Pedro Ortiz Suarez
How Should We Model the Probability of a Language?
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Of the over 7,000 languages spoken in the world, commercial language identification (LID) systems only reliably identify a few hundred in written form. Research-grade systems extend this coverage under certain circumstances, but for most languages coverage remains patchy or nonexistent. This position paper argues that this situation is largely self-imposed. In particular, it arises from a persistent framing of LID as decontextualized text classification, which obscures the central role of prior probability estimation and is reinforced by institutional incentives that favor global, fixed-prior models. We argue that improving coverage for tail languages requires rethinking LID as a routing problem and developing principled ways to incorporate environmental cues that make languages locally plausible.
CommonLID: Re-evaluating State-of-the-Art Language Identification Performance on Web Data
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Language identification (LID) is a fundamental step in curating multilingual corpora. However, LID models still perform poorly for many languages, especially on the noisy and heterogeneous web data often used to train multilingual language models. In this paper, we introduce CommonLID, a community-driven, human-annotated LID benchmark for the web domain, covering 109 languages. Many of the included languages have been previously under-served, making CommonLID a key resource for developing more representative high-quality text corpora. We show CommonLID's value by using it, alongside five other common evaluation sets, to test eight popular LID models. We analyse our results to situate our contribution and to provide an overview of the state of the art. In particular, we highlight that existing evaluations overestimate LID accuracy for many languages in the web domain. We make CommonLID and the code used to create it available under an open, permissive license.
Low-Resource, High-Impact: Building Corpora for Inclusive Language Technologies
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:This tutorial (https://tum-nlp.github.io/low-resource-tutorial) is designed for NLP practitioners, researchers, and developers working with multilingual and low-resource languages who seek to create more equitable and socially impactful language technologies. Participants will walk away with a practical toolkit for building end-to-end NLP pipelines for underrepresented languages -- from data collection and web crawling to parallel sentence mining, machine translation, and downstream applications such as text classification and multimodal reasoning. The tutorial presents strategies for tackling the challenges of data scarcity and cultural variance, offering hands-on methods and modeling frameworks. We will focus on fair, reproducible, and community-informed development approaches, grounded in real-world scenarios. We will showcase a diverse set of use cases covering over 10 languages from different language families and geopolitical contexts, including both digitally resource-rich and severely underrepresented languages.
SciLaD: A Large-Scale, Transparent, Reproducible Dataset for Natural Scientific Language Processing
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:SciLaD is a novel, large-scale dataset of scientific language constructed entirely using open-source frameworks and publicly available data sources. It comprises a curated English split containing over 10 million scientific publications and a multilingual, unfiltered TEI XML split including more than 35 million publications. We also publish the extensible pipeline for generating SciLaD. The dataset construction and processing workflow demonstrates how open-source tools can enable large-scale, scientific data curation while maintaining high data quality. Finally, we pre-train a RoBERTa model on our dataset and evaluate it across a comprehensive set of benchmarks, achieving performance comparable to other scientific language models of similar size, validating the quality and utility of SciLaD. We publish the dataset and evaluation pipeline to promote reproducibility, transparency, and further research in natural scientific language processing and understanding including scholarly document processing.
KréyoLID From Language Identification Towards Language Mining
Mar 09, 2025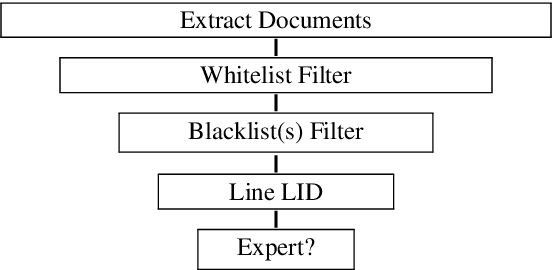
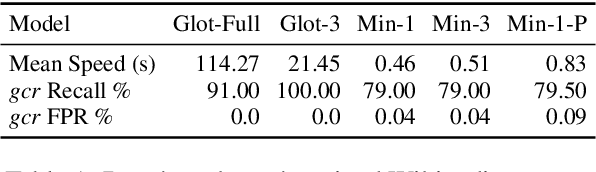
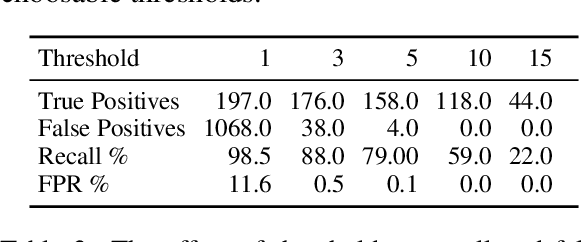
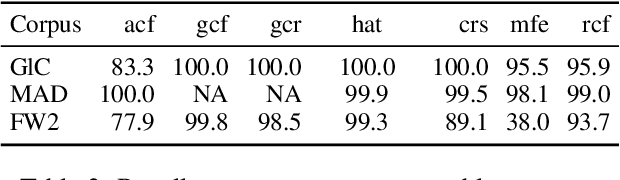
Abstract:Automatic language identification is frequently framed as a multi-class classification problem. However, when creating digital corpora for less commonly written languages, it may be more appropriate to consider it a data mining problem. For these varieties, one knows ahead of time that the vast majority of documents are of little interest. By minimizing resources spent on classifying such documents, we can create corpora much faster and with better coverage than using established pipelines. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the language mining perspective, we introduce a new pipeline and corpora for several French-based Creoles.
Data Processing for the OpenGPT-X Model Family
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive overview of the data preparation pipeline developed for the OpenGPT-X project, a large-scale initiative aimed at creating open and high-performance multilingual large language models (LLMs). The project goal is to deliver models that cover all major European languages, with a particular focus on real-world applications within the European Union. We explain all data processing steps, starting with the data selection and requirement definition to the preparation of the final datasets for model training. We distinguish between curated data and web data, as each of these categories is handled by distinct pipelines, with curated data undergoing minimal filtering and web data requiring extensive filtering and deduplication. This distinction guided the development of specialized algorithmic solutions for both pipelines. In addition to describing the processing methodologies, we provide an in-depth analysis of the datasets, increasing transparency and alignment with European data regulations. Finally, we share key insights and challenges faced during the project, offering recommendations for future endeavors in large-scale multilingual data preparation for LLMs.
Molyé: A Corpus-based Approach to Language Contact in Colonial France
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Whether or not several Creole languages which developed during the early modern period can be considered genetic descendants of European languages has been the subject of intense debate. This is in large part due to the absence of evidence of intermediate forms. This work introduces a new open corpus, the Moly\'e corpus, which combines stereotypical representations of three kinds of language variation in Europe with early attestations of French-based Creole languages across a period of 400 years. It is intended to facilitate future research on the continuity between contact situations in Europe and Creolophone (former) colonies.
mOSCAR: A Large-scale Multilingual and Multimodal Document-level Corpus
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (mLLMs) are trained on a large amount of text-image data. While most mLLMs are trained on caption-like data only, Alayrac et al. [2022] showed that additionally training them on interleaved sequences of text and images can lead to the emergence of in-context learning capabilities. However, the dataset they used, M3W, is not public and is only in English. There have been attempts to reproduce their results but the released datasets are English-only. In contrast, current multilingual and multimodal datasets are either composed of caption-like only or medium-scale or fully private data. This limits mLLM research for the 7,000 other languages spoken in the world. We therefore introduce mOSCAR, to the best of our knowledge the first large-scale multilingual and multimodal document corpus crawled from the web. It covers 163 languages, 315M documents, 214B tokens and 1.2B images. We carefully conduct a set of filtering and evaluation steps to make sure mOSCAR is sufficiently safe, diverse and of good quality. We additionally train two types of multilingual model to prove the benefits of mOSCAR: (1) a model trained on a subset of mOSCAR and captioning data and (2) a model train on captioning data only. The model additionally trained on mOSCAR shows a strong boost in few-shot learning performance across various multilingual image-text tasks and benchmarks, confirming previous findings for English-only mLLMs.
Tokenizer Choice For LLM Training: Negligible or Crucial?
Oct 18, 2023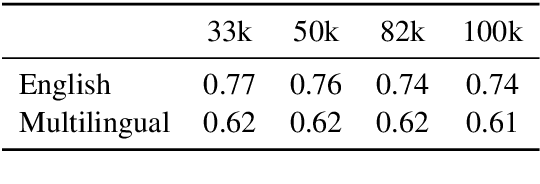
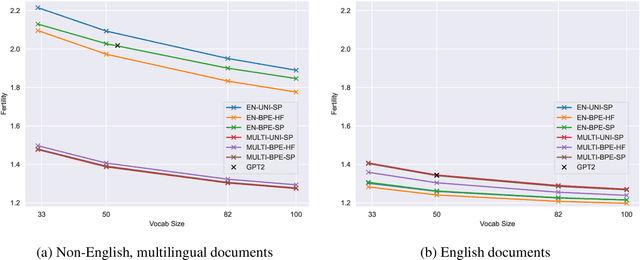
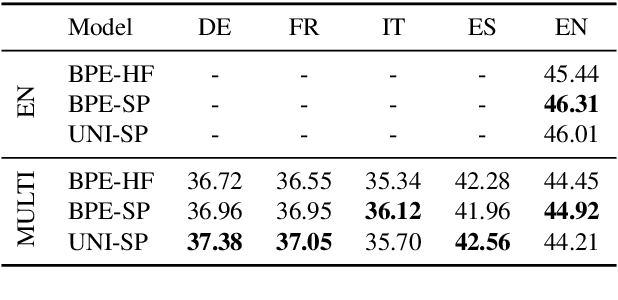
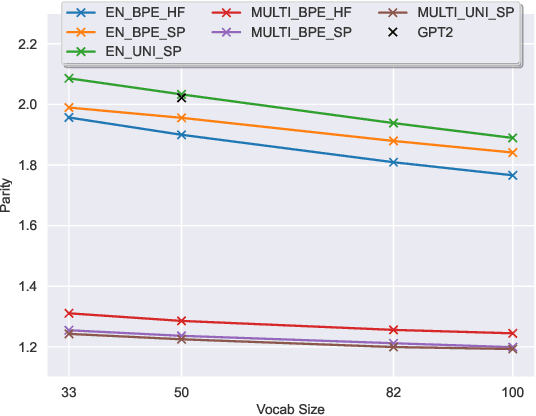
Abstract:The recent success of LLMs has been predominantly driven by curating the training dataset composition, scaling of model architectures and dataset sizes and advancements in pretraining objectives, leaving tokenizer influence as a blind spot. Shedding light on this underexplored area, we conduct a comprehensive study on the influence of tokenizer choice on LLM downstream performance by training 24 mono- and multilingual LLMs at a 2.6B parameter scale, ablating different tokenizer algorithms and parameterizations. Our studies highlight that the tokenizer choice can significantly impact the model's downstream performance, training and inference costs. In particular, we find that the common tokenizer evaluation metrics fertility and parity are not always predictive of model downstream performance, rendering these metrics a questionable proxy for the model's downstream performance. Furthermore, we show that multilingual tokenizers trained on the five most frequent European languages require vocabulary size increases of factor three in comparison to English. While English-only tokenizers have been applied to the training of multi-lingual LLMs, we find that this approach results in a severe downstream performance degradation and additional training costs of up to 68%, due to an inefficient tokenization vocabulary.
Semi-automatic staging area for high-quality structured data extraction from scientific literature
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:In this study, we propose a staging area for ingesting new superconductors' experimental data in SuperCon that is machine-collected from scientific articles. Our objective is to enhance the efficiency of updating SuperCon while maintaining or enhancing the data quality. We present a semi-automatic staging area driven by a workflow combining automatic and manual processes on the extracted database. An anomaly detection automatic process aims to pre-screen the collected data. Users can then manually correct any errors through a user interface tailored to simplify the data verification on the original PDF documents. Additionally, when a record is corrected, its raw data is collected and utilised to improve machine learning models as training data. Evaluation experiments demonstrate that our staging area significantly improves curation quality. We compare the interface with the traditional manual approach of reading PDF documents and recording information in an Excel document. Using the interface boosts the precision and recall by 6% and 50%, respectively to an average increase of 40% in F1-score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge