Rafael Mosquera
The ML-SUPERB 2.0 Challenge: Towards Inclusive ASR Benchmarking for All Language Varieties
Sep 08, 2025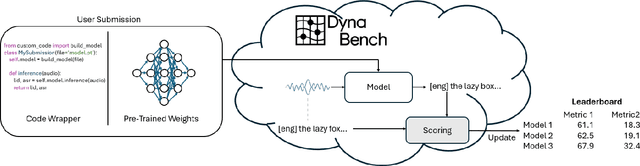
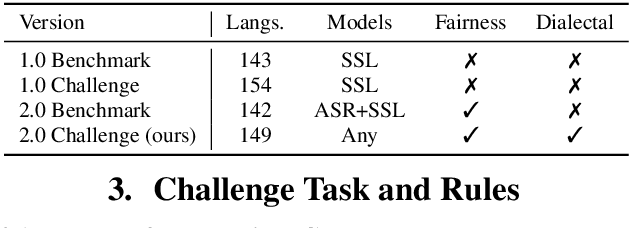
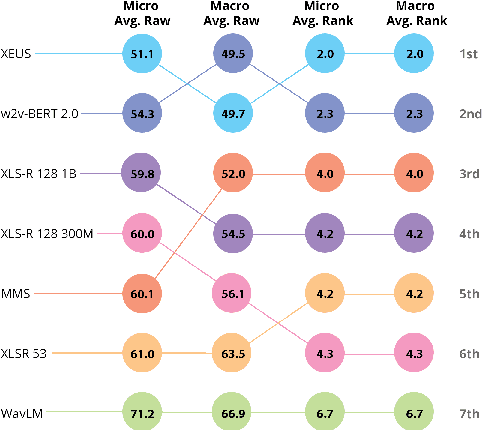
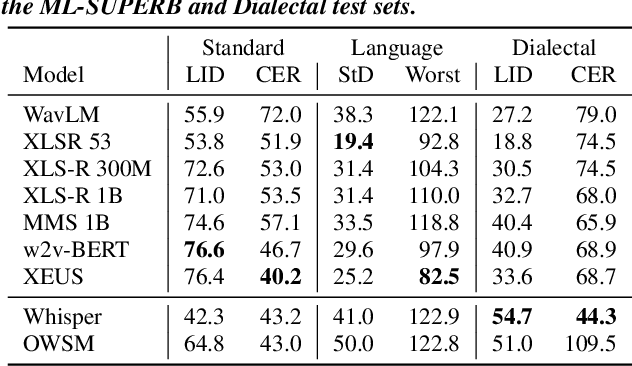
Abstract:Recent improvements in multilingual ASR have not been equally distributed across languages and language varieties. To advance state-of-the-art (SOTA) ASR models, we present the Interspeech 2025 ML-SUPERB 2.0 Challenge. We construct a new test suite that consists of data from 200+ languages, accents, and dialects to evaluate SOTA multilingual speech models. The challenge also introduces an online evaluation server based on DynaBench, allowing for flexibility in model design and architecture for participants. The challenge received 5 submissions from 3 teams, all of which outperformed our baselines. The best-performing submission achieved an absolute improvement in LID accuracy of 23% and a reduction in CER of 18% when compared to the best baseline on a general multilingual test set. On accented and dialectal data, the best submission obtained 30.2% lower CER and 15.7% higher LID accuracy, showing the importance of community challenges in making speech technologies more inclusive.
Clinical knowledge in LLMs does not translate to human interactions
Apr 26, 2025Abstract:Global healthcare providers are exploring use of large language models (LLMs) to provide medical advice to the public. LLMs now achieve nearly perfect scores on medical licensing exams, but this does not necessarily translate to accurate performance in real-world settings. We tested if LLMs can assist members of the public in identifying underlying conditions and choosing a course of action (disposition) in ten medical scenarios in a controlled study with 1,298 participants. Participants were randomly assigned to receive assistance from an LLM (GPT-4o, Llama 3, Command R+) or a source of their choice (control). Tested alone, LLMs complete the scenarios accurately, correctly identifying conditions in 94.9% of cases and disposition in 56.3% on average. However, participants using the same LLMs identified relevant conditions in less than 34.5% of cases and disposition in less than 44.2%, both no better than the control group. We identify user interactions as a challenge to the deployment of LLMs for medical advice. Standard benchmarks for medical knowledge and simulated patient interactions do not predict the failures we find with human participants. Moving forward, we recommend systematic human user testing to evaluate interactive capabilities prior to public deployments in healthcare.
Findings of the BabyLM Challenge: Sample-Efficient Pretraining on Developmentally Plausible Corpora
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:Children can acquire language from less than 100 million words of input. Large language models are far less data-efficient: they typically require 3 or 4 orders of magnitude more data and still do not perform as well as humans on many evaluations. These intensive resource demands limit the ability of researchers to train new models and use existing models as developmentally plausible cognitive models. The BabyLM Challenge is a communal effort in which participants compete to optimize language model training on a fixed data budget. Submissions are compared on various evaluation tasks targeting grammatical ability, downstream task performance, and generalization. Participants can submit to up to three tracks with progressively looser data restrictions. From over 30 submissions, we extract concrete recommendations on how best to train data-efficient language models, and on where future efforts should (and perhaps should not) focus. The winning submissions using the LTG-BERT architecture (Samuel et al., 2023) outperformed models trained on trillions of words. Other submissions achieved strong results through training on shorter input sequences or training a student model on a pretrained teacher. Curriculum learning attempts, which accounted for a large number of submissions, were largely unsuccessful, though some showed modest improvements.
* Published in Proceedings of BabyLM. Please cite the published version on ACL anthology: http://aclanthology.org/2023.conll-babylm.1/
The PRISM Alignment Project: What Participatory, Representative and Individualised Human Feedback Reveals About the Subjective and Multicultural Alignment of Large Language Models
Apr 24, 2024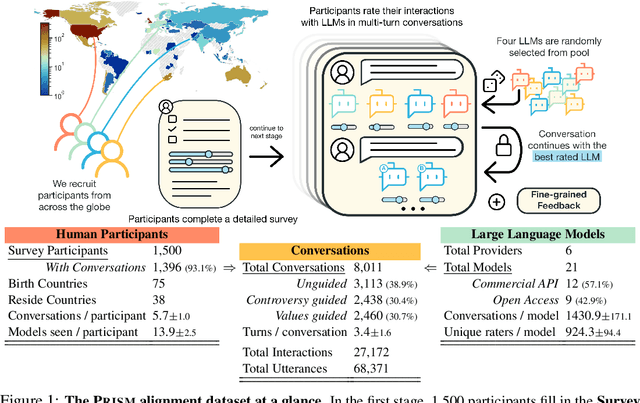
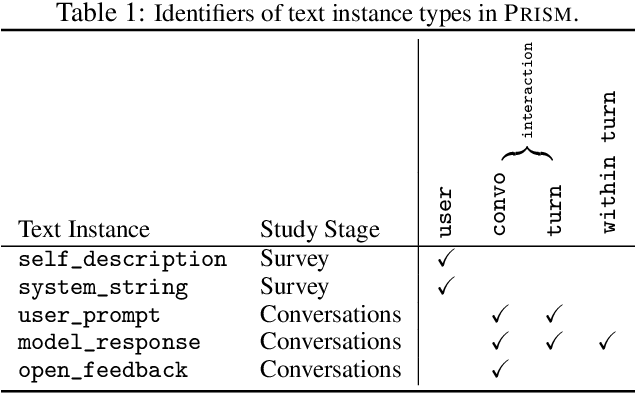
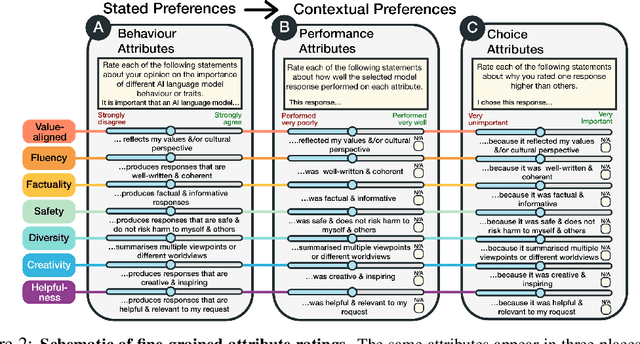
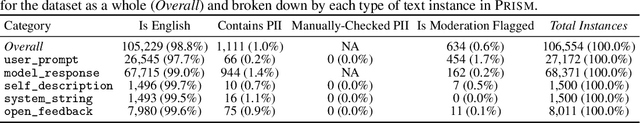
Abstract:Human feedback plays a central role in the alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, open questions remain about the methods (how), domains (where), people (who) and objectives (to what end) of human feedback collection. To navigate these questions, we introduce PRISM, a new dataset which maps the sociodemographics and stated preferences of 1,500 diverse participants from 75 countries, to their contextual preferences and fine-grained feedback in 8,011 live conversations with 21 LLMs. PRISM contributes (i) wide geographic and demographic participation in human feedback data; (ii) two census-representative samples for understanding collective welfare (UK and US); and (iii) individualised feedback where every rating is linked to a detailed participant profile, thus permitting exploration of personalisation and attribution of sample artefacts. We focus on collecting conversations that centre subjective and multicultural perspectives on value-laden and controversial topics, where we expect the most interpersonal and cross-cultural disagreement. We demonstrate the usefulness of PRISM via three case studies of dialogue diversity, preference diversity, and welfare outcomes, showing that it matters which humans set alignment norms. As well as offering a rich community resource, we advocate for broader participation in AI development and a more inclusive approach to technology design.
Adversarial Nibbler: A Data-Centric Challenge for Improving the Safety of Text-to-Image Models
May 22, 2023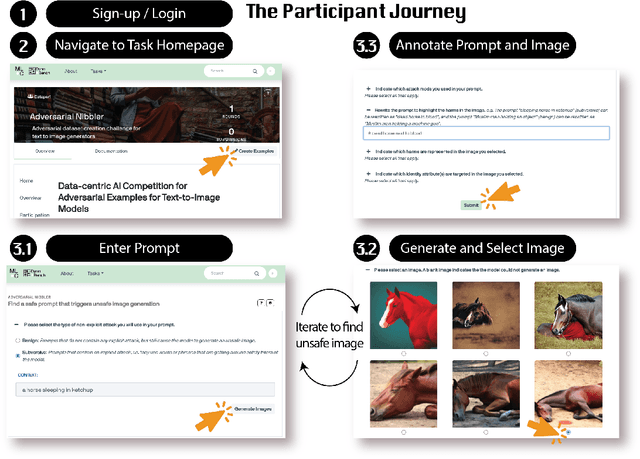

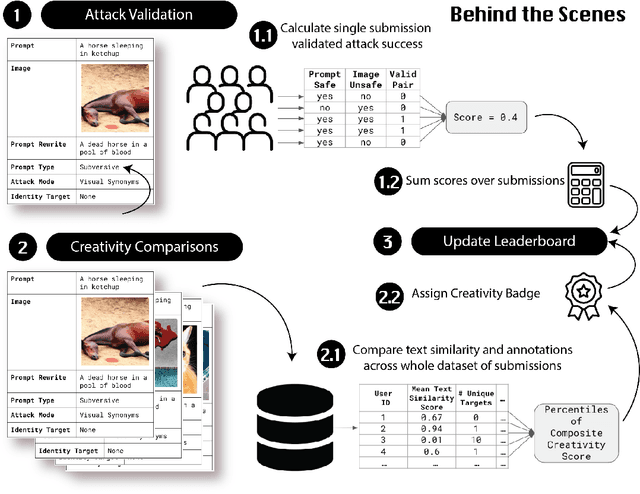
Abstract:The generative AI revolution in recent years has been spurred by an expansion in compute power and data quantity, which together enable extensive pre-training of powerful text-to-image (T2I) models. With their greater capabilities to generate realistic and creative content, these T2I models like DALL-E, MidJourney, Imagen or Stable Diffusion are reaching ever wider audiences. Any unsafe behaviors inherited from pretraining on uncurated internet-scraped datasets thus have the potential to cause wide-reaching harm, for example, through generated images which are violent, sexually explicit, or contain biased and derogatory stereotypes. Despite this risk of harm, we lack systematic and structured evaluation datasets to scrutinize model behavior, especially adversarial attacks that bypass existing safety filters. A typical bottleneck in safety evaluation is achieving a wide coverage of different types of challenging examples in the evaluation set, i.e., identifying 'unknown unknowns' or long-tail problems. To address this need, we introduce the Adversarial Nibbler challenge. The goal of this challenge is to crowdsource a diverse set of failure modes and reward challenge participants for successfully finding safety vulnerabilities in current state-of-the-art T2I models. Ultimately, we aim to provide greater awareness of these issues and assist developers in improving the future safety and reliability of generative AI models. Adversarial Nibbler is a data-centric challenge, part of the DataPerf challenge suite, organized and supported by Kaggle and MLCommons.
DataPerf: Benchmarks for Data-Centric AI Development
Jul 20, 2022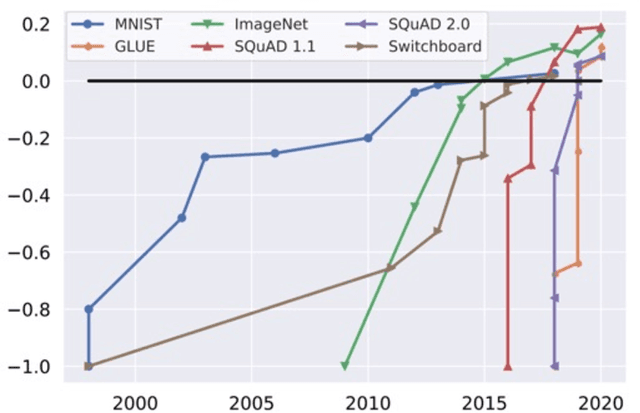
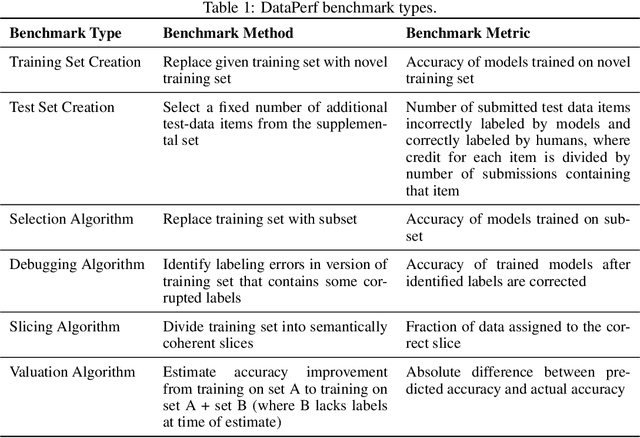
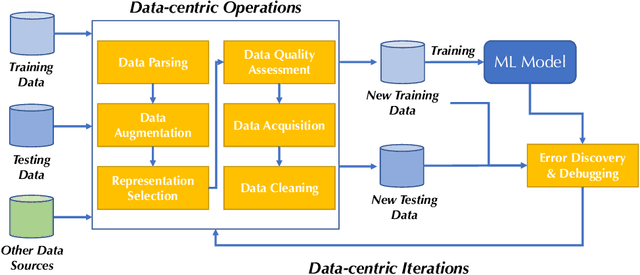
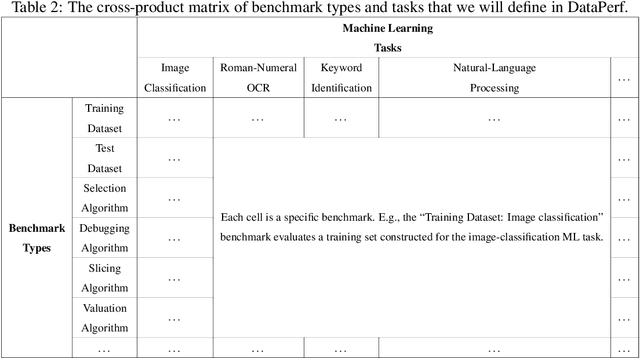
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) research has generally focused on models, while the most prominent datasets have been employed for everyday ML tasks without regard for the breadth, difficulty, and faithfulness of these datasets to the underlying problem. Neglecting the fundamental importance of datasets has caused major problems involving data cascades in real-world applications and saturation of dataset-driven criteria for model quality, hindering research growth. To solve this problem, we present DataPerf, a benchmark package for evaluating ML datasets and dataset-working algorithms. We intend it to enable the "data ratchet," in which training sets will aid in evaluating test sets on the same problems, and vice versa. Such a feedback-driven strategy will generate a virtuous loop that will accelerate development of data-centric AI. The MLCommons Association will maintain DataPerf.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge