Mugariya Farooq
Falcon-H1: A Family of Hybrid-Head Language Models Redefining Efficiency and Performance
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce Falcon-H1, a new series of large language models (LLMs) featuring hybrid architecture designs optimized for both high performance and efficiency across diverse use cases. Unlike earlier Falcon models built solely on Transformer or Mamba architectures, Falcon-H1 adopts a parallel hybrid approach that combines Transformer-based attention with State Space Models (SSMs), known for superior long-context memory and computational efficiency. We systematically revisited model design, data strategy, and training dynamics, challenging conventional practices in the field. Falcon-H1 is released in multiple configurations, including base and instruction-tuned variants at 0.5B, 1.5B, 1.5B-deep, 3B, 7B, and 34B parameters. Quantized instruction-tuned models are also available, totaling over 30 checkpoints on Hugging Face Hub. Falcon-H1 models demonstrate state-of-the-art performance and exceptional parameter and training efficiency. The flagship Falcon-H1-34B matches or outperforms models up to 70B scale, such as Qwen3-32B, Qwen2.5-72B, and Llama3.3-70B, while using fewer parameters and less data. Smaller models show similar trends: the Falcon-H1-1.5B-Deep rivals current leading 7B-10B models, and Falcon-H1-0.5B performs comparably to typical 7B models from 2024. These models excel across reasoning, mathematics, multilingual tasks, instruction following, and scientific knowledge. With support for up to 256K context tokens and 18 languages, Falcon-H1 is suitable for a wide range of applications. All models are released under a permissive open-source license, underscoring our commitment to accessible and impactful AI research.
NeurIPS 2025 E2LM Competition : Early Training Evaluation of Language Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Existing benchmarks have proven effective for assessing the performance of fully trained large language models. However, we find striking differences in the early training stages of small models, where benchmarks often fail to provide meaningful or discriminative signals. To explore how these differences arise, this competition tackles the challenge of designing scientific knowledge evaluation tasks specifically tailored for measuring early training progress of language models. Participants are invited to develop novel evaluation methodologies or adapt existing benchmarks to better capture performance differences among language models. To support this effort, we provide three pre-trained small models (0.5B, 1B, and 3B parameters), along with intermediate checkpoints sampled during training up to 200B tokens. All experiments and development work can be run on widely available free cloud-based GPU platforms, making participation accessible to researchers with limited computational resources. Submissions will be evaluated based on three criteria: the quality of the performance signal they produce, the consistency of model rankings at 1 trillion tokens of training, and their relevance to the scientific knowledge domain. By promoting the design of tailored evaluation strategies for early training, this competition aims to attract a broad range of participants from various disciplines, including those who may not be machine learning experts or have access to dedicated GPU resources. Ultimately, this initiative seeks to make foundational LLM research more systematic and benchmark-informed from the earliest phases of model development.
Alignment with Preference Optimization Is All You Need for LLM Safety
Sep 12, 2024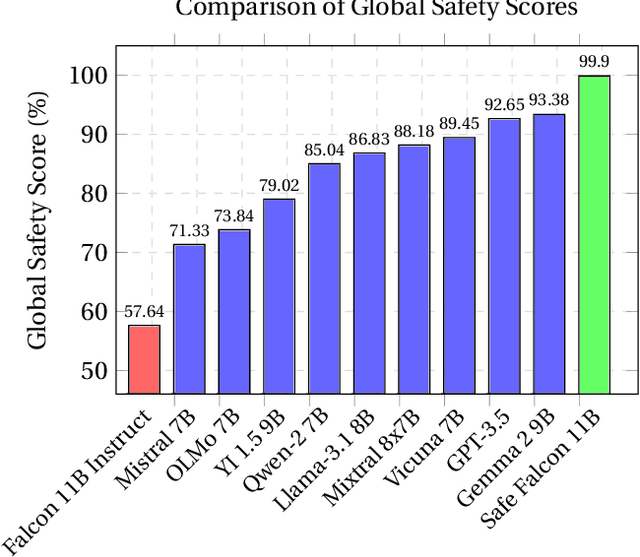
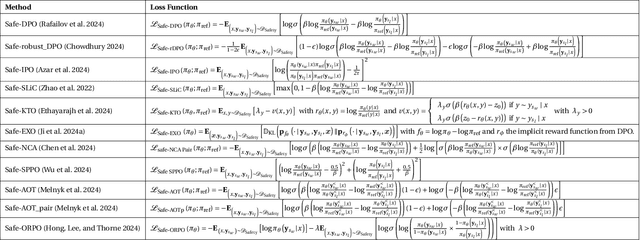
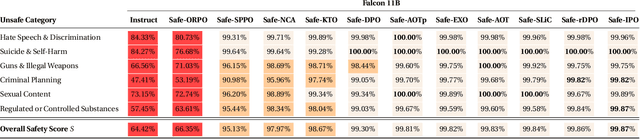
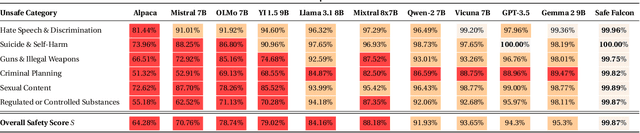
Abstract:We demonstrate that preference optimization methods can effectively enhance LLM safety. Applying various alignment techniques to the Falcon 11B model using safety datasets, we achieve a significant boost in global safety score (from $57.64\%$ to $99.90\%$) as measured by LlamaGuard 3 8B, competing with state-of-the-art models. On toxicity benchmarks, average scores in adversarial settings dropped from over $0.6$ to less than $0.07$. However, this safety improvement comes at the cost of reduced general capabilities, particularly in math, suggesting a trade-off. We identify noise contrastive alignment (Safe-NCA) as an optimal method for balancing safety and performance. Our study ultimately shows that alignment techniques can be sufficient for building safe and robust models.
Falcon2-11B Technical Report
Jul 20, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Falcon2-11B, a foundation model trained on over five trillion tokens, and its multimodal counterpart, Falcon2-11B-vlm, which is a vision-to-text model. We report our findings during the training of the Falcon2-11B which follows a multi-stage approach where the early stages are distinguished by their context length and a final stage where we use a curated, high-quality dataset. Additionally, we report the effect of doubling the batch size mid-training and how training loss spikes are affected by the learning rate. The downstream performance of the foundation model is evaluated on established benchmarks, including multilingual and code datasets. The foundation model shows strong generalization across all the tasks which makes it suitable for downstream finetuning use cases. For the vision language model, we report the performance on several benchmarks and show that our model achieves a higher average score compared to open-source models of similar size. The model weights and code of both Falcon2-11B and Falcon2-11B-vlm are made available under a permissive license.
Understanding Breast Cancer Survival: Using Causality and Language Models on Multi-omics Data
May 28, 2023



Abstract:The need for more usable and explainable machine learning models in healthcare increases the importance of developing and utilizing causal discovery algorithms, which aim to discover causal relations by analyzing observational data. Explainable approaches aid clinicians and biologists in predicting the prognosis of diseases and suggesting proper treatments. However, very little research has been conducted at the crossroads between causal discovery, genomics, and breast cancer, and we aim to bridge this gap. Moreover, evaluation of causal discovery methods on real data is in general notoriously difficult because ground-truth causal relations are usually unknown, and accordingly, in this paper, we also propose to address the evaluation problem with large language models. In particular, we exploit suitable causal discovery algorithms to investigate how various perturbations in the genome can affect the survival of patients diagnosed with breast cancer. We used three main causal discovery algorithms: PC, Greedy Equivalence Search (GES), and a Generalized Precision Matrix-based one. We experiment with a subset of The Cancer Genome Atlas, which contains information about mutations, copy number variations, protein levels, and gene expressions for 705 breast cancer patients. Our findings reveal important factors related to the vital status of patients using causal discovery algorithms. However, the reliability of these results remains a concern in the medical domain. Accordingly, as another contribution of the work, the results are validated through language models trained on biomedical literature, such as BlueBERT and other large language models trained on medical corpora. Our results profess proper utilization of causal discovery algorithms and language models for revealing reliable causal relations for clinical applications.
Surgical tool classification and localization: results and methods from the MICCAI 2022 SurgToolLoc challenge
May 11, 2023



Abstract:The ability to automatically detect and track surgical instruments in endoscopic videos can enable transformational interventions. Assessing surgical performance and efficiency, identifying skilled tool use and choreography, and planning operational and logistical aspects of OR resources are just a few of the applications that could benefit. Unfortunately, obtaining the annotations needed to train machine learning models to identify and localize surgical tools is a difficult task. Annotating bounding boxes frame-by-frame is tedious and time-consuming, yet large amounts of data with a wide variety of surgical tools and surgeries must be captured for robust training. Moreover, ongoing annotator training is needed to stay up to date with surgical instrument innovation. In robotic-assisted surgery, however, potentially informative data like timestamps of instrument installation and removal can be programmatically harvested. The ability to rely on tool installation data alone would significantly reduce the workload to train robust tool-tracking models. With this motivation in mind we invited the surgical data science community to participate in the challenge, SurgToolLoc 2022. The goal was to leverage tool presence data as weak labels for machine learning models trained to detect tools and localize them in video frames with bounding boxes. We present the results of this challenge along with many of the team's efforts. We conclude by discussing these results in the broader context of machine learning and surgical data science. The training data used for this challenge consisting of 24,695 video clips with tool presence labels is also being released publicly and can be accessed at https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser/isi-surgtoolloc-2022.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge