Deepak Alok
Multilingual Text Style Transfer: Datasets & Models for Indian Languages
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Text style transfer (TST) involves altering the linguistic style of a text while preserving its core content. This paper focuses on sentiment transfer, a vital TST subtask (Mukherjee et al., 2022a), across a spectrum of Indian languages: Hindi, Magahi, Malayalam, Marathi, Punjabi, Odia, Telugu, and Urdu, expanding upon previous work on English-Bangla sentiment transfer (Mukherjee et al., 2023). We introduce dedicated datasets of 1,000 positive and 1,000 negative style-parallel sentences for each of these eight languages. We then evaluate the performance of various benchmark models categorized into parallel, non-parallel, cross-lingual, and shared learning approaches, including the Llama2 and GPT-3.5 large language models (LLMs). Our experiments highlight the significance of parallel data in TST and demonstrate the effectiveness of the Masked Style Filling (MSF) approach (Mukherjee et al., 2023) in non-parallel techniques. Moreover, cross-lingual and joint multilingual learning methods show promise, offering insights into selecting optimal models tailored to the specific language and task requirements. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first comprehensive exploration of the TST task as sentiment transfer across a diverse set of languages.
Developing Universal Dependency Treebanks for Magahi and Braj
Apr 26, 2022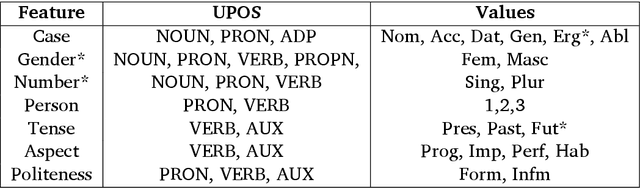
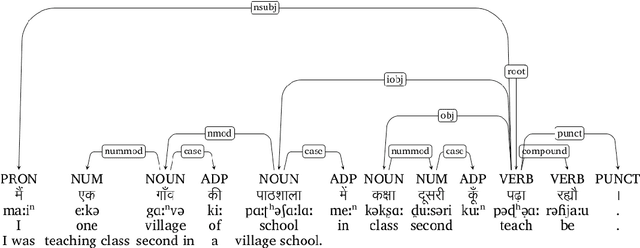
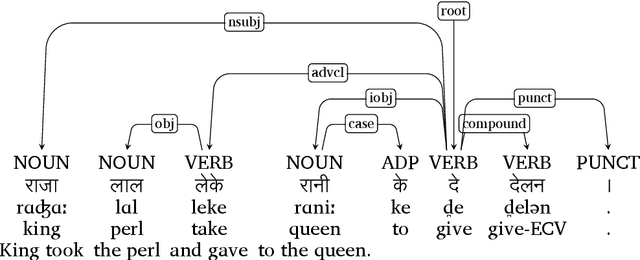
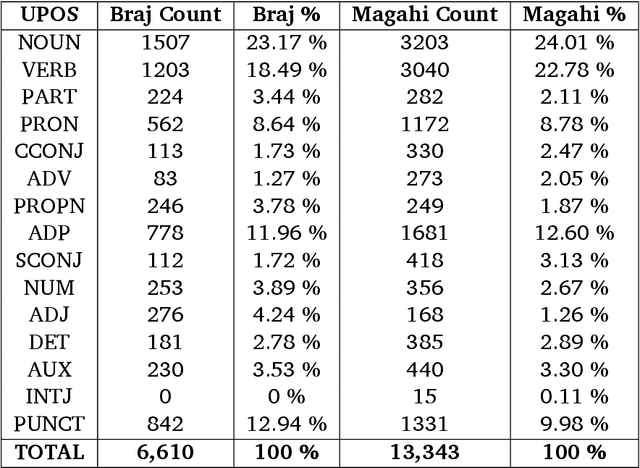
Abstract:In this paper, we discuss the development of treebanks for two low-resourced Indian languages - Magahi and Braj based on the Universal Dependencies framework. The Magahi treebank contains 945 sentences and Braj treebank around 500 sentences marked with their lemmas, part-of-speech, morphological features and universal dependencies. This paper gives a description of the different dependency relationship found in the two languages and give some statistics of the two treebanks. The dataset will be made publicly available on Universal Dependency (UD) repository (https://github.com/UniversalDependencies/UD_Magahi-MGTB/tree/master) in the next(v2.10) release.
Automatic Identification of Closely-related Indian Languages: Resources and Experiments
Mar 26, 2018
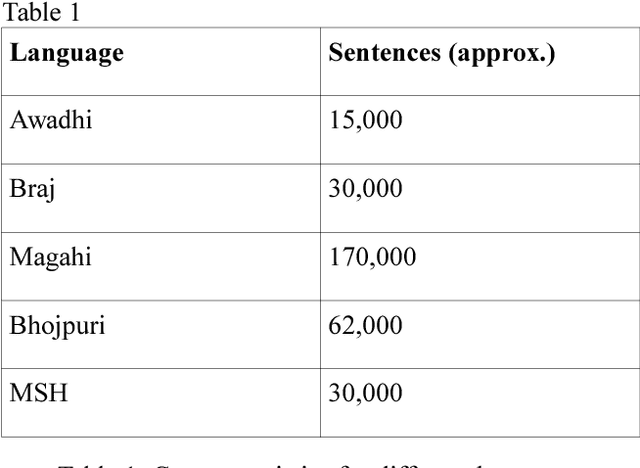
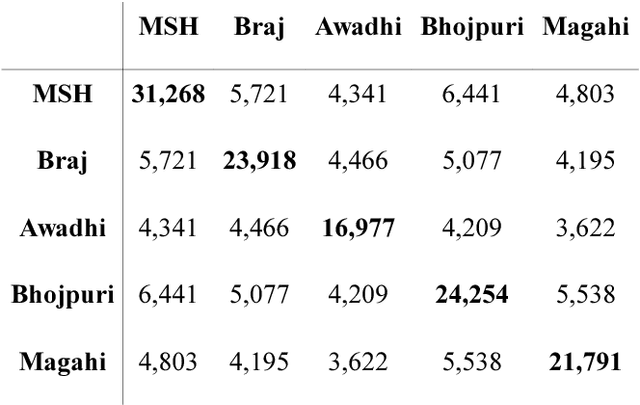
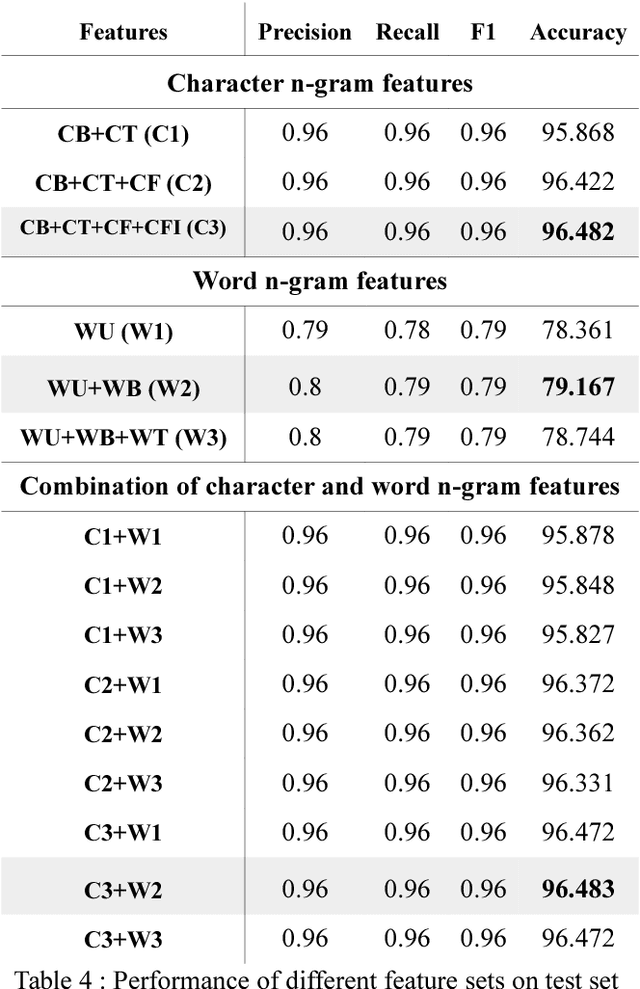
Abstract:In this paper, we discuss an attempt to develop an automatic language identification system for 5 closely-related Indo-Aryan languages of India, Awadhi, Bhojpuri, Braj, Hindi and Magahi. We have compiled a comparable corpora of varying length for these languages from various resources. We discuss the method of creation of these corpora in detail. Using these corpora, a language identification system was developed, which currently gives state of the art accuracy of 96.48\%. We also used these corpora to study the similarity between the 5 languages at the lexical level, which is the first data-based study of the extent of closeness of these languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge