Mingjun Xu
Inverse Knowledge Search over Verifiable Reasoning: Synthesizing a Scientific Encyclopedia from a Long Chains-of-Thought Knowledge Base
Oct 30, 2025



Abstract:Most scientific materials compress reasoning, presenting conclusions while omitting the derivational chains that justify them. This compression hinders verification by lacking explicit, step-wise justifications and inhibits cross-domain links by collapsing the very pathways that establish the logical and causal connections between concepts. We introduce a scalable framework that decompresses scientific reasoning, constructing a verifiable Long Chain-of-Thought (LCoT) knowledge base and projecting it into an emergent encyclopedia, SciencePedia. Our pipeline operationalizes an endpoint-driven, reductionist strategy: a Socratic agent, guided by a curriculum of around 200 courses, generates approximately 3 million first-principles questions. To ensure high fidelity, multiple independent solver models generate LCoTs, which are then rigorously filtered by prompt sanitization and cross-model answer consensus, retaining only those with verifiable endpoints. This verified corpus powers the Brainstorm Search Engine, which performs inverse knowledge search -- retrieving diverse, first-principles derivations that culminate in a target concept. This engine, in turn, feeds the Plato synthesizer, which narrates these verified chains into coherent articles. The initial SciencePedia comprises approximately 200,000 fine-grained entries spanning mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, engineering, and computation. In evaluations across six disciplines, Plato-synthesized articles (conditioned on retrieved LCoTs) exhibit substantially higher knowledge-point density and significantly lower factual error rates than an equally-prompted baseline without retrieval (as judged by an external LLM). Built on this verifiable LCoT knowledge base, this reasoning-centric approach enables trustworthy, cross-domain scientific synthesis at scale and establishes the foundation for an ever-expanding encyclopedia.
MM-R5: MultiModal Reasoning-Enhanced ReRanker via Reinforcement Learning for Document Retrieval
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal document retrieval systems enable information access across text, images, and layouts, benefiting various domains like document-based question answering, report analysis, and interactive content summarization. Rerankers improve retrieval precision by reordering retrieved candidates. However, current multimodal reranking methods remain underexplored, with significant room for improvement in both training strategies and overall effectiveness. Moreover, the lack of explicit reasoning makes it difficult to analyze and optimize these methods further. In this paper, We propose MM-R5, a MultiModal Reasoning-Enhanced ReRanker via Reinforcement Learning for Document Retrieval, aiming to provide a more effective and reliable solution for multimodal reranking tasks. MM-R5 is trained in two stages: supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL). In the SFT stage, we focus on improving instruction-following and guiding the model to generate complete and high-quality reasoning chains. To support this, we introduce a novel data construction strategy that produces rich, high-quality reasoning data. In the RL stage, we design a task-specific reward framework, including a reranking reward tailored for multimodal candidates and a composite template-based reward to further refine reasoning quality. We conduct extensive experiments on MMDocIR, a challenging public benchmark spanning multiple domains. MM-R5 achieves state-of-the-art performance on most metrics and delivers comparable results to much larger models on the remaining ones. Moreover, compared to the best retrieval-only method, MM-R5 improves recall@1 by over 4%. These results validate the effectiveness of our reasoning-enhanced training pipeline.
A Multi-Granularity Retrieval Framework for Visually-Rich Documents
May 06, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems have predominantly focused on text-based retrieval, limiting their effectiveness in handling visually-rich documents that encompass text, images, tables, and charts. To bridge this gap, we propose a unified multi-granularity multimodal retrieval framework tailored for two benchmark tasks: MMDocIR and M2KR. Our approach integrates hierarchical encoding strategies, modality-aware retrieval mechanisms, and vision-language model (VLM)-based candidate filtering to effectively capture and utilize the complex interdependencies between textual and visual modalities. By leveraging off-the-shelf vision-language models and implementing a training-free hybrid retrieval strategy, our framework demonstrates robust performance without the need for task-specific fine-tuning. Experimental evaluations reveal that incorporating layout-aware search and VLM-based candidate verification significantly enhances retrieval accuracy, achieving a top performance score of 65.56. This work underscores the potential of scalable and reproducible solutions in advancing multimodal document retrieval systems.
A Multi-Granularity Multimodal Retrieval Framework for Multimodal Document Tasks
May 01, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems have predominantly focused on text-based retrieval, limiting their effectiveness in handling visually-rich documents that encompass text, images, tables, and charts. To bridge this gap, we propose a unified multi-granularity multimodal retrieval framework tailored for two benchmark tasks: MMDocIR and M2KR. Our approach integrates hierarchical encoding strategies, modality-aware retrieval mechanisms, and reranking modules to effectively capture and utilize the complex interdependencies between textual and visual modalities. By leveraging off-the-shelf vision-language models and implementing a training-free hybridretrieval strategy, our framework demonstrates robust performance without the need for task-specific fine-tuning. Experimental evaluations reveal that incorporating layout-aware search and reranking modules significantly enhances retrieval accuracy, achieving a top performance score of 65.56. This work underscores the potential of scalable and reproducible solutions in advancing multimodal document retrieval systems.
SciLitLLM: How to Adapt LLMs for Scientific Literature Understanding
Aug 30, 2024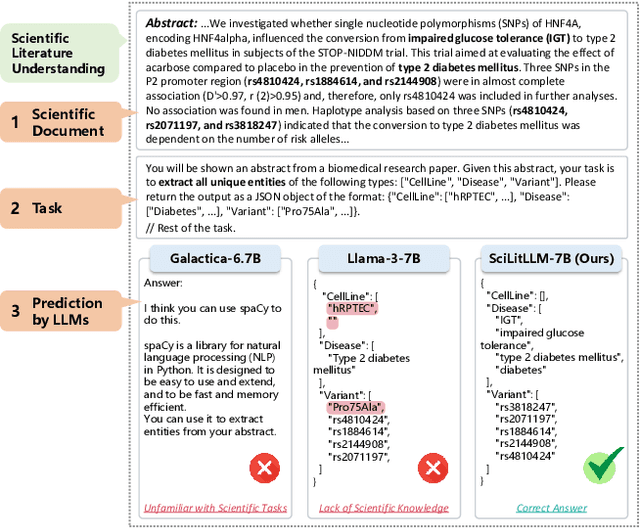
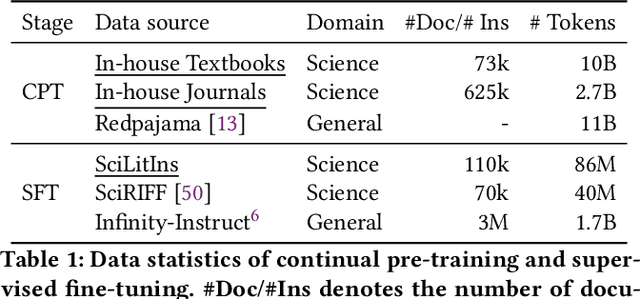
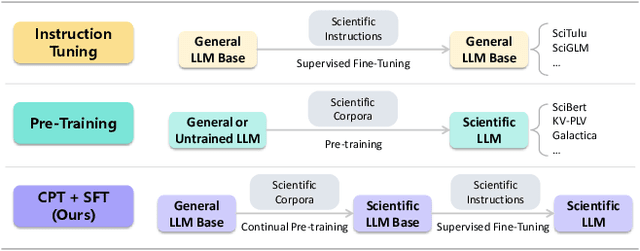
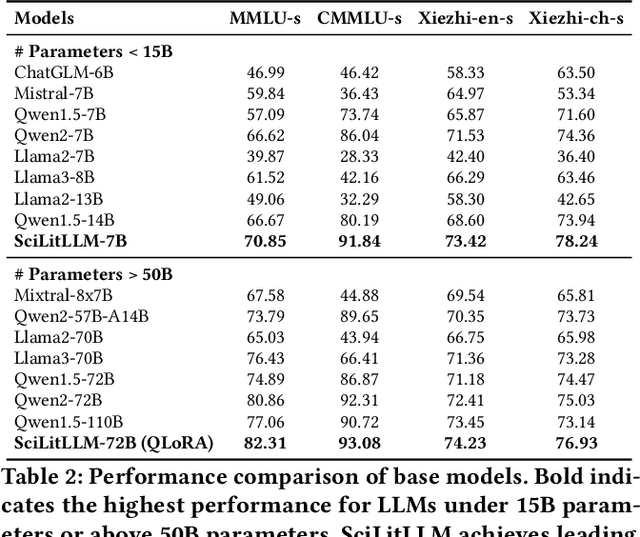
Abstract:Scientific literature understanding is crucial for extracting targeted information and garnering insights, thereby significantly advancing scientific discovery. Despite the remarkable success of Large Language Models (LLMs), they face challenges in scientific literature understanding, primarily due to (1) a lack of scientific knowledge and (2) unfamiliarity with specialized scientific tasks. To develop an LLM specialized in scientific literature understanding, we propose a hybrid strategy that integrates continual pre-training (CPT) and supervised fine-tuning (SFT), to simultaneously infuse scientific domain knowledge and enhance instruction-following capabilities for domain-specific tasks.cIn this process, we identify two key challenges: (1) constructing high-quality CPT corpora, and (2) generating diverse SFT instructions. We address these challenges through a meticulous pipeline, including PDF text extraction, parsing content error correction, quality filtering, and synthetic instruction creation. Applying this strategy, we present a suite of LLMs: SciLitLLM, specialized in scientific literature understanding. These models demonstrate promising performance on scientific literature understanding benchmarks. Our contributions are threefold: (1) We present an effective framework that integrates CPT and SFT to adapt LLMs to scientific literature understanding, which can also be easily adapted to other domains. (2) We propose an LLM-based synthesis method to generate diverse and high-quality scientific instructions, resulting in a new instruction set -- SciLitIns -- for supervised fine-tuning in less-represented scientific domains. (3) SciLitLLM achieves promising performance improvements on scientific literature understanding benchmarks.
Uni-SMART: Universal Science Multimodal Analysis and Research Transformer
Mar 15, 2024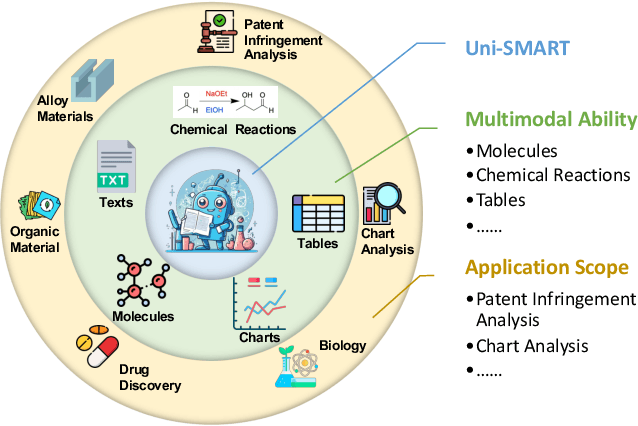
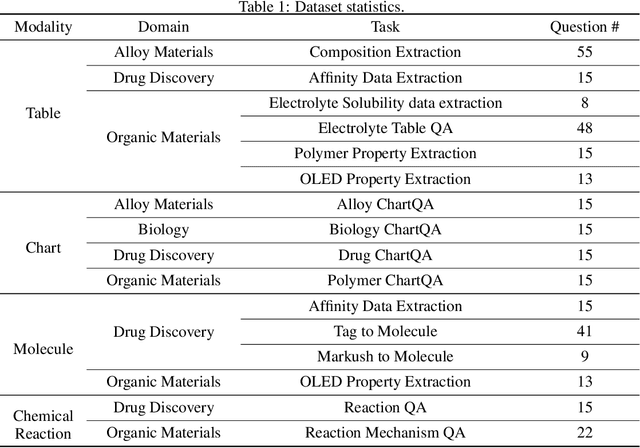
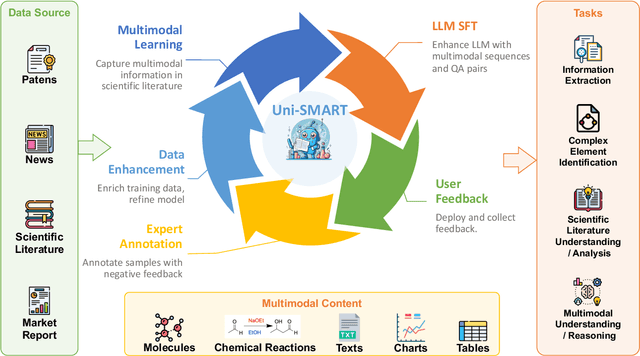
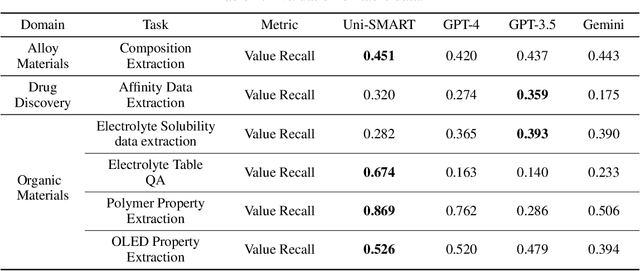
Abstract:In scientific research and its application, scientific literature analysis is crucial as it allows researchers to build on the work of others. However, the fast growth of scientific knowledge has led to a massive increase in scholarly articles, making in-depth literature analysis increasingly challenging and time-consuming. The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has offered a new way to address this challenge. Known for their strong abilities in summarizing texts, LLMs are seen as a potential tool to improve the analysis of scientific literature. However, existing LLMs have their own limits. Scientific literature often includes a wide range of multimodal elements, such as molecular structure, tables, and charts, which are hard for text-focused LLMs to understand and analyze. This issue points to the urgent need for new solutions that can fully understand and analyze multimodal content in scientific literature. To answer this demand, we present Uni-SMART (Universal Science Multimodal Analysis and Research Transformer), an innovative model designed for in-depth understanding of multimodal scientific literature. Through rigorous quantitative evaluation across several domains, Uni-SMART demonstrates superior performance over leading text-focused LLMs. Furthermore, our exploration extends to practical applications, including patent infringement detection and nuanced analysis of charts. These applications not only highlight Uni-SMART's adaptability but also its potential to revolutionize how we interact with scientific literature.
A Survey on Image-text Multimodal Models
Sep 23, 2023



Abstract:Amidst the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the convergence of visual and textual information has surfaced as a crucial frontier, leading to the advent of image-text multimodal models. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the evolution and current state of image-text multimodal models, exploring their application value, challenges, and potential research trajectories. Initially, we revisit the basic concepts and developmental milestones of these models, introducing a novel classification that segments their evolution into three distinct phases, based on their time of introduction and subsequent impact on the discipline. Furthermore, based on the tasks' significance and prevalence in the academic landscape, we propose a categorization of the tasks associated with image-text multimodal models into five major types, elucidating the recent progress and key technologies within each category. Despite the remarkable accomplishments of these models, numerous challenges and issues persist. This paper delves into the inherent challenges and limitations of image-text multimodal models, fostering the exploration of prospective research directions. Our objective is to offer an exhaustive overview of the present research landscape of image-text multimodal models and to serve as a valuable reference for future scholarly endeavors. We extend an invitation to the broader community to collaborate in enhancing the image-text multimodal model community, accessible at: \href{https://github.com/i2vec/A-survey-on-image-text-multimodal-models}{https://github.com/i2vec/A-survey-on-image-text-multimodal-models}.
Multi-view Adversarial Discriminator: Mine the Non-causal Factors for Object Detection in Unseen Domains
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:Domain shift degrades the performance of object detection models in practical applications. To alleviate the influence of domain shift, plenty of previous work try to decouple and learn the domain-invariant (common) features from source domains via domain adversarial learning (DAL). However, inspired by causal mechanisms, we find that previous methods ignore the implicit insignificant non-causal factors hidden in the common features. This is mainly due to the single-view nature of DAL. In this work, we present an idea to remove non-causal factors from common features by multi-view adversarial training on source domains, because we observe that such insignificant non-causal factors may still be significant in other latent spaces (views) due to the multi-mode structure of data. To summarize, we propose a Multi-view Adversarial Discriminator (MAD) based domain generalization model, consisting of a Spurious Correlations Generator (SCG) that increases the diversity of source domain by random augmentation and a Multi-View Domain Classifier (MVDC) that maps features to multiple latent spaces, such that the non-causal factors are removed and the domain-invariant features are purified. Extensive experiments on six benchmarks show our MAD obtains state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge