Min Gu
Oral Imaging for Malocclusion Issues Assessments: OMNI Dataset, Deep Learning Baselines and Benchmarking
May 21, 2025Abstract:Malocclusion is a major challenge in orthodontics, and its complex presentation and diverse clinical manifestations make accurate localization and diagnosis particularly important. Currently, one of the major shortcomings facing the field of dental image analysis is the lack of large-scale, accurately labeled datasets dedicated to malocclusion issues, which limits the development of automated diagnostics in the field of dentistry and leads to a lack of diagnostic accuracy and efficiency in clinical practice. Therefore, in this study, we propose the Oral and Maxillofacial Natural Images (OMNI) dataset, a novel and comprehensive dental image dataset aimed at advancing the study of analyzing dental images for issues of malocclusion. Specifically, the dataset contains 4166 multi-view images with 384 participants in data collection and annotated by professional dentists. In addition, we performed a comprehensive validation of the created OMNI dataset, including three CNN-based methods, two Transformer-based methods, and one GNN-based method, and conducted automated diagnostic experiments for malocclusion issues. The experimental results show that the OMNI dataset can facilitate the automated diagnosis research of malocclusion issues and provide a new benchmark for the research in this field. Our OMNI dataset and baseline code are publicly available at https://github.com/RoundFaceJ/OMNI.
Facial Surgery Preview Based on the Orthognathic Treatment Prediction
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:Orthognathic surgery consultation is essential to help patients understand the changes to their facial appearance after surgery. However, current visualization methods are often inefficient and inaccurate due to limited pre- and post-treatment data and the complexity of the treatment. To overcome these challenges, this study aims to develop a fully automated pipeline that generates accurate and efficient 3D previews of postsurgical facial appearances for patients with orthognathic treatment without requiring additional medical images. The study introduces novel aesthetic losses, such as mouth-convexity and asymmetry losses, to improve the accuracy of facial surgery prediction. Additionally, it proposes a specialized parametric model for 3D reconstruction of the patient, medical-related losses to guide latent code prediction network optimization, and a data augmentation scheme to address insufficient data. The study additionally employs FLAME, a parametric model, to enhance the quality of facial appearance previews by extracting facial latent codes and establishing dense correspondences between pre- and post-surgery geometries. Quantitative comparisons showed the algorithm's effectiveness, and qualitative results highlighted accurate facial contour and detail predictions. A user study confirmed that doctors and the public could not distinguish between machine learning predictions and actual postoperative results. This study aims to offer a practical, effective solution for orthognathic surgery consultations, benefiting doctors and patients.
An Implicit Parametric Morphable Dental Model
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:3D Morphable models of the human body capture variations among subjects and are useful in reconstruction and editing applications. Current dental models use an explicit mesh scene representation and model only the teeth, ignoring the gum. In this work, we present the first parametric 3D morphable dental model for both teeth and gum. Our model uses an implicit scene representation and is learned from rigidly aligned scans. It is based on a component-wise representation for each tooth and the gum, together with a learnable latent code for each of such components. It also learns a template shape thus enabling several applications such as segmentation, interpolation, and tooth replacement. Our reconstruction quality is on par with the most advanced global implicit representations while enabling novel applications. Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DMM/
Dense Representative Tooth Landmark/axis Detection Network on 3D Model
Nov 09, 2021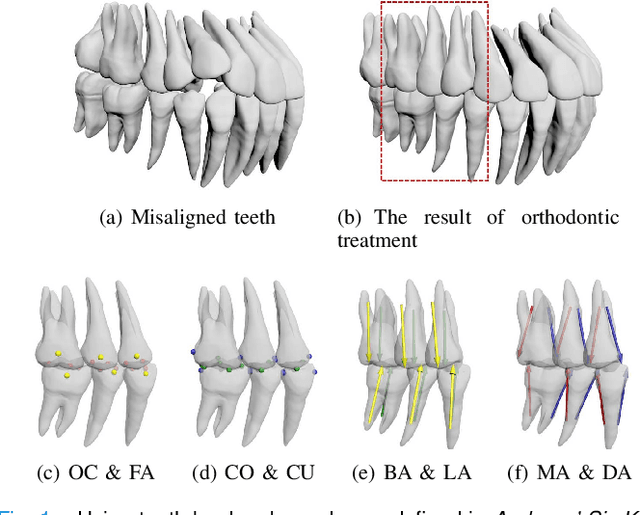
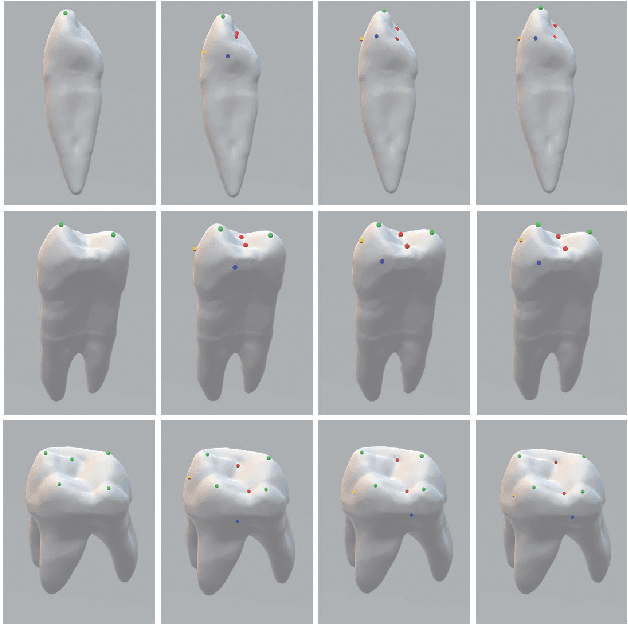
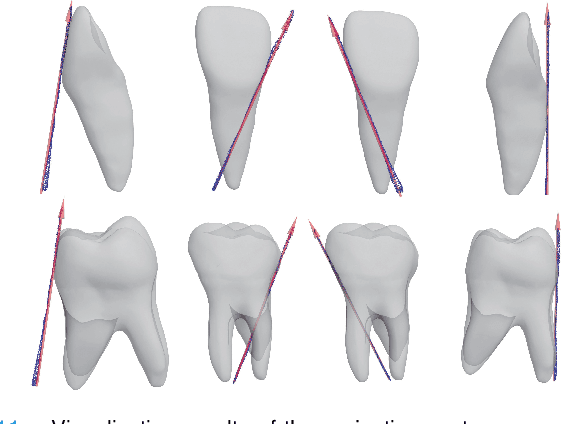
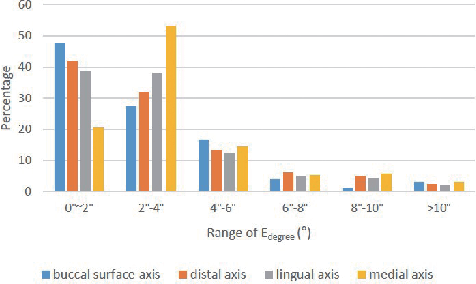
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) technology is increasingly used for digital orthodontics, but one of the challenges is to automatically and accurately detect tooth landmarks and axes. This is partly because of sophisticated geometric definitions of them, and partly due to large variations among individual tooth and across different types of tooth. As such, we propose a deep learning approach with a labeled dataset by professional dentists to the tooth landmark/axis detection on tooth model that are crucial for orthodontic treatments. Our method can extract not only tooth landmarks in the form of point (e.g. cusps), but also axes that measure the tooth angulation and inclination. The proposed network takes as input a 3D tooth model and predicts various types of the tooth landmarks and axes. Specifically, we encode the landmarks and axes as dense fields defined on the surface of the tooth model. This design choice and a set of added components make the proposed network more suitable for extracting sparse landmarks from a given 3D tooth model. Extensive evaluation of the proposed method was conducted on a set of dental models prepared by experienced dentists. Results show that our method can produce tooth landmarks with high accuracy. Our method was examined and justified via comparison with the state-of-the-art methods as well as the ablation studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge