Akanksha Bansal
Multilingual Text Style Transfer: Datasets & Models for Indian Languages
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Text style transfer (TST) involves altering the linguistic style of a text while preserving its core content. This paper focuses on sentiment transfer, a vital TST subtask (Mukherjee et al., 2022a), across a spectrum of Indian languages: Hindi, Magahi, Malayalam, Marathi, Punjabi, Odia, Telugu, and Urdu, expanding upon previous work on English-Bangla sentiment transfer (Mukherjee et al., 2023). We introduce dedicated datasets of 1,000 positive and 1,000 negative style-parallel sentences for each of these eight languages. We then evaluate the performance of various benchmark models categorized into parallel, non-parallel, cross-lingual, and shared learning approaches, including the Llama2 and GPT-3.5 large language models (LLMs). Our experiments highlight the significance of parallel data in TST and demonstrate the effectiveness of the Masked Style Filling (MSF) approach (Mukherjee et al., 2023) in non-parallel techniques. Moreover, cross-lingual and joint multilingual learning methods show promise, offering insights into selecting optimal models tailored to the specific language and task requirements. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first comprehensive exploration of the TST task as sentiment transfer across a diverse set of languages.
Text Detoxification as Style Transfer in English and Hindi
Feb 12, 2024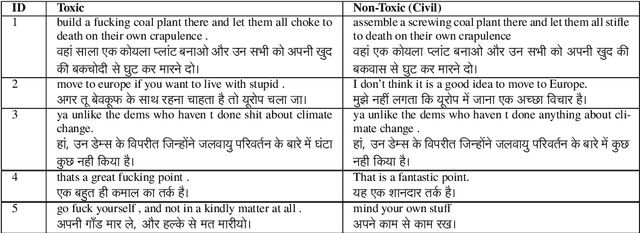
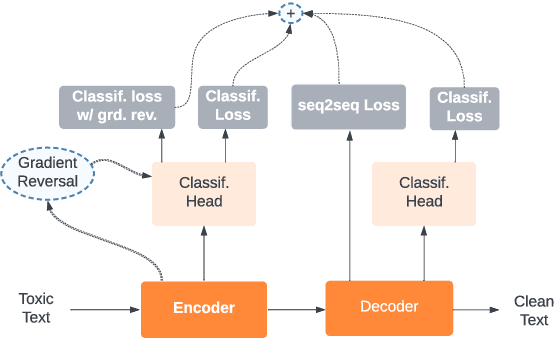

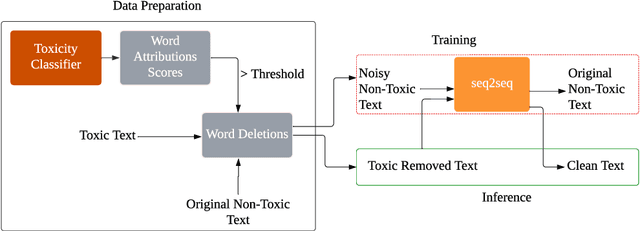
Abstract:This paper focuses on text detoxification, i.e., automatically converting toxic text into non-toxic text. This task contributes to safer and more respectful online communication and can be considered a Text Style Transfer (TST) task, where the text style changes while its content is preserved. We present three approaches: knowledge transfer from a similar task, multi-task learning approach, combining sequence-to-sequence modeling with various toxicity classification tasks, and, delete and reconstruct approach. To support our research, we utilize a dataset provided by Dementieva et al.(2021), which contains multiple versions of detoxified texts corresponding to toxic texts. In our experiments, we selected the best variants through expert human annotators, creating a dataset where each toxic sentence is paired with a single, appropriate detoxified version. Additionally, we introduced a small Hindi parallel dataset, aligning with a part of the English dataset, suitable for evaluation purposes. Our results demonstrate that our approach effectively balances text detoxication while preserving the actual content and maintaining fluency.
Developing a Multilingual Annotated Corpus of Misogyny and Aggression
Mar 16, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we discuss the development of a multilingual annotated corpus of misogyny and aggression in Indian English, Hindi, and Indian Bangla as part of a project on studying and automatically identifying misogyny and communalism on social media (the ComMA Project). The dataset is collected from comments on YouTube videos and currently contains a total of over 20,000 comments. The comments are annotated at two levels - aggression (overtly aggressive, covertly aggressive, and non-aggressive) and misogyny (gendered and non-gendered). We describe the process of data collection, the tagset used for annotation, and issues and challenges faced during the process of annotation. Finally, we discuss the results of the baseline experiments conducted to develop a classifier for misogyny in the three languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge