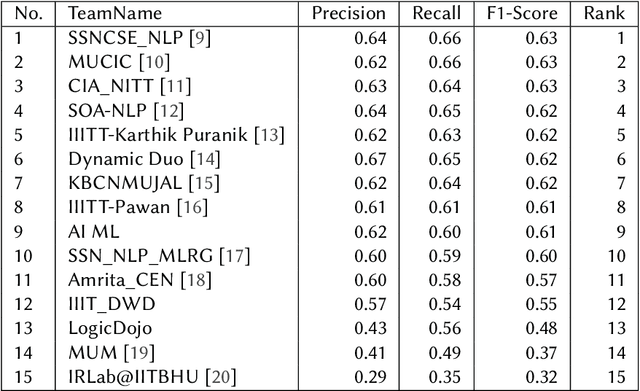
Abstract:We present the results of the Dravidian-CodeMix shared task held at FIRE 2021, a track on sentiment analysis for Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text. We describe the task, its organization, and the submitted systems. This shared task is the continuation of last year's Dravidian-CodeMix shared task held at FIRE 2020. This year's tasks included code-mixing at the intra-token and inter-token levels. Additionally, apart from Tamil and Malayalam, Kannada was also introduced. We received 22 systems for Tamil-English, 15 systems for Malayalam-English, and 15 for Kannada-English. The top system for Tamil-English, Malayalam-English and Kannada-English scored weighted average F1-score of 0.711, 0.804, and 0.630, respectively. In summary, the quality and quantity of the submission show that there is great interest in Dravidian languages in code-mixed setting and state of the art in this domain still needs more improvement.
DravidianCodeMix: Sentiment Analysis and Offensive Language Identification Dataset for Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text
Jun 17, 2021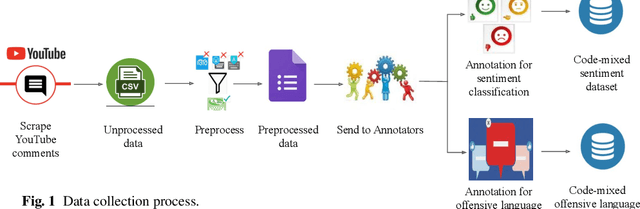
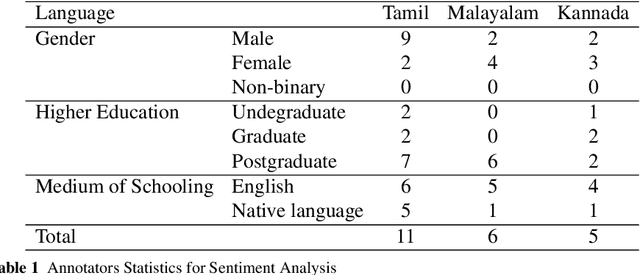
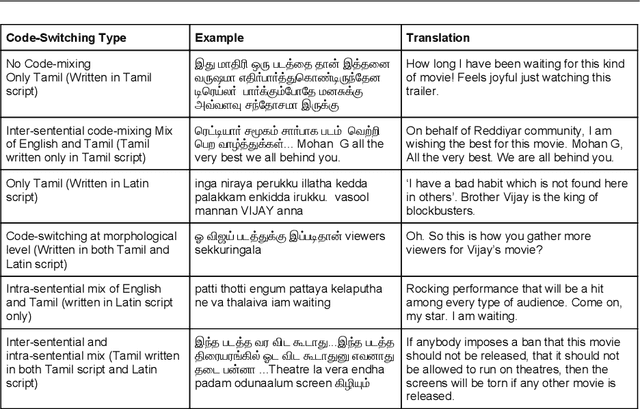
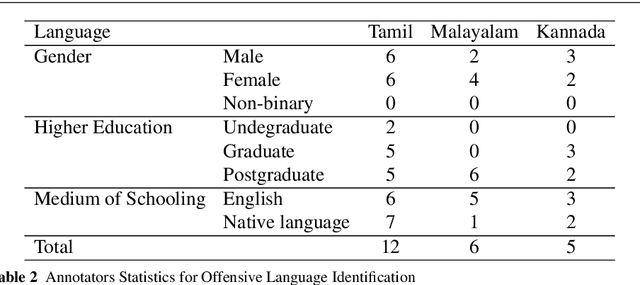
Abstract:This paper describes the development of a multilingual, manually annotated dataset for three under-resourced Dravidian languages generated from social media comments. The dataset was annotated for sentiment analysis and offensive language identification for a total of more than 60,000 YouTube comments. The dataset consists of around 44,000 comments in Tamil-English, around 7,000 comments in Kannada-English, and around 20,000 comments in Malayalam-English. The data was manually annotated by volunteer annotators and has a high inter-annotator agreement in Krippendorff's alpha. The dataset contains all types of code-mixing phenomena since it comprises user-generated content from a multilingual country. We also present baseline experiments to establish benchmarks on the dataset using machine learning methods. The dataset is available on Github (https://github.com/bharathichezhiyan/DravidianCodeMix-Dataset) and Zenodo (https://zenodo.org/record/4750858\#.YJtw0SYo\_0M).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge