Alignment with Preference Optimization Is All You Need for LLM Safety
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2024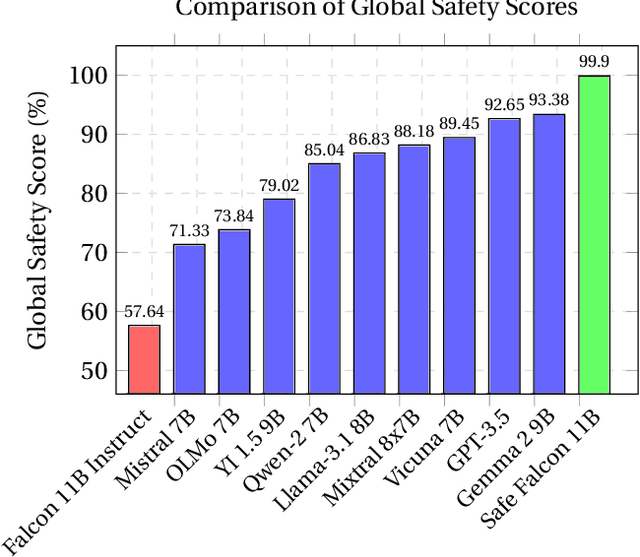
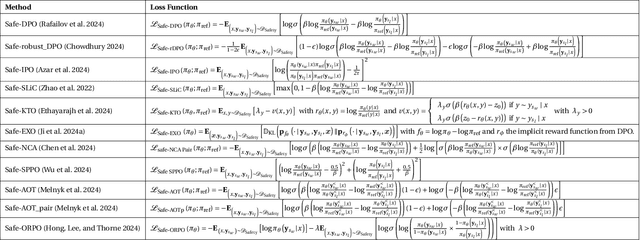
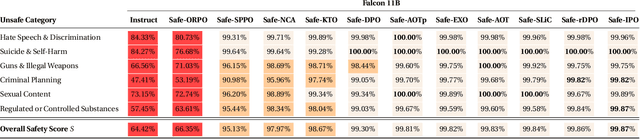
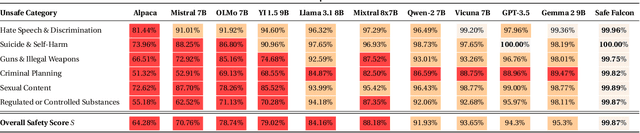
We demonstrate that preference optimization methods can effectively enhance LLM safety. Applying various alignment techniques to the Falcon 11B model using safety datasets, we achieve a significant boost in global safety score (from $57.64\%$ to $99.90\%$) as measured by LlamaGuard 3 8B, competing with state-of-the-art models. On toxicity benchmarks, average scores in adversarial settings dropped from over $0.6$ to less than $0.07$. However, this safety improvement comes at the cost of reduced general capabilities, particularly in math, suggesting a trade-off. We identify noise contrastive alignment (Safe-NCA) as an optimal method for balancing safety and performance. Our study ultimately shows that alignment techniques can be sufficient for building safe and robust models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge