Pedro Borges
King's College London
DIST-CLIP: Arbitrary Metadata and Image Guided MRI Harmonization via Disentangled Anatomy-Contrast Representations
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Deep learning holds immense promise for transforming medical image analysis, yet its clinical generalization remains profoundly limited. A major barrier is data heterogeneity. This is particularly true in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, where scanner hardware differences, diverse acquisition protocols, and varying sequence parameters introduce substantial domain shifts that obscure underlying biological signals. Data harmonization methods aim to reduce these instrumental and acquisition variability, but existing approaches remain insufficient. When applied to imaging data, image-based harmonization approaches are often restricted by the need for target images, while existing text-guided methods rely on simplistic labels that fail to capture complex acquisition details or are typically restricted to datasets with limited variability, failing to capture the heterogeneity of real-world clinical environments. To address these limitations, we propose DIST-CLIP (Disentangled Style Transfer with CLIP Guidance), a unified framework for MRI harmonization that flexibly uses either target images or DICOM metadata for guidance. Our framework explicitly disentangles anatomical content from image contrast, with the contrast representations being extracted using pre-trained CLIP encoders. These contrast embeddings are then integrated into the anatomical content via a novel Adaptive Style Transfer module. We trained and evaluated DIST-CLIP on diverse real-world clinical datasets, and showed significant improvements in performance when compared against state-of-the-art methods in both style translation fidelity and anatomical preservation, offering a flexible solution for style transfer and standardizing MRI data. Our code and weights will be made publicly available upon publication.
Dynamic causal discovery in Alzheimer's disease through latent pseudotime modelling
Nov 06, 2025



Abstract:The application of causal discovery to diseases like Alzheimer's (AD) is limited by the static graph assumptions of most methods; such models cannot account for an evolving pathophysiology, modulated by a latent disease pseudotime. We propose to apply an existing latent variable model to real-world AD data, inferring a pseudotime that orders patients along a data-driven disease trajectory independent of chronological age, then learning how causal relationships evolve. Pseudotime outperformed age in predicting diagnosis (AUC 0.82 vs 0.59). Incorporating minimal, disease-agnostic background knowledge substantially improved graph accuracy and orientation. Our framework reveals dynamic interactions between novel (NfL, GFAP) and established AD markers, enabling practical causal discovery despite violated assumptions.
A methodology for clinically driven interactive segmentation evaluation
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Interactive segmentation is a promising strategy for building robust, generalisable algorithms for volumetric medical image segmentation. However, inconsistent and clinically unrealistic evaluation hinders fair comparison and misrepresents real-world performance. We propose a clinically grounded methodology for defining evaluation tasks and metrics, and built a software framework for constructing standardised evaluation pipelines. We evaluate state-of-the-art algorithms across heterogeneous and complex tasks and observe that (i) minimising information loss when processing user interactions is critical for model robustness, (ii) adaptive-zooming mechanisms boost robustness and speed convergence, (iii) performance drops if validation prompting behaviour/budgets differ from training, (iv) 2D methods perform well with slab-like images and coarse targets, but 3D context helps with large or irregularly shaped targets, (v) performance of non-medical-domain models (e.g. SAM2) degrades with poor contrast and complex shapes.
Deep generative computed perfusion-deficit mapping of ischaemic stroke
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Focal deficits in ischaemic stroke result from impaired perfusion downstream of a critical vascular occlusion. While parenchymal lesions are traditionally used to predict clinical deficits, the underlying pattern of disrupted perfusion provides information upstream of the lesion, potentially yielding earlier predictive and localizing signals. Such perfusion maps can be derived from routine CT angiography (CTA) widely deployed in clinical practice. Analysing computed perfusion maps from 1,393 CTA-imaged-patients with acute ischaemic stroke, we use deep generative inference to localise neural substrates of NIHSS sub-scores. We show that our approach replicates known lesion-deficit relations without knowledge of the lesion itself and reveals novel neural dependents. The high achieved anatomical fidelity suggests acute CTA-derived computed perfusion maps may be of substantial clinical-and-scientific value in rich phenotyping of acute stroke. Using only hyperacute imaging, deep generative inference could power highly expressive models of functional anatomical relations in ischaemic stroke within the pre-interventional window.
Framework to generate perfusion map from CT and CTA images in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A longitudinal and cross-sectional study
Apr 05, 2024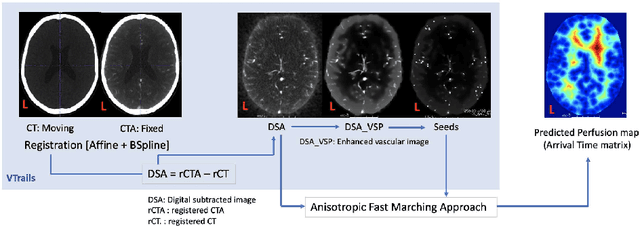
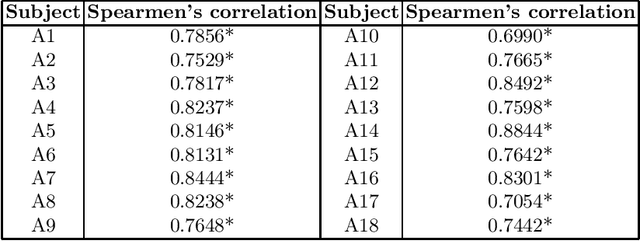
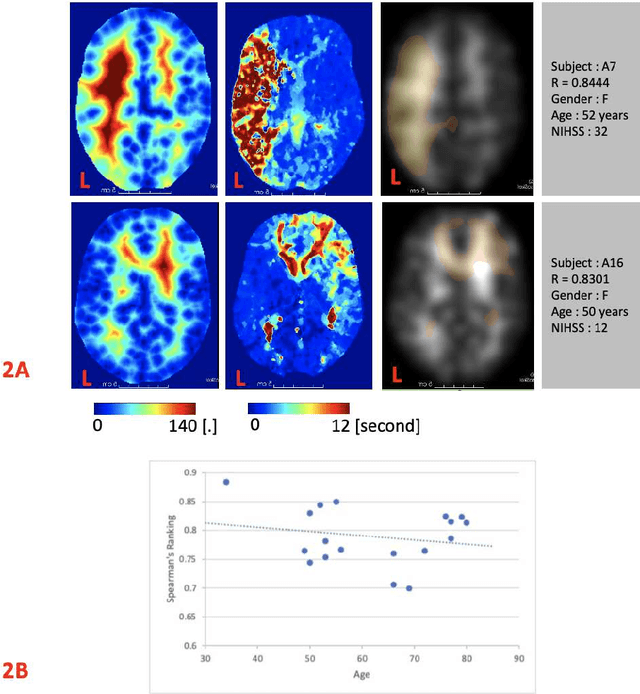
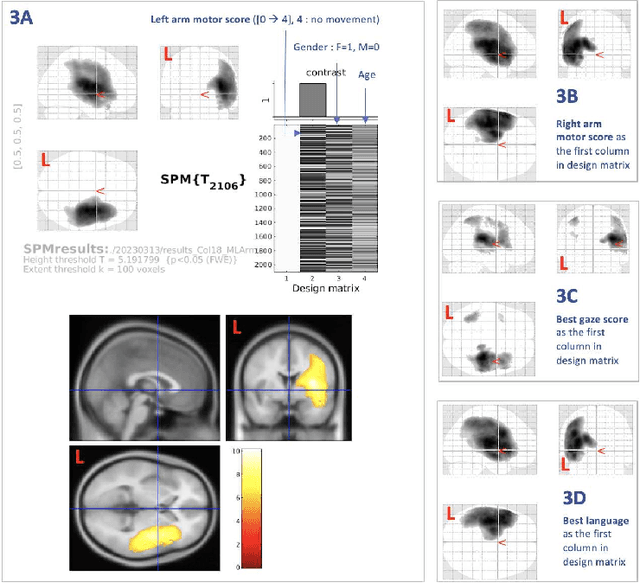
Abstract:Stroke is a leading cause of disability and death. Effective treatment decisions require early and informative vascular imaging. 4D perfusion imaging is ideal but rarely available within the first hour after stroke, whereas plain CT and CTA usually are. Hence, we propose a framework to extract a predicted perfusion map (PPM) derived from CT and CTA images. In all eighteen patients, we found significantly high spatial similarity (with average Spearman's correlation = 0.7893) between our predicted perfusion map (PPM) and the T-max map derived from 4D-CTP. Voxelwise correlations between the PPM and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) subscores for L/R hand motor, gaze, and language on a large cohort of 2,110 subjects reliably mapped symptoms to expected infarct locations. Therefore our PPM could serve as an alternative for 4D perfusion imaging, if the latter is unavailable, to investigate blood perfusion in the first hours after hospital admission.
A 3D generative model of pathological multi-modal MR images and segmentations
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:Generative modelling and synthetic data can be a surrogate for real medical imaging datasets, whose scarcity and difficulty to share can be a nuisance when delivering accurate deep learning models for healthcare applications. In recent years, there has been an increased interest in using these models for data augmentation and synthetic data sharing, using architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) or diffusion models (DMs). Nonetheless, the application of synthetic data to tasks such as 3D magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) segmentation remains limited due to the lack of labels associated with the generated images. Moreover, many of the proposed generative MRI models lack the ability to generate arbitrary modalities due to the absence of explicit contrast conditioning. These limitations prevent the user from adjusting the contrast and content of the images and obtaining more generalisable data for training task-specific models. In this work, we propose brainSPADE3D, a 3D generative model for brain MRI and associated segmentations, where the user can condition on specific pathological phenotypes and contrasts. The proposed joint imaging-segmentation generative model is shown to generate high-fidelity synthetic images and associated segmentations, with the ability to combine pathologies. We demonstrate how the model can alleviate issues with segmentation model performance when unexpected pathologies are present in the data.
Can segmentation models be trained with fully synthetically generated data?
Sep 17, 2022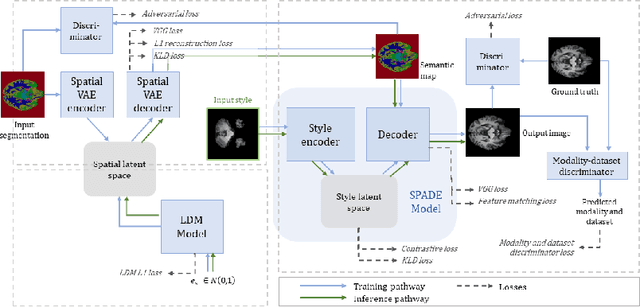
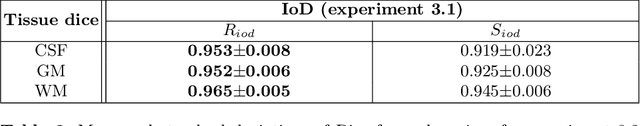
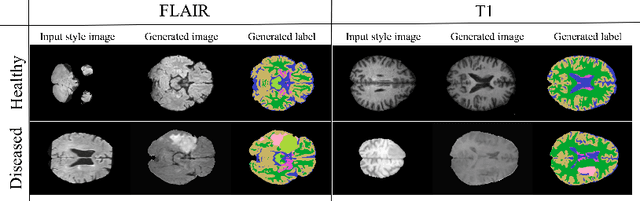
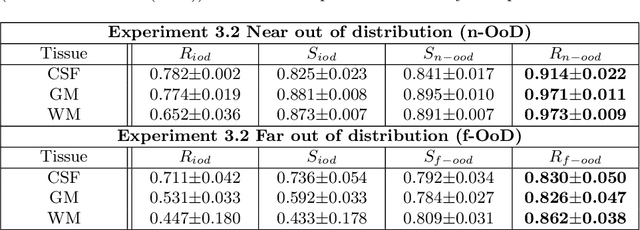
Abstract:In order to achieve good performance and generalisability, medical image segmentation models should be trained on sizeable datasets with sufficient variability. Due to ethics and governance restrictions, and the costs associated with labelling data, scientific development is often stifled, with models trained and tested on limited data. Data augmentation is often used to artificially increase the variability in the data distribution and improve model generalisability. Recent works have explored deep generative models for image synthesis, as such an approach would enable the generation of an effectively infinite amount of varied data, addressing the generalisability and data access problems. However, many proposed solutions limit the user's control over what is generated. In this work, we propose brainSPADE, a model which combines a synthetic diffusion-based label generator with a semantic image generator. Our model can produce fully synthetic brain labels on-demand, with or without pathology of interest, and then generate a corresponding MRI image of an arbitrary guided style. Experiments show that brainSPADE synthetic data can be used to train segmentation models with performance comparable to that of models trained on real data.
Morphology-preserving Autoregressive 3D Generative Modelling of the Brain
Sep 07, 2022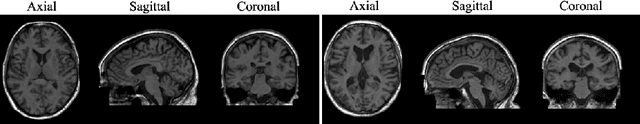
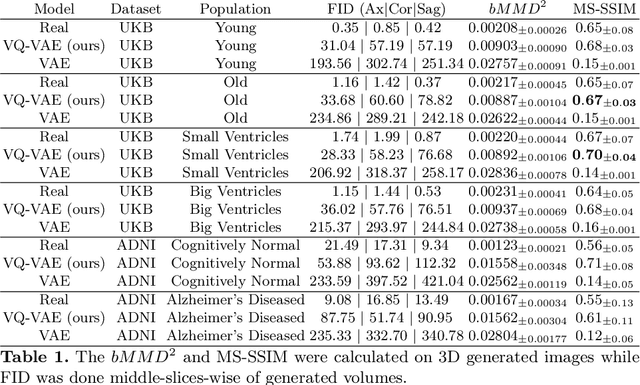
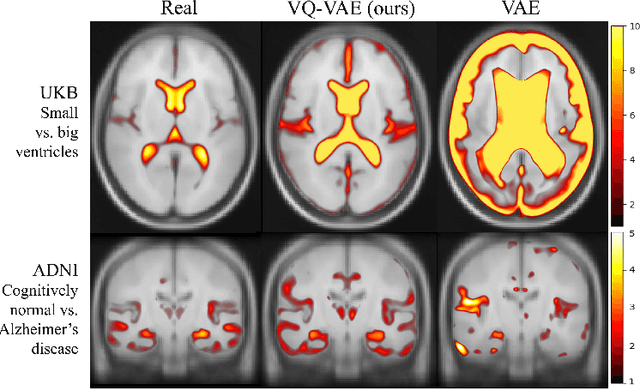
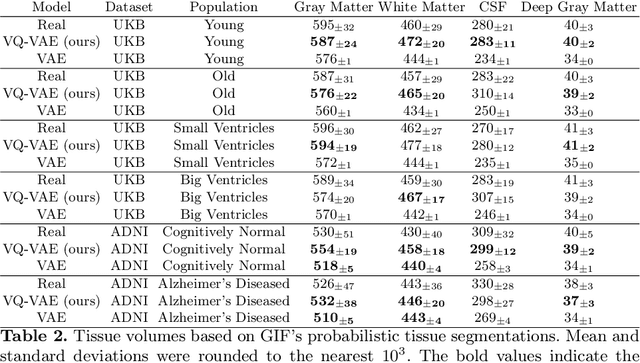
Abstract:Human anatomy, morphology, and associated diseases can be studied using medical imaging data. However, access to medical imaging data is restricted by governance and privacy concerns, data ownership, and the cost of acquisition, thus limiting our ability to understand the human body. A possible solution to this issue is the creation of a model able to learn and then generate synthetic images of the human body conditioned on specific characteristics of relevance (e.g., age, sex, and disease status). Deep generative models, in the form of neural networks, have been recently used to create synthetic 2D images of natural scenes. Still, the ability to produce high-resolution 3D volumetric imaging data with correct anatomical morphology has been hampered by data scarcity and algorithmic and computational limitations. This work proposes a generative model that can be scaled to produce anatomically correct, high-resolution, and realistic images of the human brain, with the necessary quality to allow further downstream analyses. The ability to generate a potentially unlimited amount of data not only enables large-scale studies of human anatomy and pathology without jeopardizing patient privacy, but also significantly advances research in the field of anomaly detection, modality synthesis, learning under limited data, and fair and ethical AI. Code and trained models are available at: https://github.com/AmigoLab/SynthAnatomy.
Acquisition-invariant brain MRI segmentation with informative uncertainties
Nov 07, 2021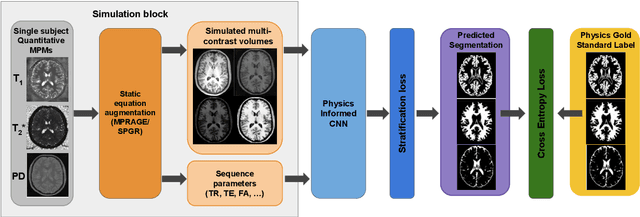
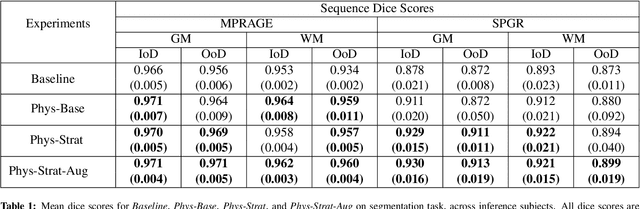
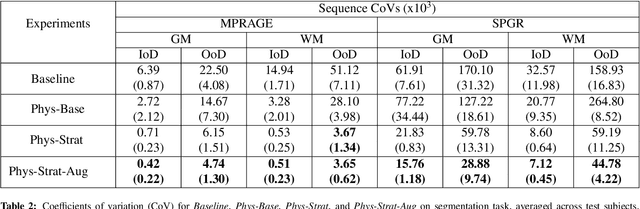
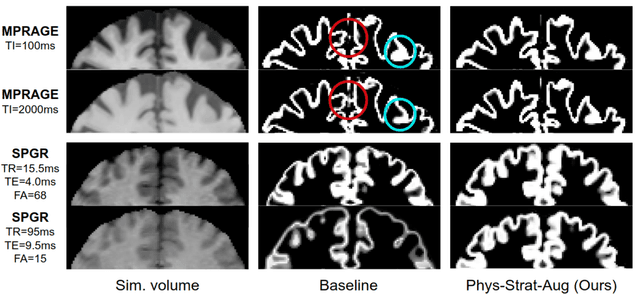
Abstract:Combining multi-site data can strengthen and uncover trends, but is a task that is marred by the influence of site-specific covariates that can bias the data and therefore any downstream analyses. Post-hoc multi-site correction methods exist but have strong assumptions that often do not hold in real-world scenarios. Algorithms should be designed in a way that can account for site-specific effects, such as those that arise from sequence parameter choices, and in instances where generalisation fails, should be able to identify such a failure by means of explicit uncertainty modelling. This body of work showcases such an algorithm, that can become robust to the physics of acquisition in the context of segmentation tasks, while simultaneously modelling uncertainty. We demonstrate that our method not only generalises to complete holdout datasets, preserving segmentation quality, but does so while also accounting for site-specific sequence choices, which also allows it to perform as a harmonisation tool.
The role of MRI physics in brain segmentation CNNs: achieving acquisition invariance and instructive uncertainties
Nov 04, 2021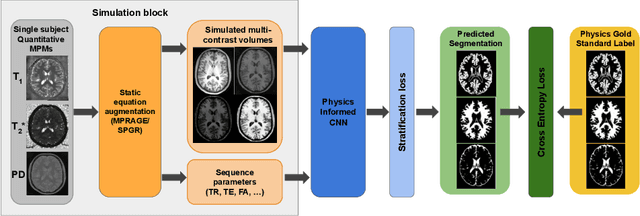
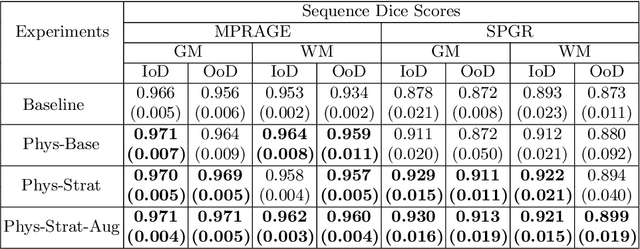
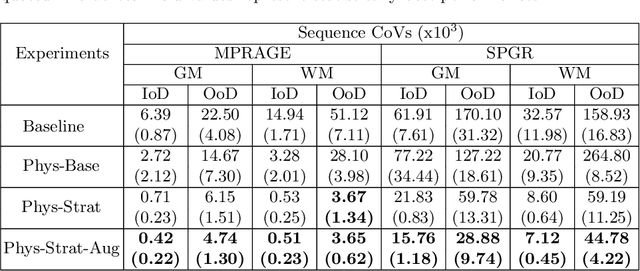
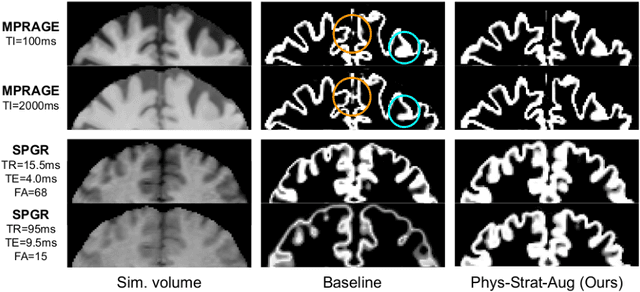
Abstract:Being able to adequately process and combine data arising from different sites is crucial in neuroimaging, but is difficult, owing to site, sequence and acquisition-parameter dependent biases. It is important therefore to design algorithms that are not only robust to images of differing contrasts, but also be able to generalise well to unseen ones, with a quantifiable measure of uncertainty. In this paper we demonstrate the efficacy of a physics-informed, uncertainty-aware, segmentation network that employs augmentation-time MR simulations and homogeneous batch feature stratification to achieve acquisition invariance. We show that the proposed approach also accurately extrapolates to out-of-distribution sequence samples, providing well calibrated volumetric bounds on these. We demonstrate a significant improvement in terms of coefficients of variation, backed by uncertainty based volumetric validation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge