Richard J. Chen
Evidence-based diagnostic reasoning with multi-agent copilot for human pathology
Jun 26, 2025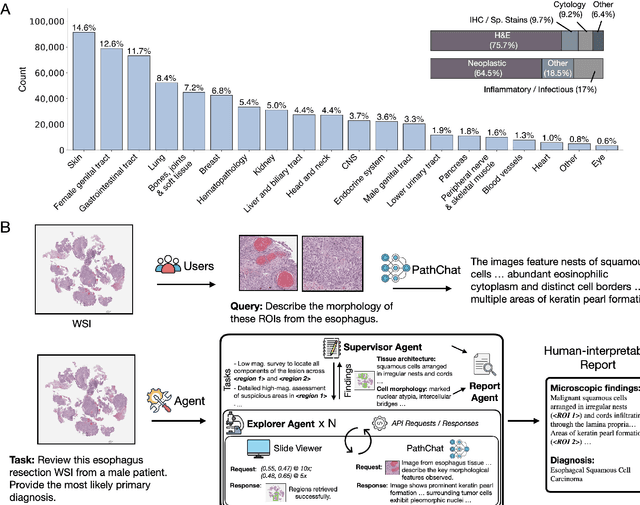
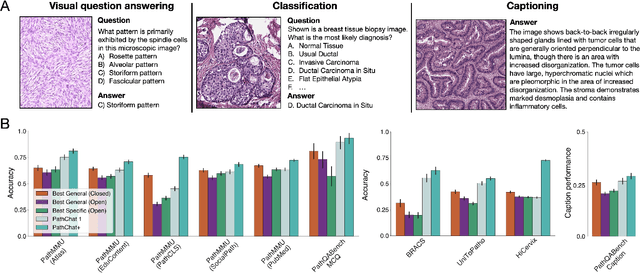
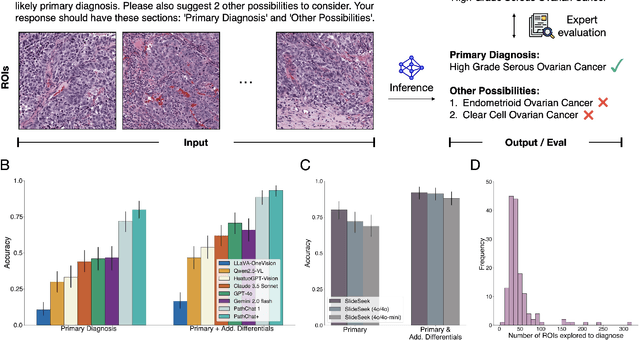
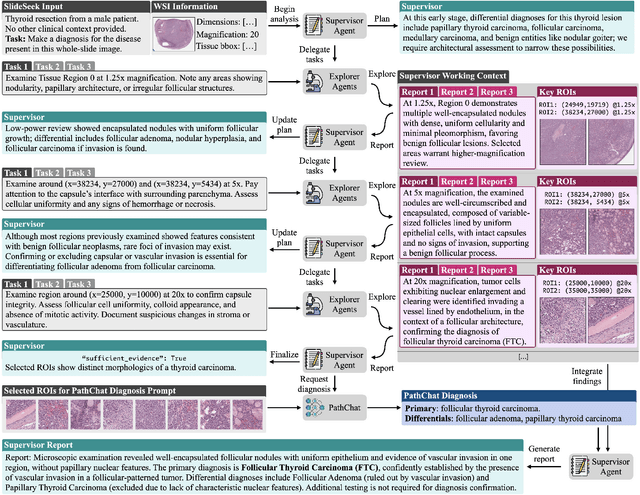
Abstract:Pathology is experiencing rapid digital transformation driven by whole-slide imaging and artificial intelligence (AI). While deep learning-based computational pathology has achieved notable success, traditional models primarily focus on image analysis without integrating natural language instruction or rich, text-based context. Current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in computational pathology face limitations, including insufficient training data, inadequate support and evaluation for multi-image understanding, and a lack of autonomous, diagnostic reasoning capabilities. To address these limitations, we introduce PathChat+, a new MLLM specifically designed for human pathology, trained on over 1 million diverse, pathology-specific instruction samples and nearly 5.5 million question answer turns. Extensive evaluations across diverse pathology benchmarks demonstrated that PathChat+ substantially outperforms the prior PathChat copilot, as well as both state-of-the-art (SOTA) general-purpose and other pathology-specific models. Furthermore, we present SlideSeek, a reasoning-enabled multi-agent AI system leveraging PathChat+ to autonomously evaluate gigapixel whole-slide images (WSIs) through iterative, hierarchical diagnostic reasoning, reaching high accuracy on DDxBench, a challenging open-ended differential diagnosis benchmark, while also capable of generating visually grounded, humanly-interpretable summary reports.
Do Multiple Instance Learning Models Transfer?
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) is a cornerstone approach in computational pathology (CPath) for generating clinically meaningful slide-level embeddings from gigapixel tissue images. However, MIL often struggles with small, weakly supervised clinical datasets. In contrast to fields such as NLP and conventional computer vision, where transfer learning is widely used to address data scarcity, the transferability of MIL models remains poorly understood. In this study, we systematically evaluate the transfer learning capabilities of pretrained MIL models by assessing 11 models across 21 pretraining tasks for morphological and molecular subtype prediction. Our results show that pretrained MIL models, even when trained on different organs than the target task, consistently outperform models trained from scratch. Moreover, pretraining on pancancer datasets enables strong generalization across organs and tasks, outperforming slide foundation models while using substantially less pretraining data. These findings highlight the robust adaptability of MIL models and demonstrate the benefits of leveraging transfer learning to boost performance in CPath. Lastly, we provide a resource which standardizes the implementation of MIL models and collection of pretrained model weights on popular CPath tasks, available at https://github.com/mahmoodlab/MIL-Lab
Molecular-driven Foundation Model for Oncologic Pathology
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Foundation models are reshaping computational pathology by enabling transfer learning, where models pre-trained on vast datasets can be adapted for downstream diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic response tasks. Despite these advances, foundation models are still limited in their ability to encode the entire gigapixel whole-slide images without additional training and often lack complementary multimodal data. Here, we introduce Threads, a slide-level foundation model capable of generating universal representations of whole-slide images of any size. Threads was pre-trained using a multimodal learning approach on a diverse cohort of 47,171 hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained tissue sections, paired with corresponding genomic and transcriptomic profiles - the largest such paired dataset to be used for foundation model development to date. This unique training paradigm enables Threads to capture the tissue's underlying molecular composition, yielding powerful representations applicable to a wide array of downstream tasks. In extensive benchmarking across 54 oncology tasks, including clinical subtyping, grading, mutation prediction, immunohistochemistry status determination, treatment response prediction, and survival prediction, Threads outperformed all baselines while demonstrating remarkable generalizability and label efficiency. It is particularly well suited for predicting rare events, further emphasizing its clinical utility. We intend to make the model publicly available for the broader community.
Multimodal Whole Slide Foundation Model for Pathology
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:The field of computational pathology has been transformed with recent advances in foundation models that encode histopathology region-of-interests (ROIs) into versatile and transferable feature representations via self-supervised learning (SSL). However, translating these advancements to address complex clinical challenges at the patient and slide level remains constrained by limited clinical data in disease-specific cohorts, especially for rare clinical conditions. We propose TITAN, a multimodal whole slide foundation model pretrained using 335,645 WSIs via visual self-supervised learning and vision-language alignment with corresponding pathology reports and 423,122 synthetic captions generated from a multimodal generative AI copilot for pathology. Without any finetuning or requiring clinical labels, TITAN can extract general-purpose slide representations and generate pathology reports that generalize to resource-limited clinical scenarios such as rare disease retrieval and cancer prognosis. We evaluate TITAN on diverse clinical tasks and find that TITAN outperforms both ROI and slide foundation models across machine learning settings such as linear probing, few-shot and zero-shot classification, rare cancer retrieval and cross-modal retrieval, and pathology report generation.
Multistain Pretraining for Slide Representation Learning in Pathology
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Developing self-supervised learning (SSL) models that can learn universal and transferable representations of H&E gigapixel whole-slide images (WSIs) is becoming increasingly valuable in computational pathology. These models hold the potential to advance critical tasks such as few-shot classification, slide retrieval, and patient stratification. Existing approaches for slide representation learning extend the principles of SSL from small images (e.g., 224 x 224 patches) to entire slides, usually by aligning two different augmentations (or views) of the slide. Yet the resulting representation remains constrained by the limited clinical and biological diversity of the views. Instead, we postulate that slides stained with multiple markers, such as immunohistochemistry, can be used as different views to form a rich task-agnostic training signal. To this end, we introduce Madeleine, a multimodal pretraining strategy for slide representation learning. Madeleine is trained with a dual global-local cross-stain alignment objective on large cohorts of breast cancer samples (N=4,211 WSIs across five stains) and kidney transplant samples (N=12,070 WSIs across four stains). We demonstrate the quality of slide representations learned by Madeleine on various downstream evaluations, ranging from morphological and molecular classification to prognostic prediction, comprising 21 tasks using 7,299 WSIs from multiple medical centers. Code is available at https://github.com/mahmoodlab/MADELEINE.
Multimodal Prototyping for cancer survival prediction
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal survival methods combining gigapixel histology whole-slide images (WSIs) and transcriptomic profiles are particularly promising for patient prognostication and stratification. Current approaches involve tokenizing the WSIs into smaller patches (>10,000 patches) and transcriptomics into gene groups, which are then integrated using a Transformer for predicting outcomes. However, this process generates many tokens, which leads to high memory requirements for computing attention and complicates post-hoc interpretability analyses. Instead, we hypothesize that we can: (1) effectively summarize the morphological content of a WSI by condensing its constituting tokens using morphological prototypes, achieving more than 300x compression; and (2) accurately characterize cellular functions by encoding the transcriptomic profile with biological pathway prototypes, all in an unsupervised fashion. The resulting multimodal tokens are then processed by a fusion network, either with a Transformer or an optimal transport cross-alignment, which now operates with a small and fixed number of tokens without approximations. Extensive evaluation on six cancer types shows that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods with much less computation while unlocking new interpretability analyses.
HEST-1k: A Dataset for Spatial Transcriptomics and Histology Image Analysis
Jun 23, 2024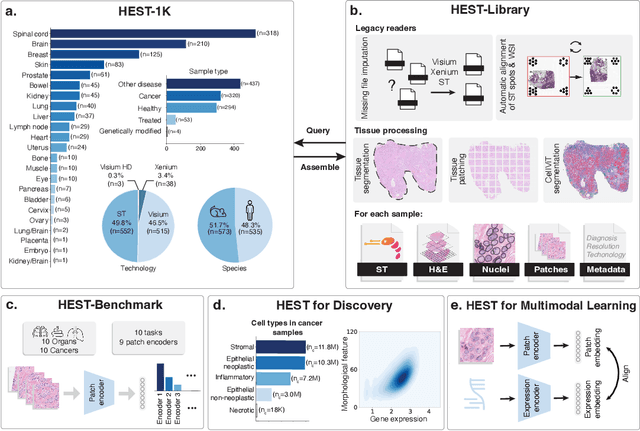
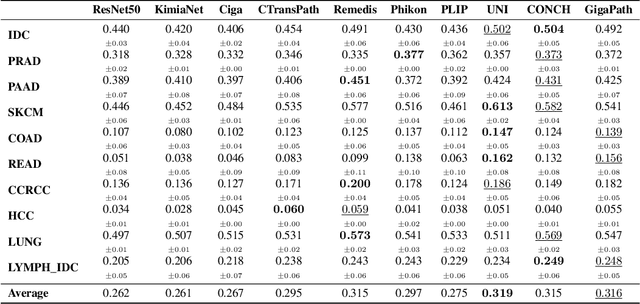
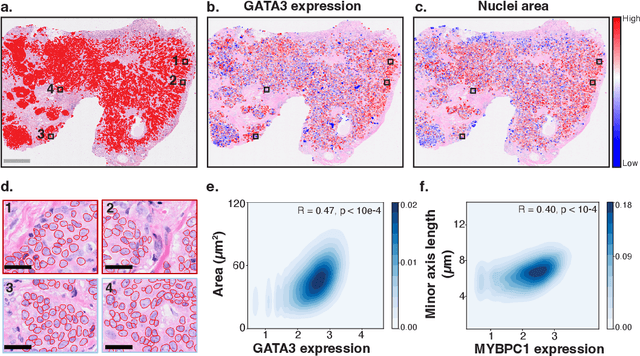
Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics (ST) enables interrogating the molecular composition of tissue with ever-increasing resolution, depth, and sensitivity. However, costs, rapidly evolving technology, and lack of standards have constrained computational methods in ST to narrow tasks and small cohorts. In addition, the underlying tissue morphology as reflected by H&E-stained whole slide images (WSIs) encodes rich information often overlooked in ST studies. Here, we introduce HEST-1k, a collection of 1,108 spatial transcriptomic profiles, each linked to a WSI and metadata. HEST-1k was assembled using HEST-Library from 131 public and internal cohorts encompassing 25 organs, two species (Homo Sapiens and Mus Musculus), and 320 cancer samples from 25 cancer types. HEST-1k processing enabled the identification of 1.5 million expression--morphology pairs and 60 million nuclei. HEST-1k is tested on three use cases: (1) benchmarking foundation models for histopathology (HEST-Benchmark), (2) biomarker identification, and (3) multimodal representation learning. HEST-1k, HEST-Library, and HEST-Benchmark can be freely accessed via https://github.com/mahmoodlab/hest.
Morphological Prototyping for Unsupervised Slide Representation Learning in Computational Pathology
May 19, 2024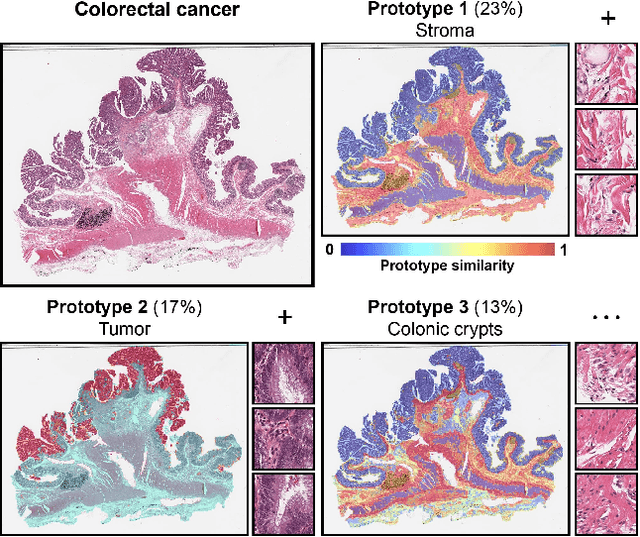
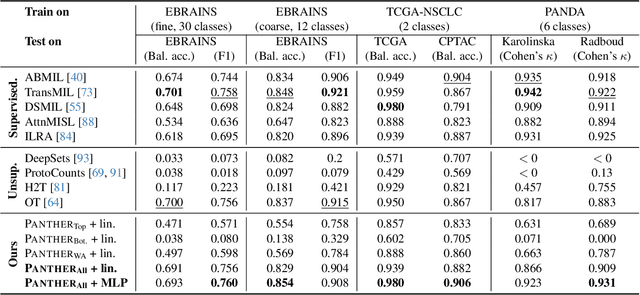
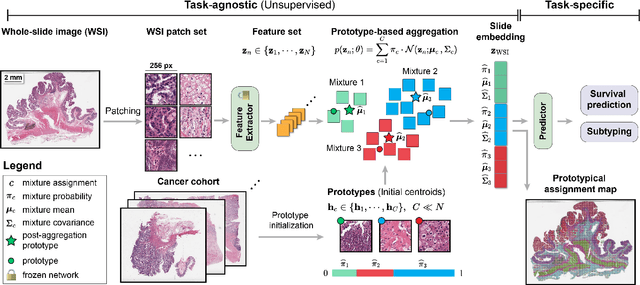
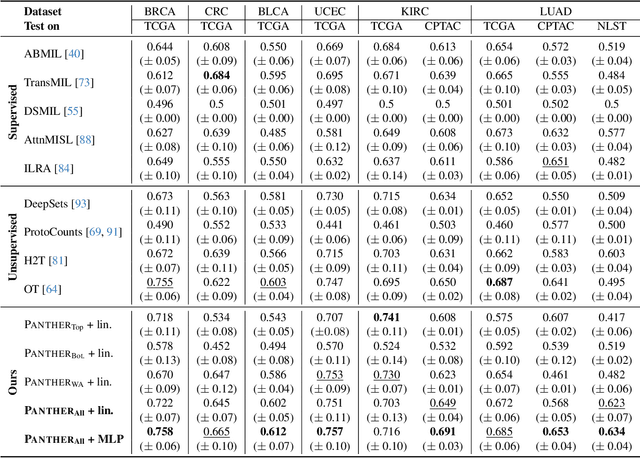
Abstract:Representation learning of pathology whole-slide images (WSIs) has been has primarily relied on weak supervision with Multiple Instance Learning (MIL). However, the slide representations resulting from this approach are highly tailored to specific clinical tasks, which limits their expressivity and generalization, particularly in scenarios with limited data. Instead, we hypothesize that morphological redundancy in tissue can be leveraged to build a task-agnostic slide representation in an unsupervised fashion. To this end, we introduce PANTHER, a prototype-based approach rooted in the Gaussian mixture model that summarizes the set of WSI patches into a much smaller set of morphological prototypes. Specifically, each patch is assumed to have been generated from a mixture distribution, where each mixture component represents a morphological exemplar. Utilizing the estimated mixture parameters, we then construct a compact slide representation that can be readily used for a wide range of downstream tasks. By performing an extensive evaluation of PANTHER on subtyping and survival tasks using 13 datasets, we show that 1) PANTHER outperforms or is on par with supervised MIL baselines and 2) the analysis of morphological prototypes brings new qualitative and quantitative insights into model interpretability.
Transcriptomics-guided Slide Representation Learning in Computational Pathology
May 19, 2024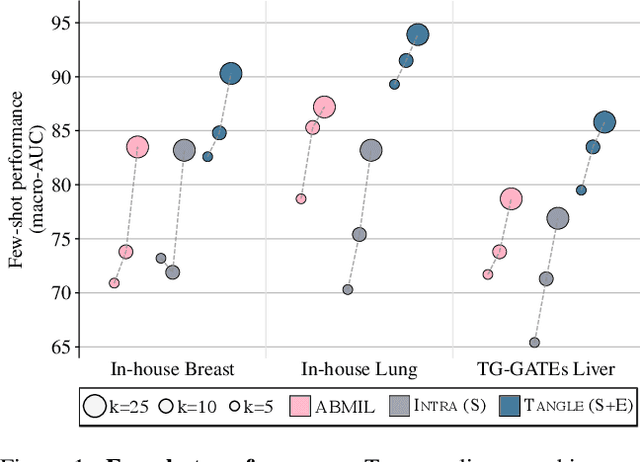
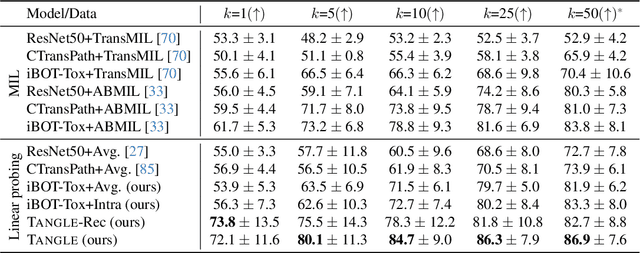
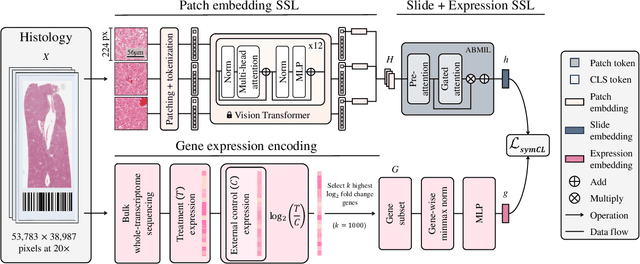
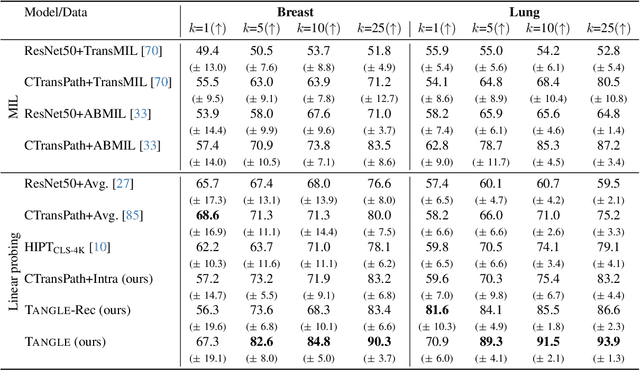
Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has been successful in building patch embeddings of small histology images (e.g., 224x224 pixels), but scaling these models to learn slide embeddings from the entirety of giga-pixel whole-slide images (WSIs) remains challenging. Here, we leverage complementary information from gene expression profiles to guide slide representation learning using multimodal pre-training. Expression profiles constitute highly detailed molecular descriptions of a tissue that we hypothesize offer a strong task-agnostic training signal for learning slide embeddings. Our slide and expression (S+E) pre-training strategy, called Tangle, employs modality-specific encoders, the outputs of which are aligned via contrastive learning. Tangle was pre-trained on samples from three different organs: liver (n=6,597 S+E pairs), breast (n=1,020), and lung (n=1,012) from two different species (Homo sapiens and Rattus norvegicus). Across three independent test datasets consisting of 1,265 breast WSIs, 1,946 lung WSIs, and 4,584 liver WSIs, Tangle shows significantly better few-shot performance compared to supervised and SSL baselines. When assessed using prototype-based classification and slide retrieval, Tangle also shows a substantial performance improvement over all baselines. Code available at https://github.com/mahmoodlab/TANGLE.
A Foundational Multimodal Vision Language AI Assistant for Human Pathology
Dec 13, 2023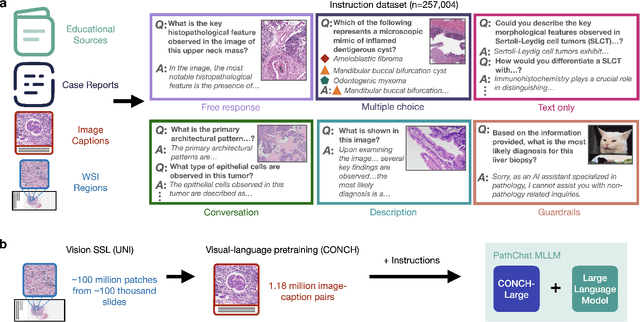
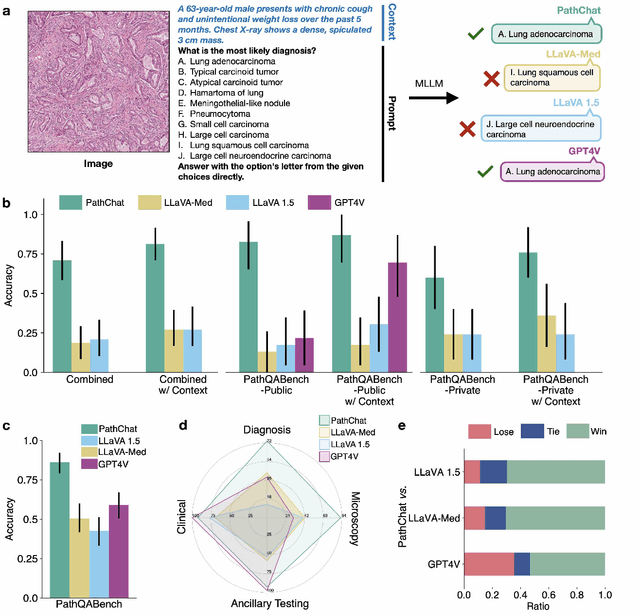
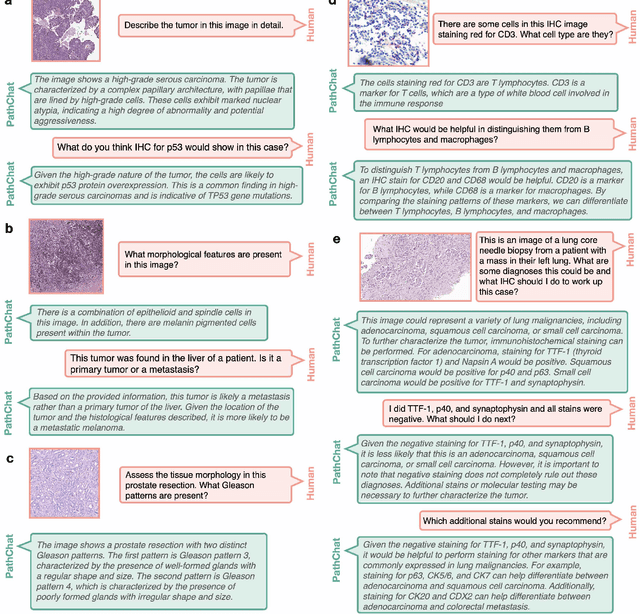
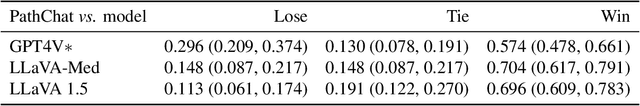
Abstract:The field of computational pathology has witnessed remarkable progress in the development of both task-specific predictive models and task-agnostic self-supervised vision encoders. However, despite the explosive growth of generative artificial intelligence (AI), there has been limited study on building general purpose, multimodal AI assistants tailored to pathology. Here we present PathChat, a vision-language generalist AI assistant for human pathology using an in-house developed foundational vision encoder pretrained on 100 million histology images from over 100,000 patient cases and 1.18 million pathology image-caption pairs. The vision encoder is then combined with a pretrained large language model and the whole system is finetuned on over 250,000 diverse disease agnostic visual language instructions. We compare PathChat against several multimodal vision language AI assistants as well as GPT4V, which powers the commercially available multimodal general purpose AI assistant ChatGPT-4. When relevant clinical context is provided with the histology image, PathChat achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 87% on multiple-choice questions based on publicly available cases of diverse tissue origins and disease models. Additionally, using open-ended questions and human expert evaluation, we found that overall PathChat produced more accurate and pathologist-preferable responses to diverse queries related to pathology. As an interactive and general vision language AI assistant that can flexibly handle both visual and natural language inputs, PathChat can potentially find impactful applications in pathology education, research, and human-in-the-loop clinical decision making.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge