Rongguo Zhang
crossMoDA Challenge: Evolution of Cross-Modality Domain Adaptation Techniques for Vestibular Schwannoma and Cochlea Segmentation from 2021 to 2023
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:The cross-Modality Domain Adaptation (crossMoDA) challenge series, initiated in 2021 in conjunction with the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), focuses on unsupervised cross-modality segmentation, learning from contrast-enhanced T1 (ceT1) and transferring to T2 MRI. The task is an extreme example of domain shift chosen to serve as a meaningful and illustrative benchmark. From a clinical application perspective, it aims to automate Vestibular Schwannoma (VS) and cochlea segmentation on T2 scans for more cost-effective VS management. Over time, the challenge objectives have evolved to enhance its clinical relevance. The challenge evolved from using single-institutional data and basic segmentation in 2021 to incorporating multi-institutional data and Koos grading in 2022, and by 2023, it included heterogeneous routine data and sub-segmentation of intra- and extra-meatal tumour components. In this work, we report the findings of the 2022 and 2023 editions and perform a retrospective analysis of the challenge progression over the years. The observations from the successive challenge contributions indicate that the number of outliers decreases with an expanding dataset. This is notable since the diversity of scanning protocols of the datasets concurrently increased. The winning approach of the 2023 edition reduced the number of outliers on the 2021 and 2022 testing data, demonstrating how increased data heterogeneity can enhance segmentation performance even on homogeneous data. However, the cochlea Dice score declined in 2023, likely due to the added complexity from tumour sub-annotations affecting overall segmentation performance. While progress is still needed for clinically acceptable VS segmentation, the plateauing performance suggests that a more challenging cross-modal task may better serve future benchmarking.
YUAN 2.0: A Large Language Model with Localized Filtering-based Attention
Dec 04, 2023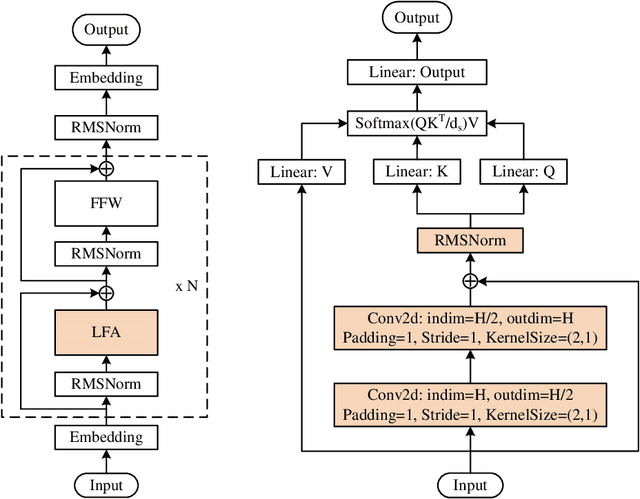
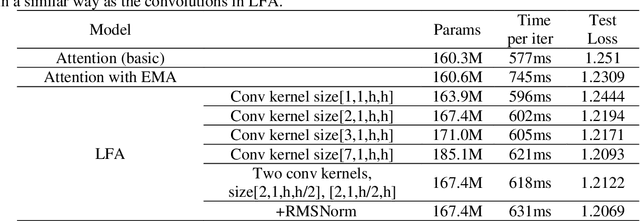
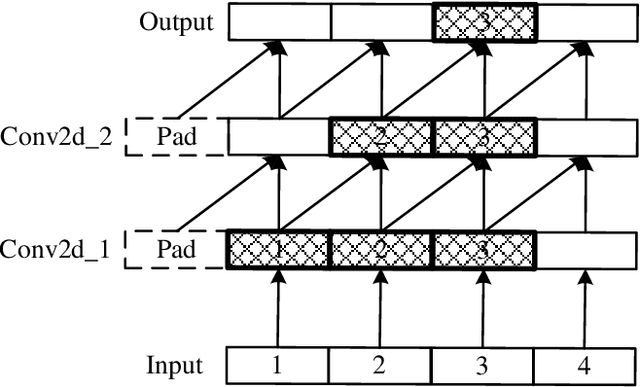
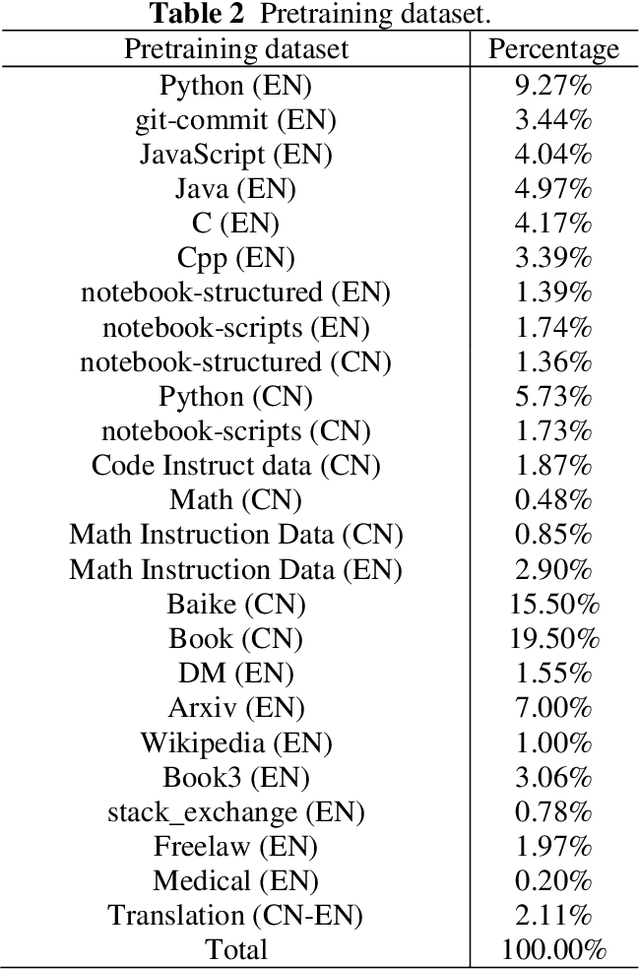
Abstract:In this work, we develop and release Yuan 2.0, a series of large language models with parameters ranging from 2.1 billion to 102.6 billion. The Localized Filtering-based Attention (LFA) is introduced to incorporate prior knowledge of local dependencies of natural language into Attention. A data filtering and generating system is presented to build pre-training and fine-tuning dataset in high quality. A distributed training method with non-uniform pipeline parallel, data parallel, and optimizer parallel is proposed, which greatly reduces the bandwidth requirements of intra-node communication, and achieves good performance in large-scale distributed training. Yuan 2.0 models display impressive ability in code generation, math problem-solving, and chatting compared with existing models. The latest version of YUAN 2.0, including model weights and source code, is accessible at Github.
MMMNA-Net for Overall Survival Time Prediction of Brain Tumor Patients
Jun 13, 2022



Abstract:Overall survival (OS) time is one of the most important evaluation indices for gliomas situations. Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans play an important role in the study of glioma prognosis OS time. Several deep learning-based methods are proposed for the OS time prediction on multi-modal MRI problems. However, these methods usually fuse multi-modal information at the beginning or at the end of the deep learning networks and lack the fusion of features from different scales. In addition, the fusion at the end of networks always adapts global with global (eg. fully connected after concatenation of global average pooling output) or local with local (eg. bilinear pooling), which loses the information of local with global. In this paper, we propose a novel method for multi-modal OS time prediction of brain tumor patients, which contains an improved nonlocal features fusion module introduced on different scales. Our method obtains a relative 8.76% improvement over the current state-of-art method (0.6989 vs. 0.6426 on accuracy). Extensive testing demonstrates that our method could adapt to situations with missing modalities. The code is available at https://github.com/TangWen920812/mmmna-net.
RPLHR-CT Dataset and Transformer Baseline for Volumetric Super-Resolution from CT Scans
Jun 13, 2022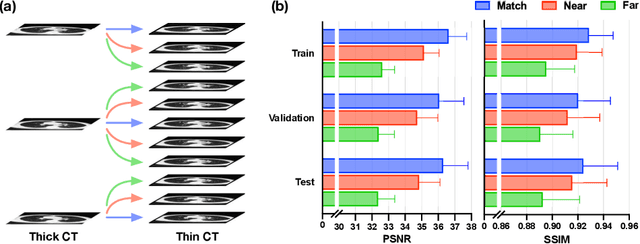
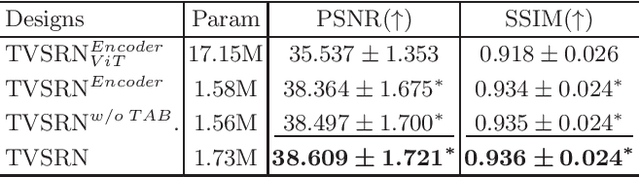
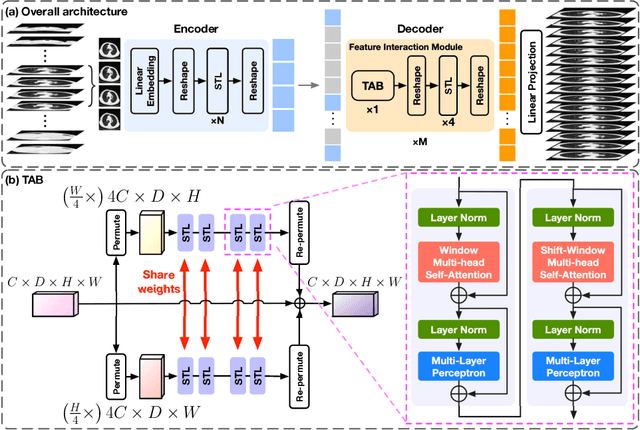
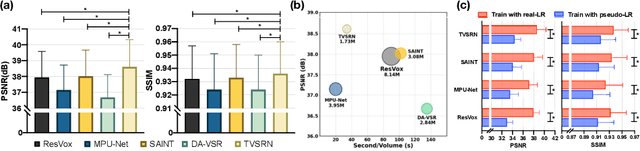
Abstract:In clinical practice, anisotropic volumetric medical images with low through-plane resolution are commonly used due to short acquisition time and lower storage cost. Nevertheless, the coarse resolution may lead to difficulties in medical diagnosis by either physicians or computer-aided diagnosis algorithms. Deep learning-based volumetric super-resolution (SR) methods are feasible ways to improve resolution, with convolutional neural networks (CNN) at their core. Despite recent progress, these methods are limited by inherent properties of convolution operators, which ignore content relevance and cannot effectively model long-range dependencies. In addition, most of the existing methods use pseudo-paired volumes for training and evaluation, where pseudo low-resolution (LR) volumes are generated by a simple degradation of their high-resolution (HR) counterparts. However, the domain gap between pseudo- and real-LR volumes leads to the poor performance of these methods in practice. In this paper, we build the first public real-paired dataset RPLHR-CT as a benchmark for volumetric SR, and provide baseline results by re-implementing four state-of-the-art CNN-based methods. Considering the inherent shortcoming of CNN, we also propose a transformer volumetric super-resolution network (TVSRN) based on attention mechanisms, dispensing with convolutions entirely. This is the first research to use a pure transformer for CT volumetric SR. The experimental results show that TVSRN significantly outperforms all baselines on both PSNR and SSIM. Moreover, the TVSRN method achieves a better trade-off between the image quality, the number of parameters, and the running time. Data and code are available at https://github.com/smilenaxx/RPLHR-CT.
Transformer Lesion Tracker
Jun 13, 2022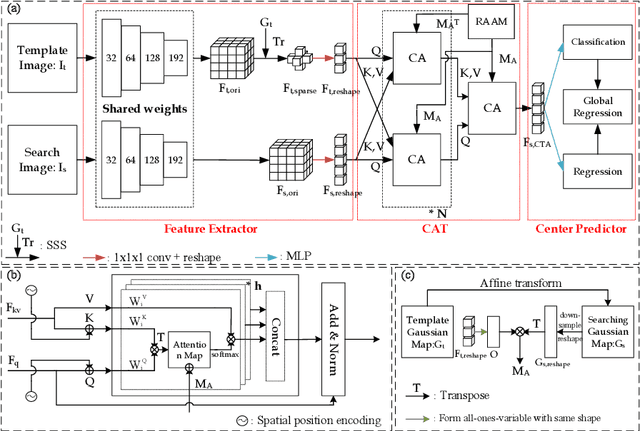
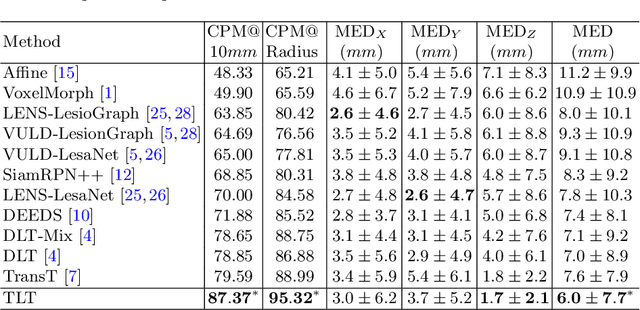
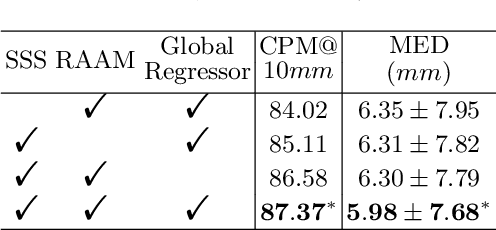
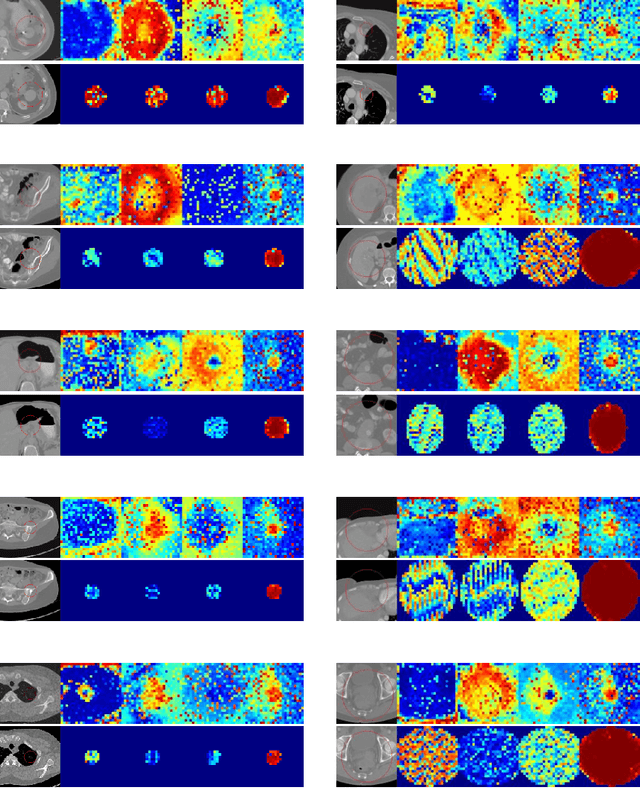
Abstract:Evaluating lesion progression and treatment response via longitudinal lesion tracking plays a critical role in clinical practice. Automated approaches for this task are motivated by prohibitive labor costs and time consumption when lesion matching is done manually. Previous methods typically lack the integration of local and global information. In this work, we propose a transformer-based approach, termed Transformer Lesion Tracker (TLT). Specifically, we design a Cross Attention-based Transformer (CAT) to capture and combine both global and local information to enhance feature extraction. We also develop a Registration-based Anatomical Attention Module (RAAM) to introduce anatomical information to CAT so that it can focus on useful feature knowledge. A Sparse Selection Strategy (SSS) is presented for selecting features and reducing memory footprint in Transformer training. In addition, we use a global regression to further improve model performance. We conduct experiments on a public dataset to show the superiority of our method and find that our model performance has improved the average Euclidean center error by at least 14.3% (6mm vs. 7mm) compared with the state-of-the-art (SOTA). Code is available at https://github.com/TangWen920812/TLT.
Yuan 1.0: Large-Scale Pre-trained Language Model in Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Learning
Oct 12, 2021



Abstract:Recent work like GPT-3 has demonstrated excellent performance of Zero-Shot and Few-Shot learning on many natural language processing (NLP) tasks by scaling up model size, dataset size and the amount of computation. However, training a model like GPT-3 requires huge amount of computational resources which makes it challengeable to researchers. In this work, we propose a method that incorporates large-scale distributed training performance into model architecture design. With this method, Yuan 1.0, the current largest singleton language model with 245B parameters, achieves excellent performance on thousands GPUs during training, and the state-of-the-art results on NLP tasks. A data processing method is designed to efficiently filter massive amount of raw data. The current largest high-quality Chinese corpus with 5TB high quality texts is built based on this method. In addition, a calibration and label expansion method is proposed to improve the Zero-Shot and Few-Shot performance, and steady improvement is observed on the accuracy of various tasks. Yuan 1.0 presents strong capacity of natural language generation, and the generated articles are difficult to distinguish from the human-written ones.
Automatic Calcium Scoring in Cardiac and Chest CT Using DenseRAUnet
Jul 26, 2019



Abstract:Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a common and strong threat to human beings, featuring high prevalence, disability and mortality. The amount of coronary artery calcification (CAC) is an effective factor for CVD risk evaluation. Conventionally, CAC is quantified using ECG-synchronized cardiac CT but rarely from general chest CT scans. However, compared with ECG-synchronized cardiac CT, chest CT is more prevalent and economical in clinical practice. To address this, we propose an automatic method based on Dense U-Net to segment coronary calcium pixels on both types of CT scans. Our contribution is two-fold. First, we propose a novel network called DenseRAUnet, which takes advantage of Dense U-net, ResNet and atrous convolutions. We prove the robustness and generalizability of our model by training it exclusively on chest CT while test on both types of CT scans. Second, we design a loss function combining bootstrap with IoU function to balance foreground and background classes. DenseRAUnet is trained in a 2.5D fashion and tested on a private dataset consisting of 144 scans. Results show an F1-score of 0.75, with 0.83 accuracy of predicting cardiovascular disease risk.
Cross-view Relation Networks for Mammogram Mass Detection
Jul 01, 2019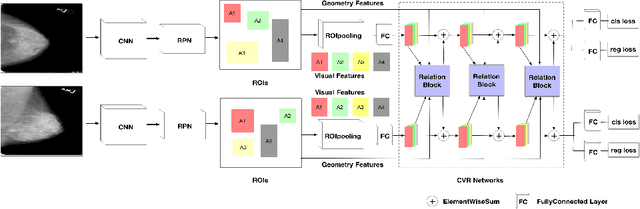
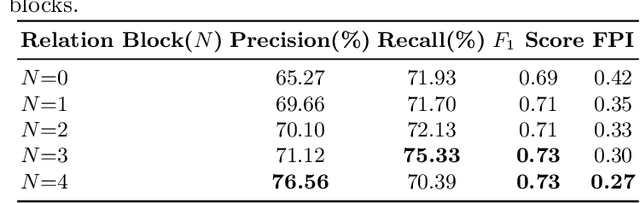
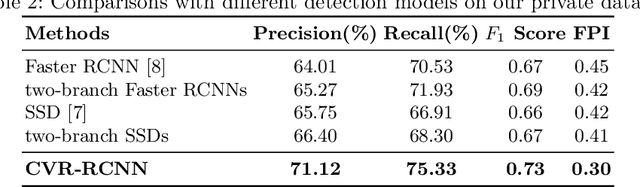
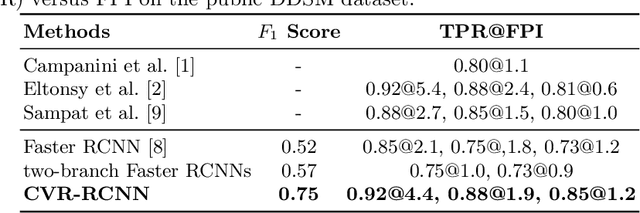
Abstract:Mammogram is the most effective imaging modality for the mass lesion detection of breast cancer at the early stage. The information from the two paired views (i.e., medio-lateral oblique and cranio-caudal) are highly relational and complementary, and this is crucial for doctors' decisions in clinical practice. However, existing mass detection methods do not consider jointly learning effective features from the two relational views. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel mammogram mass detection framework, termed Cross-View Relation Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (CVR-RCNN). The proposed CVR-RCNN is expected to capture the latent relation information between the corresponding mass region of interests (ROIs) from the two paired views. Evaluations on a new large-scale private dataset and a public mammogram dataset show that the proposed CVR-RCNN outperforms existing state-of-the-art mass detection methods. Meanwhile, our experimental results suggest that incorporating the relation information across two views helps to train a superior detection model, which is a promising avenue for mammogram mass detection.
Group-Attention Single-Shot Detector (GA-SSD): Finding Pulmonary Nodules in Large-Scale CT Images
Dec 18, 2018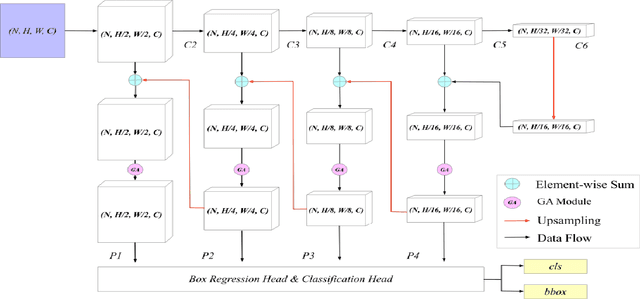
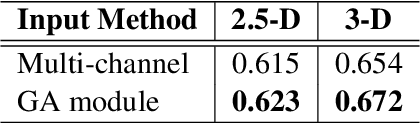
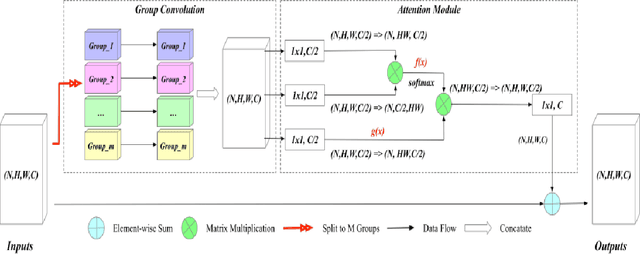
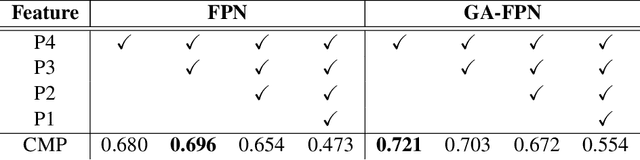
Abstract:Early diagnosis of pulmonary nodules (PNs) can improve the survival rate of patients and yet is a challenging task for radiologists due to the image noise and artifacts in computed tomography (CT) images. In this paper, we propose a novel and effective abnormality detector implementing the attention mechanism and group convolution on 3D single-shot detector (SSD) called group-attention SSD (GA-SSD). We find that group convolution is effective in extracting rich context information between continuous slices, and attention network can learn the target features automatically. We collected a large-scale dataset that contained 4146 CT scans with annotations of varying types and sizes of PNs (even PNs smaller than 3mm were annotated). To the best of our knowledge, this dataset is the largest cohort with relatively complete annotations for PNs detection. Our experimental results show that the proposed group-attention SSD outperforms the classic SSD framework as well as the state-of-the-art 3DCNN, especially on some challenging lesion types.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge