Zhipeng Bao
Walk through Paintings: Egocentric World Models from Internet Priors
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:What if a video generation model could not only imagine a plausible future, but the correct one, accurately reflecting how the world changes with each action? We address this question by presenting the Egocentric World Model (EgoWM), a simple, architecture-agnostic method that transforms any pretrained video diffusion model into an action-conditioned world model, enabling controllable future prediction. Rather than training from scratch, we repurpose the rich world priors of Internet-scale video models and inject motor commands through lightweight conditioning layers. This allows the model to follow actions faithfully while preserving realism and strong generalization. Our approach scales naturally across embodiments and action spaces, ranging from 3-DoF mobile robots to 25-DoF humanoids, where predicting egocentric joint-angle-driven dynamics is substantially more challenging. The model produces coherent rollouts for both navigation and manipulation tasks, requiring only modest fine-tuning. To evaluate physical correctness independently of visual appearance, we introduce the Structural Consistency Score (SCS), which measures whether stable scene elements evolve consistently with the provided actions. EgoWM improves SCS by up to 80 percent over prior state-of-the-art navigation world models, while achieving up to six times lower inference latency and robust generalization to unseen environments, including navigation inside paintings.
Large Language Model-assisted Autonomous Vehicle Recovery from Immobilization
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Despite significant advancements in recent decades, autonomous vehicles (AVs) continue to face challenges in navigating certain traffic scenarios where human drivers excel. In such situations, AVs often become immobilized, disrupting overall traffic flow. Current recovery solutions, such as remote intervention (which is costly and inefficient) and manual takeover (which excludes non-drivers and limits AV accessibility), are inadequate. This paper introduces StuckSolver, a novel Large Language Model (LLM) driven recovery framework that enables AVs to resolve immobilization scenarios through self-reasoning and/or passenger-guided decision-making. StuckSolver is designed as a plug-in add-on module that operates on top of the AV's existing perception-planning-control stack, requiring no modification to its internal architecture. Instead, it interfaces with standard sensor data streams to detect immobilization states, interpret environmental context, and generate high-level recovery commands that can be executed by the AV's native planner. We evaluate StuckSolver on the Bench2Drive benchmark and in custom-designed uncertainty scenarios. Results show that StuckSolver achieves near-state-of-the-art performance through autonomous self-reasoning alone and exhibits further improvements when passenger guidance is incorporated.
Your Ride, Your Rules: Psychology and Cognition Enabled Automated Driving Systems
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Despite rapid advances in autonomous driving, current autonomous vehicles (AVs) lack effective bidirectional communication with occupants, limiting personalization and recovery from immobilization. This reduces comfort and trust, potentially slowing broader AV adoption. We propose PACE-ADS (Psychology and Cognition Enabled Automated Driving Systems), a human-centered autonomy framework that enables AVs to sense, interpret, and respond to both external traffic and internal occupant states. PACE-ADS comprises three foundation model-based agents: a Driver Agent that analyzes the driving context, a Psychologist Agent that interprets occupant psychological signals (e.g., EEG, heart rate, facial expressions) and cognitive commands (e.g., speech), and a Coordinator Agent that integrates these inputs to produce high-level behavior decisions and operational parameters. Rather than replacing existing AV modules, PACE-ADS complements them by operating at the behavioral level, delegating low-level control to native AV systems. This separation enables closed-loop adaptation and supports integration across diverse platforms. We evaluate PACE-ADS in simulation across varied scenarios involving traffic lights, pedestrians, work zones, and car following. Results show that PACE-ADS adapts driving styles to occupant states, improves ride comfort, and enables safe recovery from immobilization via autonomous reasoning or human guidance. Our findings highlight the promise of LLM-based frameworks for bridging the gap between machine autonomy and human-centered driving.
Diff-2-in-1: Bridging Generation and Dense Perception with Diffusion Models
Nov 07, 2024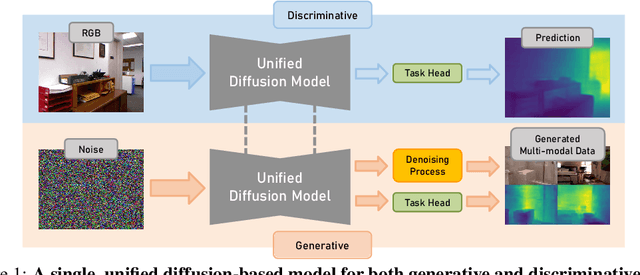
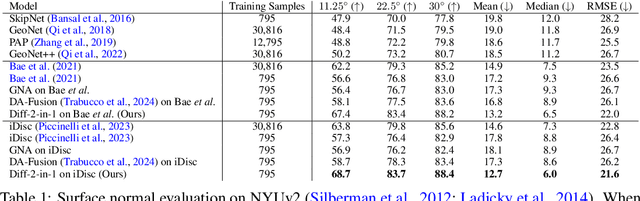
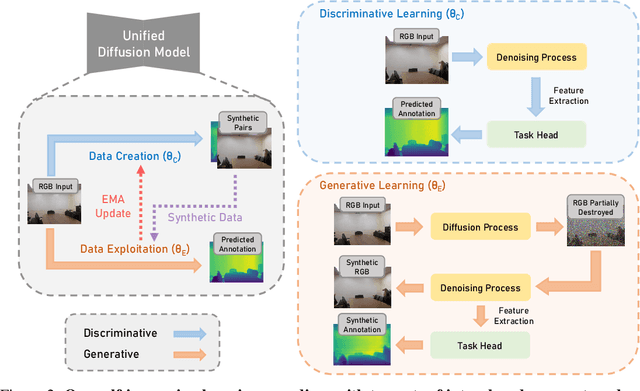
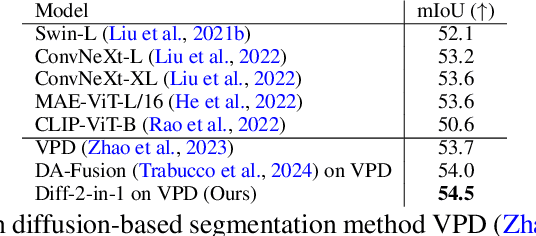
Abstract:Beyond high-fidelity image synthesis, diffusion models have recently exhibited promising results in dense visual perception tasks. However, most existing work treats diffusion models as a standalone component for perception tasks, employing them either solely for off-the-shelf data augmentation or as mere feature extractors. In contrast to these isolated and thus sub-optimal efforts, we introduce a unified, versatile, diffusion-based framework, Diff-2-in-1, that can simultaneously handle both multi-modal data generation and dense visual perception, through a unique exploitation of the diffusion-denoising process. Within this framework, we further enhance discriminative visual perception via multi-modal generation, by utilizing the denoising network to create multi-modal data that mirror the distribution of the original training set. Importantly, Diff-2-in-1 optimizes the utilization of the created diverse and faithful data by leveraging a novel self-improving learning mechanism. Comprehensive experimental evaluations validate the effectiveness of our framework, showcasing consistent performance improvements across various discriminative backbones and high-quality multi-modal data generation characterized by both realism and usefulness.
ReferEverything: Towards Segmenting Everything We Can Speak of in Videos
Oct 30, 2024


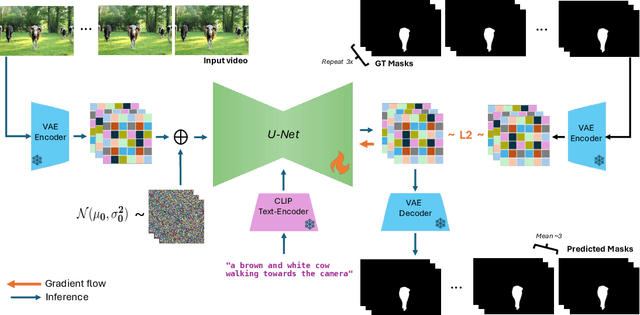
Abstract:We present REM, a framework for segmenting a wide range of concepts in video that can be described through natural language. Our method capitalizes on visual-language representations learned by video diffusion models on Internet-scale datasets. A key insight of our approach is preserving as much of the generative model's original representation as possible, while fine-tuning it on narrow-domain Referral Object Segmentation datasets. As a result, our framework can accurately segment and track rare and unseen objects, despite being trained on object masks from a limited set of categories. Additionally, it can generalize to non-object dynamic concepts, such as waves crashing in the ocean, as demonstrated in our newly introduced benchmark for Referral Video Process Segmentation (Ref-VPS). Our experiments show that REM performs on par with state-of-the-art approaches on in-domain datasets, like Ref-DAVIS, while outperforming them by up to twelve points in terms of region similarity on out-of-domain data, leveraging the power of Internet-scale pre-training.
Lexicon3D: Probing Visual Foundation Models for Complex 3D Scene Understanding
Sep 05, 2024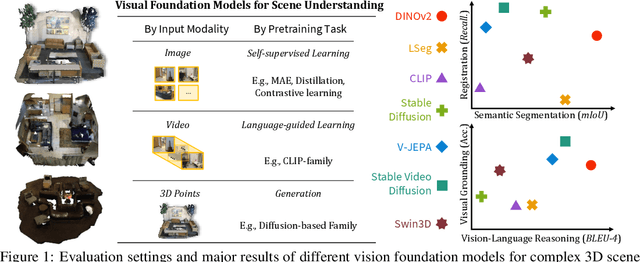
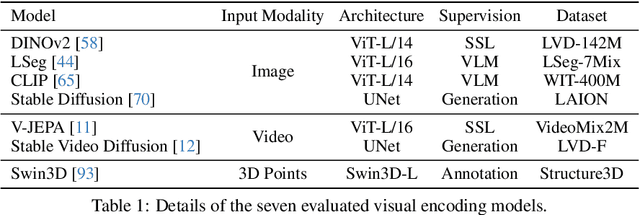
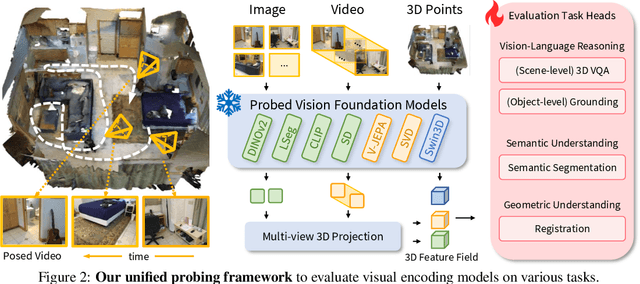
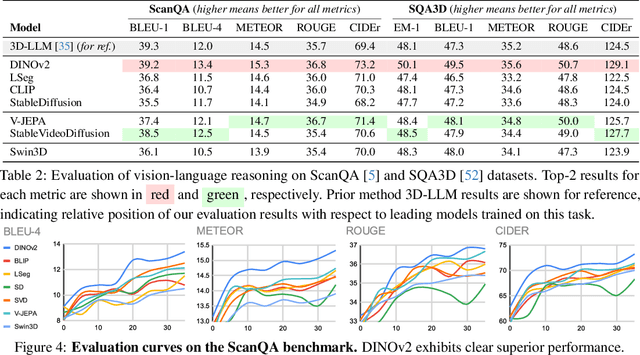
Abstract:Complex 3D scene understanding has gained increasing attention, with scene encoding strategies playing a crucial role in this success. However, the optimal scene encoding strategies for various scenarios remain unclear, particularly compared to their image-based counterparts. To address this issue, we present a comprehensive study that probes various visual encoding models for 3D scene understanding, identifying the strengths and limitations of each model across different scenarios. Our evaluation spans seven vision foundation encoders, including image-based, video-based, and 3D foundation models. We evaluate these models in four tasks: Vision-Language Scene Reasoning, Visual Grounding, Segmentation, and Registration, each focusing on different aspects of scene understanding. Our evaluations yield key findings: DINOv2 demonstrates superior performance, video models excel in object-level tasks, diffusion models benefit geometric tasks, and language-pretrained models show unexpected limitations in language-related tasks. These insights challenge some conventional understandings, provide novel perspectives on leveraging visual foundation models, and highlight the need for more flexible encoder selection in future vision-language and scene-understanding tasks.
Separate-and-Enhance: Compositional Finetuning for Text2Image Diffusion Models
Dec 10, 2023



Abstract:Despite recent significant strides achieved by diffusion-based Text-to-Image (T2I) models, current systems are still less capable of ensuring decent compositional generation aligned with text prompts, particularly for the multi-object generation. This work illuminates the fundamental reasons for such misalignment, pinpointing issues related to low attention activation scores and mask overlaps. While previous research efforts have individually tackled these issues, we assert that a holistic approach is paramount. Thus, we propose two novel objectives, the Separate loss and the Enhance loss, that reduce object mask overlaps and maximize attention scores, respectively. Our method diverges from conventional test-time-adaptation techniques, focusing on finetuning critical parameters, which enhances scalability and generalizability. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate the superior performance of our model in terms of image realism, text-image alignment, and adaptability, notably outperforming prominent baselines. Ultimately, this research paves the way for T2I diffusion models with enhanced compositional capacities and broader applicability. The project webpage is available at https://zpbao.github.io/projects/SepEn/.
Multi-task View Synthesis with Neural Radiance Fields
Sep 29, 2023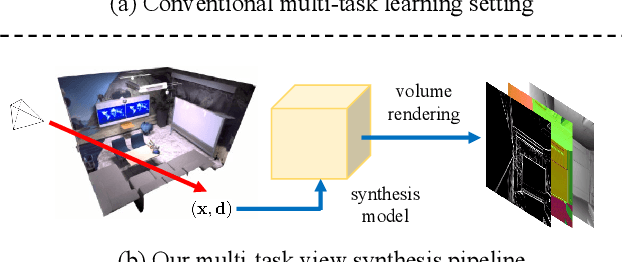
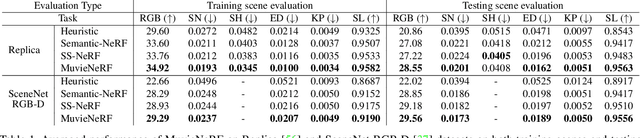
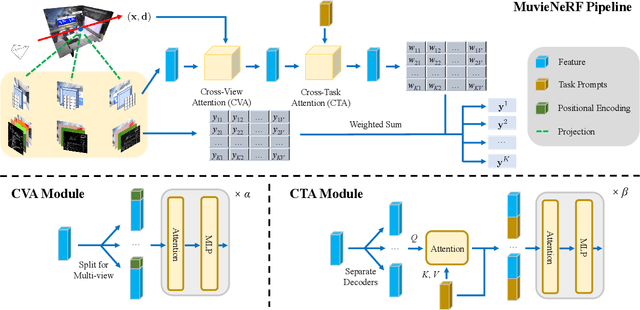
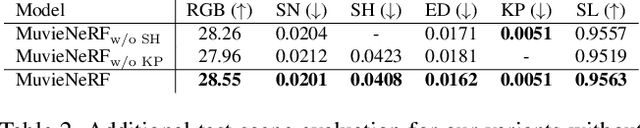
Abstract:Multi-task visual learning is a critical aspect of computer vision. Current research, however, predominantly concentrates on the multi-task dense prediction setting, which overlooks the intrinsic 3D world and its multi-view consistent structures, and lacks the capability for versatile imagination. In response to these limitations, we present a novel problem setting -- multi-task view synthesis (MTVS), which reinterprets multi-task prediction as a set of novel-view synthesis tasks for multiple scene properties, including RGB. To tackle the MTVS problem, we propose MuvieNeRF, a framework that incorporates both multi-task and cross-view knowledge to simultaneously synthesize multiple scene properties. MuvieNeRF integrates two key modules, the Cross-Task Attention (CTA) and Cross-View Attention (CVA) modules, enabling the efficient use of information across multiple views and tasks. Extensive evaluation on both synthetic and realistic benchmarks demonstrates that MuvieNeRF is capable of simultaneously synthesizing different scene properties with promising visual quality, even outperforming conventional discriminative models in various settings. Notably, we show that MuvieNeRF exhibits universal applicability across a range of NeRF backbones. Our code is available at https://github.com/zsh2000/MuvieNeRF.
Object Discovery from Motion-Guided Tokens
Mar 27, 2023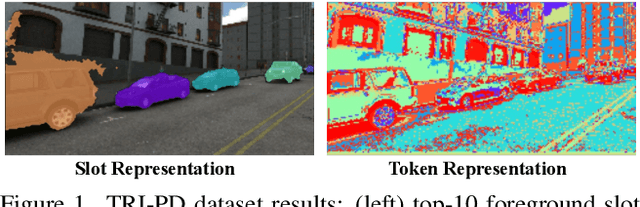
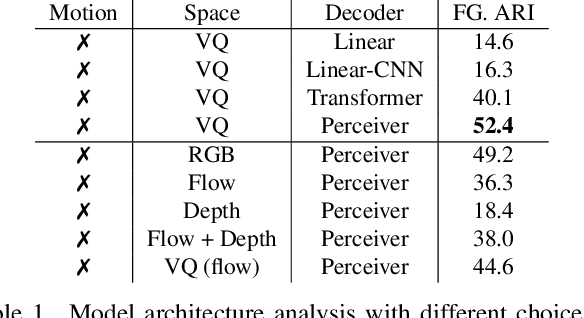
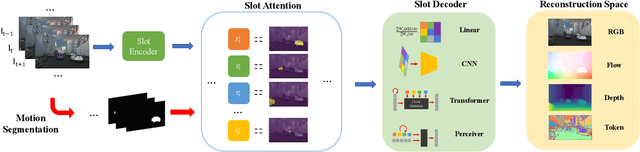
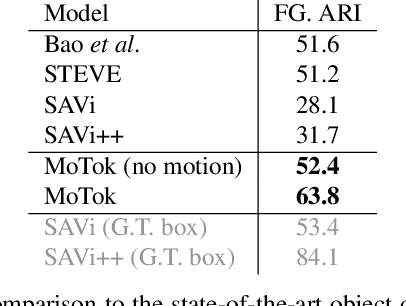
Abstract:Object discovery -- separating objects from the background without manual labels -- is a fundamental open challenge in computer vision. Previous methods struggle to go beyond clustering of low-level cues, whether handcrafted (e.g., color, texture) or learned (e.g., from auto-encoders). In this work, we augment the auto-encoder representation learning framework with two key components: motion-guidance and mid-level feature tokenization. Although both have been separately investigated, we introduce a new transformer decoder showing that their benefits can compound thanks to motion-guided vector quantization. We show that our architecture effectively leverages the synergy between motion and tokenization, improving upon the state of the art on both synthetic and real datasets. Our approach enables the emergence of interpretable object-specific mid-level features, demonstrating the benefits of motion-guidance (no labeling) and quantization (interpretability, memory efficiency).
Beyond RGB: Scene-Property Synthesis with Neural Radiance Fields
Jun 09, 2022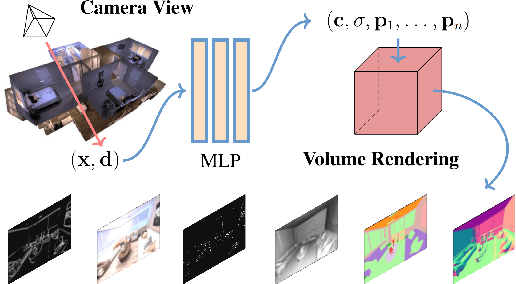
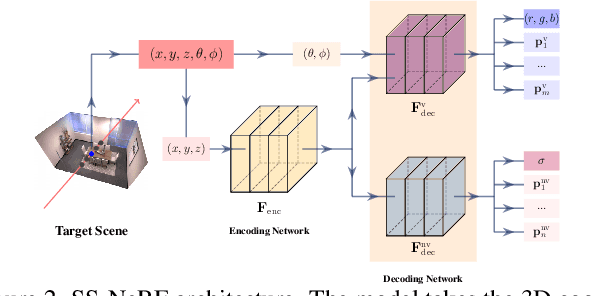
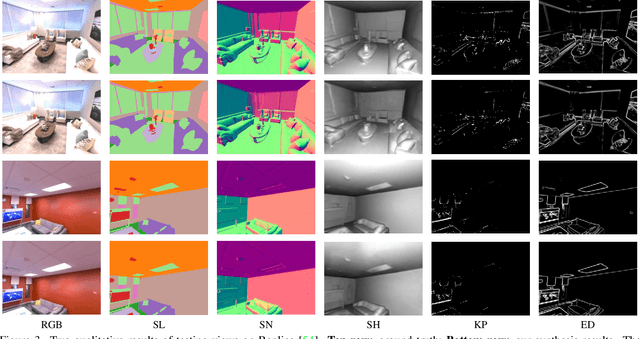
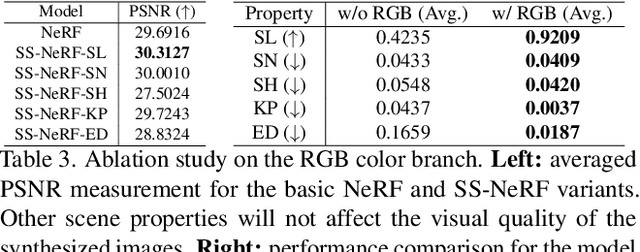
Abstract:Comprehensive 3D scene understanding, both geometrically and semantically, is important for real-world applications such as robot perception. Most of the existing work has focused on developing data-driven discriminative models for scene understanding. This paper provides a new approach to scene understanding, from a synthesis model perspective, by leveraging the recent progress on implicit 3D representation and neural rendering. Building upon the great success of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), we introduce Scene-Property Synthesis with NeRF (SS-NeRF) that is able to not only render photo-realistic RGB images from novel viewpoints, but also render various accurate scene properties (e.g., appearance, geometry, and semantics). By doing so, we facilitate addressing a variety of scene understanding tasks under a unified framework, including semantic segmentation, surface normal estimation, reshading, keypoint detection, and edge detection. Our SS-NeRF framework can be a powerful tool for bridging generative learning and discriminative learning, and thus be beneficial to the investigation of a wide range of interesting problems, such as studying task relationships within a synthesis paradigm, transferring knowledge to novel tasks, facilitating downstream discriminative tasks as ways of data augmentation, and serving as auto-labeller for data creation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge