Mingtong Zhang
PolaRiS: Scalable Real-to-Sim Evaluations for Generalist Robot Policies
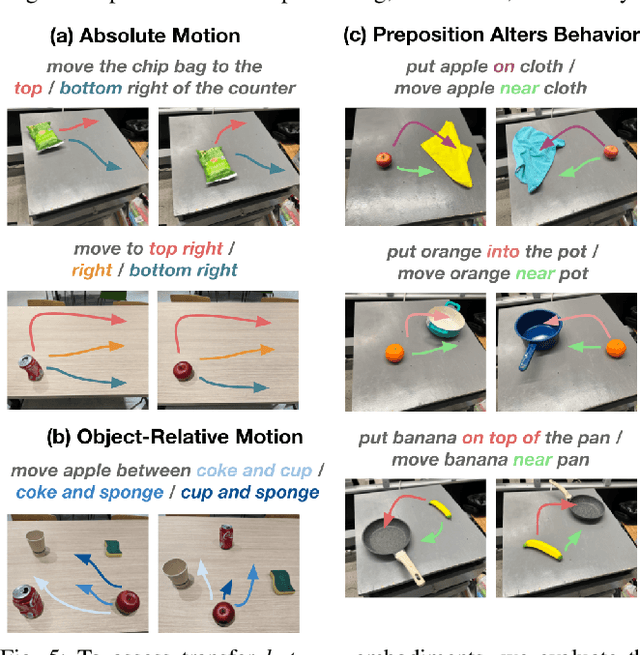
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:A significant challenge for robot learning research is our ability to accurately measure and compare the performance of robot policies. Benchmarking in robotics is historically challenging due to the stochasticity, reproducibility, and time-consuming nature of real-world rollouts. This challenge is exacerbated for recent generalist policies, which has to be evaluated across a wide variety of scenes and tasks. Evaluation in simulation offers a scalable complement to real world evaluations, but the visual and physical domain gap between existing simulation benchmarks and the real world has made them an unreliable signal for policy improvement. Furthermore, building realistic and diverse simulated environments has traditionally required significant human effort and expertise. To bridge the gap, we introduce Policy Evaluation and Environment Reconstruction in Simulation (PolaRiS), a scalable real-to-sim framework for high-fidelity simulated robot evaluation. PolaRiS utilizes neural reconstruction methods to turn short video scans of real-world scenes into interactive simulation environments. Additionally, we develop a simple simulation data co-training recipe that bridges remaining real-to-sim gaps and enables zero-shot evaluation in unseen simulation environments. Through extensive paired evaluations between simulation and the real world, we demonstrate that PolaRiS evaluations provide a much stronger correlation to real world generalist policy performance than existing simulated benchmarks. Its simplicity also enables rapid creation of diverse simulated environments. As such, this work takes a step towards distributed and democratized evaluation for the next generation of robotic foundation models.
SeFA-Policy: Fast and Accurate Visuomotor Policy Learning with Selective Flow Alignment
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Developing efficient and accurate visuomotor policies poses a central challenge in robotic imitation learning. While recent rectified flow approaches have advanced visuomotor policy learning, they suffer from a key limitation: After iterative distillation, generated actions may deviate from the ground-truth actions corresponding to the current visual observation, leading to accumulated error as the reflow process repeats and unstable task execution. We present Selective Flow Alignment (SeFA), an efficient and accurate visuomotor policy learning framework. SeFA resolves this challenge by a selective flow alignment strategy, which leverages expert demonstrations to selectively correct generated actions and restore consistency with observations, while preserving multimodality. This design introduces a consistency correction mechanism that ensures generated actions remain observation-aligned without sacrificing the efficiency of one-step flow inference. Extensive experiments across both simulated and real-world manipulation tasks show that SeFA Policy surpasses state-of-the-art diffusion-based and flow-based policies, achieving superior accuracy and robustness while reducing inference latency by over 98%. By unifying rectified flow efficiency with observation-consistent action generation, SeFA provides a scalable and dependable solution for real-time visuomotor policy learning. Code is available on https://github.com/RongXueZoe/SeFA.
RoboVerse: Towards a Unified Platform, Dataset and Benchmark for Scalable and Generalizable Robot Learning
Apr 26, 2025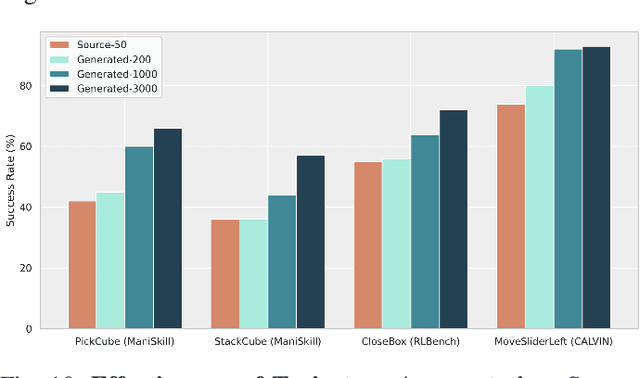
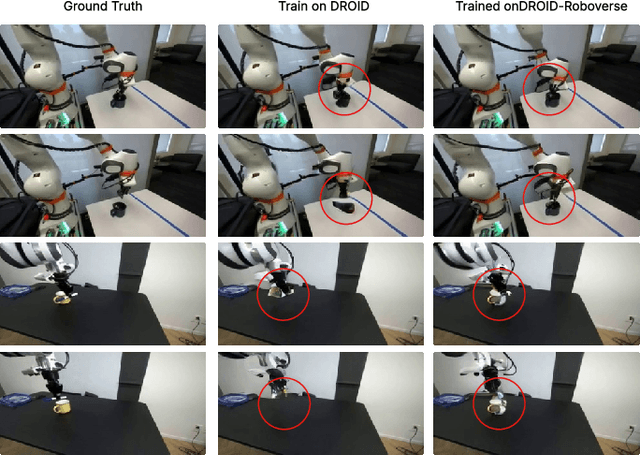

Abstract:Data scaling and standardized evaluation benchmarks have driven significant advances in natural language processing and computer vision. However, robotics faces unique challenges in scaling data and establishing evaluation protocols. Collecting real-world data is resource-intensive and inefficient, while benchmarking in real-world scenarios remains highly complex. Synthetic data and simulation offer promising alternatives, yet existing efforts often fall short in data quality, diversity, and benchmark standardization. To address these challenges, we introduce RoboVerse, a comprehensive framework comprising a simulation platform, a synthetic dataset, and unified benchmarks. Our simulation platform supports multiple simulators and robotic embodiments, enabling seamless transitions between different environments. The synthetic dataset, featuring high-fidelity physics and photorealistic rendering, is constructed through multiple approaches. Additionally, we propose unified benchmarks for imitation learning and reinforcement learning, enabling evaluation across different levels of generalization. At the core of the simulation platform is MetaSim, an infrastructure that abstracts diverse simulation environments into a universal interface. It restructures existing simulation environments into a simulator-agnostic configuration system, as well as an API aligning different simulator functionalities, such as launching simulation environments, loading assets with initial states, stepping the physics engine, etc. This abstraction ensures interoperability and extensibility. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that RoboVerse enhances the performance of imitation learning, reinforcement learning, world model learning, and sim-to-real transfer. These results validate the reliability of our dataset and benchmarks, establishing RoboVerse as a robust solution for advancing robot learning.
KUDA: Keypoints to Unify Dynamics Learning and Visual Prompting for Open-Vocabulary Robotic Manipulation
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs), significant progress has been made in developing open-vocabulary robotic manipulation systems. However, many existing approaches overlook the importance of object dynamics, limiting their applicability to more complex, dynamic tasks. In this work, we introduce KUDA, an open-vocabulary manipulation system that integrates dynamics learning and visual prompting through keypoints, leveraging both VLMs and learning-based neural dynamics models. Our key insight is that a keypoint-based target specification is simultaneously interpretable by VLMs and can be efficiently translated into cost functions for model-based planning. Given language instructions and visual observations, KUDA first assigns keypoints to the RGB image and queries the VLM to generate target specifications. These abstract keypoint-based representations are then converted into cost functions, which are optimized using a learned dynamics model to produce robotic trajectories. We evaluate KUDA on a range of manipulation tasks, including free-form language instructions across diverse object categories, multi-object interactions, and deformable or granular objects, demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework. The project page is available at http://kuda-dynamics.github.io.
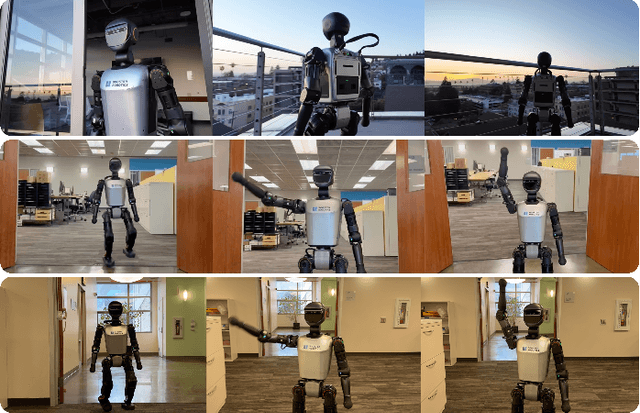
Learning from Massive Human Videos for Universal Humanoid Pose Control
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Scalable learning of humanoid robots is crucial for their deployment in real-world applications. While traditional approaches primarily rely on reinforcement learning or teleoperation to achieve whole-body control, they are often limited by the diversity of simulated environments and the high costs of demonstration collection. In contrast, human videos are ubiquitous and present an untapped source of semantic and motion information that could significantly enhance the generalization capabilities of humanoid robots. This paper introduces Humanoid-X, a large-scale dataset of over 20 million humanoid robot poses with corresponding text-based motion descriptions, designed to leverage this abundant data. Humanoid-X is curated through a comprehensive pipeline: data mining from the Internet, video caption generation, motion retargeting of humans to humanoid robots, and policy learning for real-world deployment. With Humanoid-X, we further train a large humanoid model, UH-1, which takes text instructions as input and outputs corresponding actions to control a humanoid robot. Extensive simulated and real-world experiments validate that our scalable training approach leads to superior generalization in text-based humanoid control, marking a significant step toward adaptable, real-world-ready humanoid robots.
Dynamic 3D Gaussian Tracking for Graph-Based Neural Dynamics Modeling
Oct 24, 2024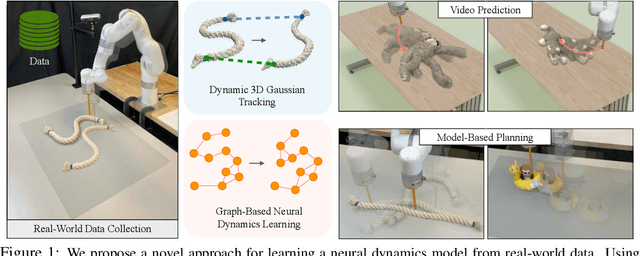

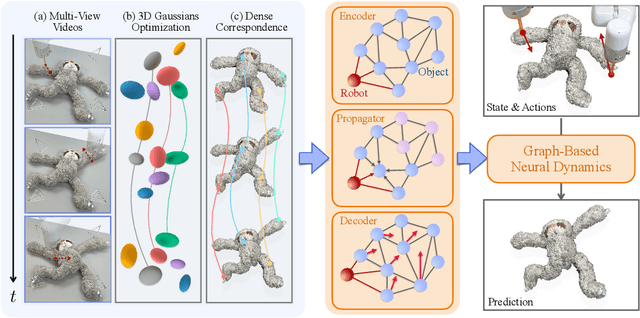

Abstract:Videos of robots interacting with objects encode rich information about the objects' dynamics. However, existing video prediction approaches typically do not explicitly account for the 3D information from videos, such as robot actions and objects' 3D states, limiting their use in real-world robotic applications. In this work, we introduce a framework to learn object dynamics directly from multi-view RGB videos by explicitly considering the robot's action trajectories and their effects on scene dynamics. We utilize the 3D Gaussian representation of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to train a particle-based dynamics model using Graph Neural Networks. This model operates on sparse control particles downsampled from the densely tracked 3D Gaussian reconstructions. By learning the neural dynamics model on offline robot interaction data, our method can predict object motions under varying initial configurations and unseen robot actions. The 3D transformations of Gaussians can be interpolated from the motions of control particles, enabling the rendering of predicted future object states and achieving action-conditioned video prediction. The dynamics model can also be applied to model-based planning frameworks for object manipulation tasks. We conduct experiments on various kinds of deformable materials, including ropes, clothes, and stuffed animals, demonstrating our framework's ability to model complex shapes and dynamics. Our project page is available at https://gs-dynamics.github.io.
Open X-Embodiment: Robotic Learning Datasets and RT-X Models
Oct 17, 2023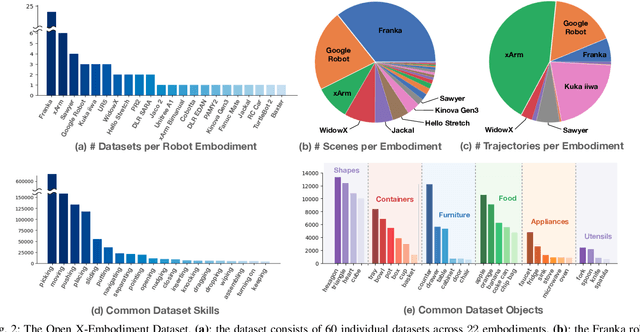
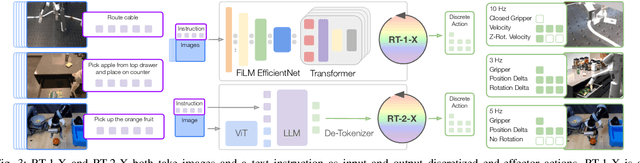
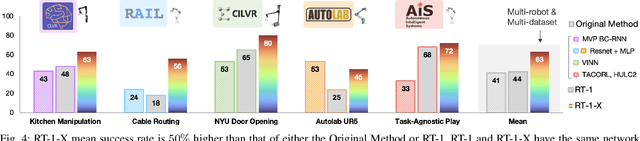
Abstract:Large, high-capacity models trained on diverse datasets have shown remarkable successes on efficiently tackling downstream applications. In domains from NLP to Computer Vision, this has led to a consolidation of pretrained models, with general pretrained backbones serving as a starting point for many applications. Can such a consolidation happen in robotics? Conventionally, robotic learning methods train a separate model for every application, every robot, and even every environment. Can we instead train generalist X-robot policy that can be adapted efficiently to new robots, tasks, and environments? In this paper, we provide datasets in standardized data formats and models to make it possible to explore this possibility in the context of robotic manipulation, alongside experimental results that provide an example of effective X-robot policies. We assemble a dataset from 22 different robots collected through a collaboration between 21 institutions, demonstrating 527 skills (160266 tasks). We show that a high-capacity model trained on this data, which we call RT-X, exhibits positive transfer and improves the capabilities of multiple robots by leveraging experience from other platforms. More details can be found on the project website $\href{https://robotics-transformer-x.github.io}{\text{robotics-transformer-x.github.io}}$.
D$^3$Fields: Dynamic 3D Descriptor Fields for Zero-Shot Generalizable Robotic Manipulation
Oct 08, 2023



Abstract:Scene representation has been a crucial design choice in robotic manipulation systems. An ideal representation should be 3D, dynamic, and semantic to meet the demands of diverse manipulation tasks. However, previous works often lack all three properties simultaneously. In this work, we introduce D$^3$Fields - dynamic 3D descriptor fields. These fields capture the dynamics of the underlying 3D environment and encode both semantic features and instance masks. Specifically, we project arbitrary 3D points in the workspace onto multi-view 2D visual observations and interpolate features derived from foundational models. The resulting fused descriptor fields allow for flexible goal specifications using 2D images with varied contexts, styles, and instances. To evaluate the effectiveness of these descriptor fields, we apply our representation to a wide range of robotic manipulation tasks in a zero-shot manner. Through extensive evaluation in both real-world scenarios and simulations, we demonstrate that D$^3$Fields are both generalizable and effective for zero-shot robotic manipulation tasks. In quantitative comparisons with state-of-the-art dense descriptors, such as Dense Object Nets and DINO, D$^3$Fields exhibit significantly better generalization abilities and manipulation accuracy.
Beyond RGB: Scene-Property Synthesis with Neural Radiance Fields
Jun 09, 2022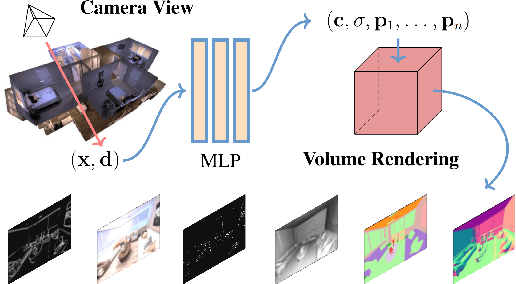
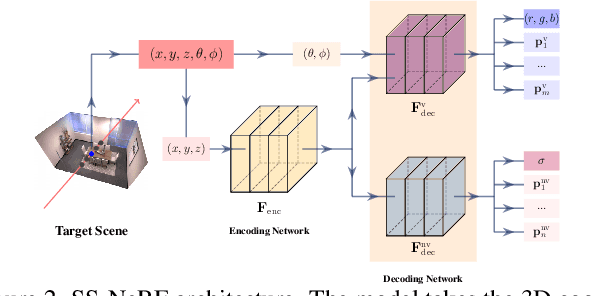
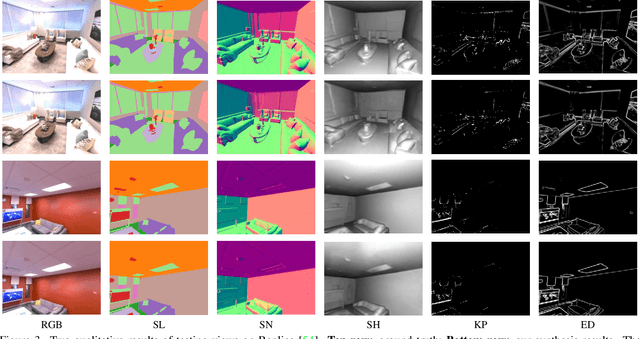
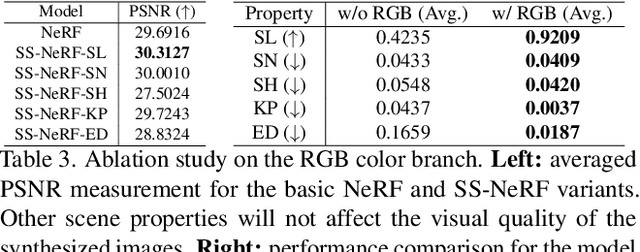
Abstract:Comprehensive 3D scene understanding, both geometrically and semantically, is important for real-world applications such as robot perception. Most of the existing work has focused on developing data-driven discriminative models for scene understanding. This paper provides a new approach to scene understanding, from a synthesis model perspective, by leveraging the recent progress on implicit 3D representation and neural rendering. Building upon the great success of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), we introduce Scene-Property Synthesis with NeRF (SS-NeRF) that is able to not only render photo-realistic RGB images from novel viewpoints, but also render various accurate scene properties (e.g., appearance, geometry, and semantics). By doing so, we facilitate addressing a variety of scene understanding tasks under a unified framework, including semantic segmentation, surface normal estimation, reshading, keypoint detection, and edge detection. Our SS-NeRF framework can be a powerful tool for bridging generative learning and discriminative learning, and thus be beneficial to the investigation of a wide range of interesting problems, such as studying task relationships within a synthesis paradigm, transferring knowledge to novel tasks, facilitating downstream discriminative tasks as ways of data augmentation, and serving as auto-labeller for data creation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge