Mohamed Elgharib
Max Planck Institute for Informatics, Saarland Informatics Campus
EventNeuS: 3D Mesh Reconstruction from a Single Event Camera
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Event cameras offer a considerable alternative to RGB cameras in many scenarios. While there are recent works on event-based novel-view synthesis, dense 3D mesh reconstruction remains scarcely explored and existing event-based techniques are severely limited in their 3D reconstruction accuracy. To address this limitation, we present EventNeuS, a self-supervised neural model for learning 3D representations from monocular colour event streams. Our approach, for the first time, combines 3D signed distance function and density field learning with event-based supervision. Furthermore, we introduce spherical harmonics encodings into our model for enhanced handling of view-dependent effects. EventNeuS outperforms existing approaches by a significant margin, achieving 34% lower Chamfer distance and 31% lower mean absolute error on average compared to the best previous method.
* 13 pages, 10 figures, 3 tables; project page: https://4dqv.mpi-inf.mpg.de/EventNeuS/
Dynamic EventNeRF: Reconstructing General Dynamic Scenes from Multi-view Event Cameras
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:Volumetric reconstruction of dynamic scenes is an important problem in computer vision. It is especially challenging in poor lighting and with fast motion. It is partly due to the limitations of RGB cameras: To capture fast motion without much blur, the framerate must be increased, which in turn requires more lighting. In contrast, event cameras, which record changes in pixel brightness asynchronously, are much less dependent on lighting, making them more suitable for recording fast motion. We hence propose the first method to spatiotemporally reconstruct a scene from sparse multi-view event streams and sparse RGB frames. We train a sequence of cross-faded time-conditioned NeRF models, one per short recording segment. The individual segments are supervised with a set of event- and RGB-based losses and sparse-view regularisation. We assemble a real-world multi-view camera rig with six static event cameras around the object and record a benchmark multi-view event stream dataset of challenging motions. Our work outperforms RGB-based baselines, producing state-of-the-art results, and opens up the topic of multi-view event-based reconstruction as a new path for fast scene capture beyond RGB cameras. The code and the data will be released soon at https://4dqv.mpi-inf.mpg.de/DynEventNeRF/
GaussianHeads: End-to-End Learning of Drivable Gaussian Head Avatars from Coarse-to-fine Representations
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:Real-time rendering of human head avatars is a cornerstone of many computer graphics applications, such as augmented reality, video games, and films, to name a few. Recent approaches address this challenge with computationally efficient geometry primitives in a carefully calibrated multi-view setup. Albeit producing photorealistic head renderings, it often fails to represent complex motion changes such as the mouth interior and strongly varying head poses. We propose a new method to generate highly dynamic and deformable human head avatars from multi-view imagery in real-time. At the core of our method is a hierarchical representation of head models that allows to capture the complex dynamics of facial expressions and head movements. First, with rich facial features extracted from raw input frames, we learn to deform the coarse facial geometry of the template mesh. We then initialize 3D Gaussians on the deformed surface and refine their positions in a fine step. We train this coarse-to-fine facial avatar model along with the head pose as a learnable parameter in an end-to-end framework. This enables not only controllable facial animation via video inputs, but also high-fidelity novel view synthesis of challenging facial expressions, such as tongue deformations and fine-grained teeth structure under large motion changes. Moreover, it encourages the learned head avatar to generalize towards new facial expressions and head poses at inference time. We demonstrate the performance of our method with comparisons against the related methods on different datasets, spanning challenging facial expression sequences across multiple identities. We also show the potential application of our approach by demonstrating a cross-identity facial performance transfer application.
Lite2Relight: 3D-aware Single Image Portrait Relighting
Jul 15, 2024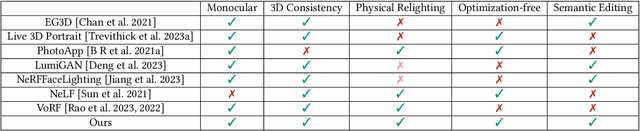
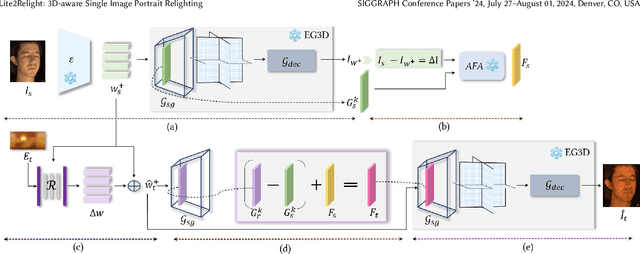
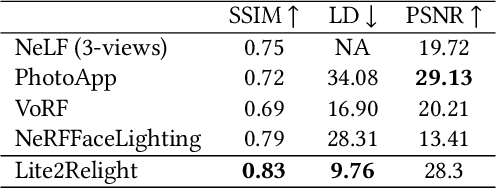

Abstract:Achieving photorealistic 3D view synthesis and relighting of human portraits is pivotal for advancing AR/VR applications. Existing methodologies in portrait relighting demonstrate substantial limitations in terms of generalization and 3D consistency, coupled with inaccuracies in physically realistic lighting and identity preservation. Furthermore, personalization from a single view is difficult to achieve and often requires multiview images during the testing phase or involves slow optimization processes. This paper introduces Lite2Relight, a novel technique that can predict 3D consistent head poses of portraits while performing physically plausible light editing at interactive speed. Our method uniquely extends the generative capabilities and efficient volumetric representation of EG3D, leveraging a lightstage dataset to implicitly disentangle face reflectance and perform relighting under target HDRI environment maps. By utilizing a pre-trained geometry-aware encoder and a feature alignment module, we map input images into a relightable 3D space, enhancing them with a strong face geometry and reflectance prior. Through extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations, we show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of efficacy, photorealism, and practical application. This includes producing 3D-consistent results of the full head, including hair, eyes, and expressions. Lite2Relight paves the way for large-scale adoption of photorealistic portrait editing in various domains, offering a robust, interactive solution to a previously constrained problem. Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/Lite2Relight/
Live2Diff: Live Stream Translation via Uni-directional Attention in Video Diffusion Models
Jul 11, 2024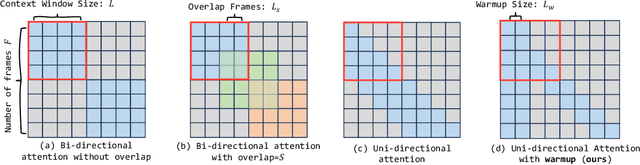
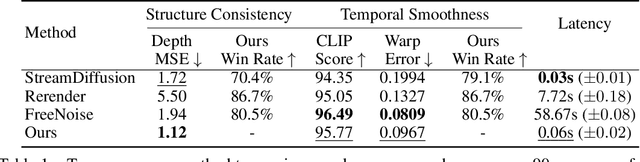
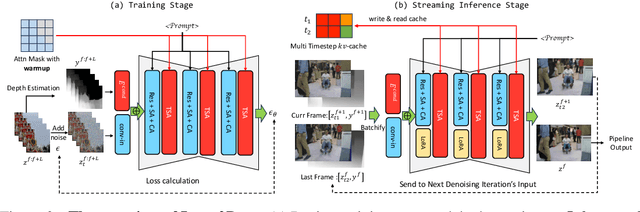
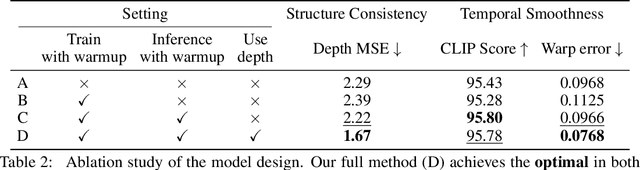
Abstract:Large Language Models have shown remarkable efficacy in generating streaming data such as text and audio, thanks to their temporally uni-directional attention mechanism, which models correlations between the current token and previous tokens. However, video streaming remains much less explored, despite a growing need for live video processing. State-of-the-art video diffusion models leverage bi-directional temporal attention to model the correlations between the current frame and all the surrounding (i.e. including future) frames, which hinders them from processing streaming videos. To address this problem, we present Live2Diff, the first attempt at designing a video diffusion model with uni-directional temporal attention, specifically targeting live streaming video translation. Compared to previous works, our approach ensures temporal consistency and smoothness by correlating the current frame with its predecessors and a few initial warmup frames, without any future frames. Additionally, we use a highly efficient denoising scheme featuring a KV-cache mechanism and pipelining, to facilitate streaming video translation at interactive framerates. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed attention mechanism and pipeline, outperforming previous methods in terms of temporal smoothness and/or efficiency.
AvatarStudio: Text-driven Editing of 3D Dynamic Human Head Avatars
Jun 02, 2023
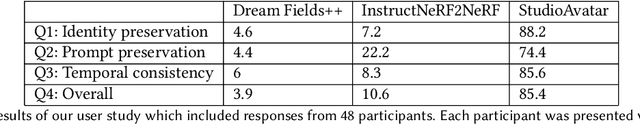
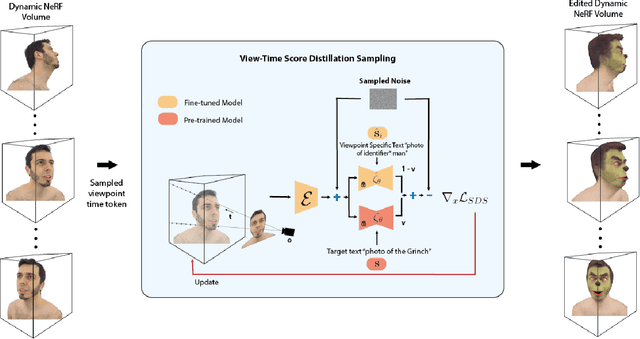
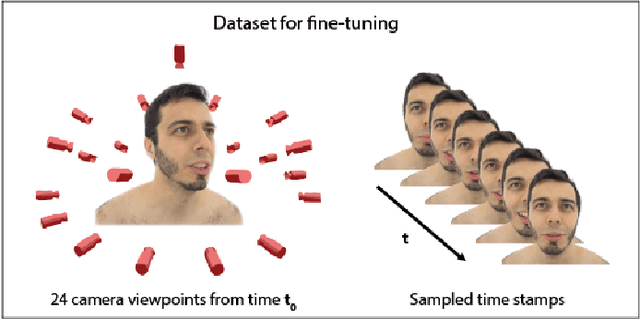
Abstract:Capturing and editing full head performances enables the creation of virtual characters with various applications such as extended reality and media production. The past few years witnessed a steep rise in the photorealism of human head avatars. Such avatars can be controlled through different input data modalities, including RGB, audio, depth, IMUs and others. While these data modalities provide effective means of control, they mostly focus on editing the head movements such as the facial expressions, head pose and/or camera viewpoint. In this paper, we propose AvatarStudio, a text-based method for editing the appearance of a dynamic full head avatar. Our approach builds on existing work to capture dynamic performances of human heads using neural radiance field (NeRF) and edits this representation with a text-to-image diffusion model. Specifically, we introduce an optimization strategy for incorporating multiple keyframes representing different camera viewpoints and time stamps of a video performance into a single diffusion model. Using this personalized diffusion model, we edit the dynamic NeRF by introducing view-and-time-aware Score Distillation Sampling (VT-SDS) following a model-based guidance approach. Our method edits the full head in a canonical space, and then propagates these edits to remaining time steps via a pretrained deformation network. We evaluate our method visually and numerically via a user study, and results show that our method outperforms existing approaches. Our experiments validate the design choices of our method and highlight that our edits are genuine, personalized, as well as 3D- and time-consistent.
GVP: Generative Volumetric Primitives
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:Advances in 3D-aware generative models have pushed the boundary of image synthesis with explicit camera control. To achieve high-resolution image synthesis, several attempts have been made to design efficient generators, such as hybrid architectures with both 3D and 2D components. However, such a design compromises multiview consistency, and the design of a pure 3D generator with high resolution is still an open problem. In this work, we present Generative Volumetric Primitives (GVP), the first pure 3D generative model that can sample and render 512-resolution images in real-time. GVP jointly models a number of volumetric primitives and their spatial information, both of which can be efficiently generated via a 2D convolutional network. The mixture of these primitives naturally captures the sparsity and correspondence in the 3D volume. The training of such a generator with a high degree of freedom is made possible through a knowledge distillation technique. Experiments on several datasets demonstrate superior efficiency and 3D consistency of GVP over the state-of-the-art.
HQ3DAvatar: High Quality Controllable 3D Head Avatar
Mar 25, 2023Abstract:Multi-view volumetric rendering techniques have recently shown great potential in modeling and synthesizing high-quality head avatars. A common approach to capture full head dynamic performances is to track the underlying geometry using a mesh-based template or 3D cube-based graphics primitives. While these model-based approaches achieve promising results, they often fail to learn complex geometric details such as the mouth interior, hair, and topological changes over time. This paper presents a novel approach to building highly photorealistic digital head avatars. Our method learns a canonical space via an implicit function parameterized by a neural network. It leverages multiresolution hash encoding in the learned feature space, allowing for high-quality, faster training and high-resolution rendering. At test time, our method is driven by a monocular RGB video. Here, an image encoder extracts face-specific features that also condition the learnable canonical space. This encourages deformation-dependent texture variations during training. We also propose a novel optical flow based loss that ensures correspondences in the learned canonical space, thus encouraging artifact-free and temporally consistent renderings. We show results on challenging facial expressions and show free-viewpoint renderings at interactive real-time rates for medium image resolutions. Our method outperforms all existing approaches, both visually and numerically. We will release our multiple-identity dataset to encourage further research. Our Project page is available at: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/HQ3DAvatar/
An Implicit Parametric Morphable Dental Model
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:3D Morphable models of the human body capture variations among subjects and are useful in reconstruction and editing applications. Current dental models use an explicit mesh scene representation and model only the teeth, ignoring the gum. In this work, we present the first parametric 3D morphable dental model for both teeth and gum. Our model uses an implicit scene representation and is learned from rigidly aligned scans. It is based on a component-wise representation for each tooth and the gum, together with a learnable latent code for each of such components. It also learns a template shape thus enabling several applications such as segmentation, interpolation, and tooth replacement. Our reconstruction quality is on par with the most advanced global implicit representations while enabling novel applications. Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DMM/
gCoRF: Generative Compositional Radiance Fields
Oct 31, 2022Abstract:3D generative models of objects enable photorealistic image synthesis with 3D control. Existing methods model the scene as a global scene representation, ignoring the compositional aspect of the scene. Compositional reasoning can enable a wide variety of editing applications, in addition to enabling generalizable 3D reasoning. In this paper, we present a compositional generative model, where each semantic part of the object is represented as an independent 3D representation learned from only in-the-wild 2D data. We start with a global generative model (GAN) and learn to decompose it into different semantic parts using supervision from 2D segmentation masks. We then learn to composite independently sampled parts in order to create coherent global scenes. Different parts can be independently sampled while keeping the rest of the object fixed. We evaluate our method on a wide variety of objects and parts and demonstrate editing applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge