Michal Shmueli-Scheuer
Robustness as an Emergent Property of Task Performance
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Robustness is often regarded as a critical future challenge for real-world applications, where stability is essential. However, as models often learn tasks in a similar order, we hypothesize that easier tasks will be easier regardless of how they are presented to the model. Indeed, in this paper, we show that as models approach high performance on a task, robustness is effectively achieved. Through an empirical analysis of multiple models across diverse datasets and configurations (e.g., paraphrases, different temperatures), we find a strong positive correlation. Moreover, we find that robustness is primarily driven by task-specific competence rather than inherent model-level properties, challenging current approaches that treat robustness as an independent capability. Thus, from a high-level perspective, we may expect that as new tasks saturate, model robustness on these tasks will emerge accordingly. For researchers, this implies that explicit efforts to measure and improve robustness may warrant reduced emphasis, as such robustness is likely to develop alongside performance gains. For practitioners, it acts as a sign that indeed the tasks that the literature deals with are unreliable, but on easier past tasks, the models are reliable and ready for real-world deployment.
ErrorMap and ErrorAtlas: Charting the Failure Landscape of Large Language Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLM) benchmarks tell us when models fail, but not why they fail. A wrong answer on a reasoning dataset may stem from formatting issues, calculation errors, or dataset noise rather than weak reasoning. Without disentangling such causes, benchmarks remain incomplete and cannot reliably guide model improvement. We introduce ErrorMap, the first method to chart the sources of LLM failure. It extracts a model's unique "failure signature", clarifies what benchmarks measure, and broadens error identification to reduce blind spots. This helps developers debug models, aligns benchmark goals with outcomes, and supports informed model selection. ErrorMap works on any model or dataset with the same logic. Applying our method to 35 datasets and 83 models we generate ErrorAtlas, a taxonomy of model errors, revealing recurring failure patterns. ErrorAtlas highlights error types that are currently underexplored in LLM research, such as omissions of required details in the output and question misinterpretation. By shifting focus from where models succeed to why they fail, ErrorMap and ErrorAtlas enable advanced evaluation - one that exposes hidden weaknesses and directs progress. Unlike success, typically measured by task-level metrics, our approach introduces a deeper evaluation layer that can be applied globally across models and tasks, offering richer insights into model behavior and limitations. We make the taxonomy and code publicly available with plans to periodically update ErrorAtlas as new benchmarks and models emerge.
Think Again! The Effect of Test-Time Compute on Preferences, Opinions, and Beliefs of Large Language Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become deeply integrated into human life and increasingly influence decision-making, it's crucial to evaluate whether and to what extent they exhibit subjective preferences, opinions, and beliefs. These tendencies may stem from biases within the models, which may shape their behavior, influence the advice and recommendations they offer to users, and potentially reinforce certain viewpoints. This paper presents the Preference, Opinion, and Belief survey (POBs), a benchmark developed to assess LLMs' subjective inclinations across societal, cultural, ethical, and personal domains. We applied our benchmark to evaluate leading open- and closed-source LLMs, measuring desired properties such as reliability, neutrality, and consistency. In addition, we investigated the effect of increasing the test-time compute, through reasoning and self-reflection mechanisms, on those metrics. While effective in other tasks, our results show that these mechanisms offer only limited gains in our domain. Furthermore, we reveal that newer model versions are becoming less consistent and more biased toward specific viewpoints, highlighting a blind spot and a concerning trend. POBS: https://ibm.github.io/POBS
Survey on Evaluation of LLM-based Agents
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:The emergence of LLM-based agents represents a paradigm shift in AI, enabling autonomous systems to plan, reason, use tools, and maintain memory while interacting with dynamic environments. This paper provides the first comprehensive survey of evaluation methodologies for these increasingly capable agents. We systematically analyze evaluation benchmarks and frameworks across four critical dimensions: (1) fundamental agent capabilities, including planning, tool use, self-reflection, and memory; (2) application-specific benchmarks for web, software engineering, scientific, and conversational agents; (3) benchmarks for generalist agents; and (4) frameworks for evaluating agents. Our analysis reveals emerging trends, including a shift toward more realistic, challenging evaluations with continuously updated benchmarks. We also identify critical gaps that future research must address-particularly in assessing cost-efficiency, safety, and robustness, and in developing fine-grained, and scalable evaluation methods. This survey maps the rapidly evolving landscape of agent evaluation, reveals the emerging trends in the field, identifies current limitations, and proposes directions for future research.
DOVE: A Large-Scale Multi-Dimensional Predictions Dataset Towards Meaningful LLM Evaluation
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Recent work found that LLMs are sensitive to a wide range of arbitrary prompt dimensions, including the type of delimiters, answer enumerators, instruction wording, and more. This throws into question popular single-prompt evaluation practices. We present DOVE (Dataset Of Variation Evaluation) a large-scale dataset containing prompt perturbations of various evaluation benchmarks. In contrast to previous work, we examine LLM sensitivity from an holistic perspective, and assess the joint effects of perturbations along various dimensions, resulting in thousands of perturbations per instance. We evaluate several model families against DOVE, leading to several findings, including efficient methods for choosing well-performing prompts, observing that few-shot examples reduce sensitivity, and identifying instances which are inherently hard across all perturbations. DOVE consists of more than 250M prompt perturbations and model outputs, which we make publicly available to spur a community-wide effort toward meaningful, robust, and efficient evaluation. Browse the data, contribute, and more: https://slab-nlp.github.io/DOVE/
The Mighty ToRR: A Benchmark for Table Reasoning and Robustness
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Despite its real-world significance, model performance on tabular data remains underexplored, leaving uncertainty about which model to rely on and which prompt configuration to adopt. To address this gap, we create ToRR, a benchmark for Table Reasoning and Robustness, that measures model performance and robustness on table-related tasks. The benchmark includes 10 datasets that cover different types of table reasoning capabilities across varied domains. ToRR goes beyond model performance rankings, and is designed to reflect whether models can handle tabular data consistently and robustly, across a variety of common table representation formats. We present a leaderboard as well as comprehensive analyses of the results of leading models over ToRR. Our results reveal a striking pattern of brittle model behavior, where even strong models are unable to perform robustly on tabular data tasks. Although no specific table format leads to consistently better performance, we show that testing over multiple formats is crucial for reliably estimating model capabilities. Moreover, we show that the reliability boost from testing multiple prompts can be equivalent to adding more test examples. Overall, our findings show that table understanding and reasoning tasks remain a significant challenge.
Stay Tuned: An Empirical Study of the Impact of Hyperparameters on LLM Tuning in Real-World Applications
Jul 25, 2024
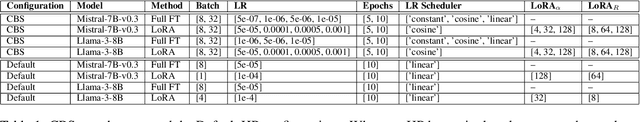

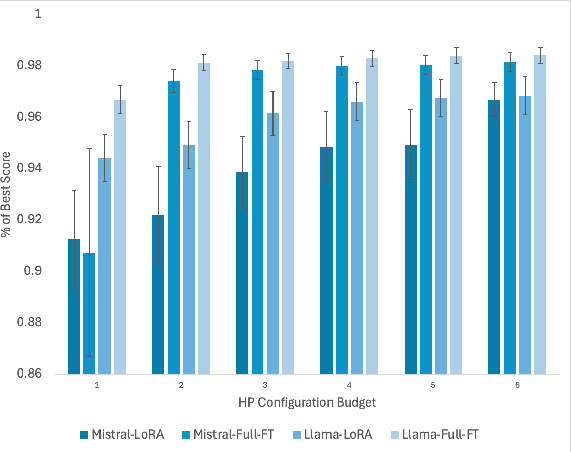
Abstract:Fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) is an effective method to enhance their performance on downstream tasks. However, choosing the appropriate setting of tuning hyperparameters (HPs) is a labor-intensive and computationally expensive process. Here, we provide recommended HP configurations for practical use-cases that represent a better starting point for practitioners, when considering two SOTA LLMs and two commonly used tuning methods. We describe Coverage-based Search (CBS), a process for ranking HP configurations based on an offline extensive grid search, such that the top ranked configurations collectively provide a practical robust recommendation for a wide range of datasets and domains. We focus our experiments on Llama-3-8B and Mistral-7B, as well as full fine-tuning and LoRa, conducting a total of > 10,000 tuning experiments. Our results suggest that, in general, Llama-3-8B and LoRA should be preferred, when possible. Moreover, we show that for both models and tuning methods, exploring only a few HP configurations, as recommended by our analysis, can provide excellent results in practice, making this work a valuable resource for practitioners.
Benchmark Agreement Testing Done Right: A Guide for LLM Benchmark Evaluation
Jul 18, 2024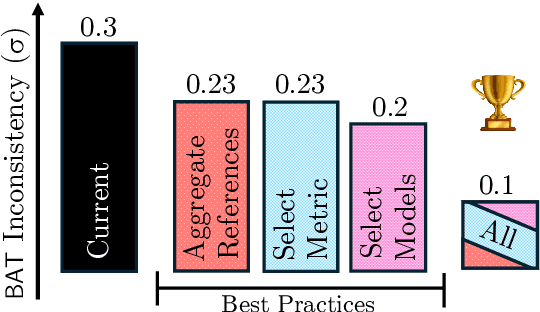
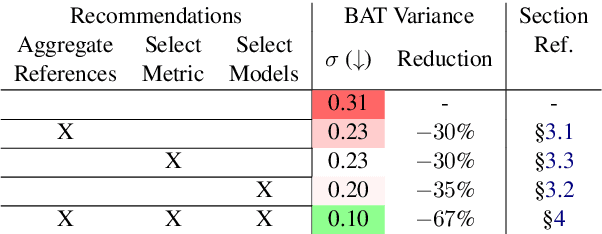
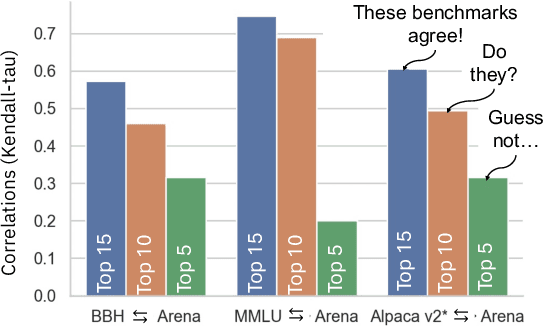
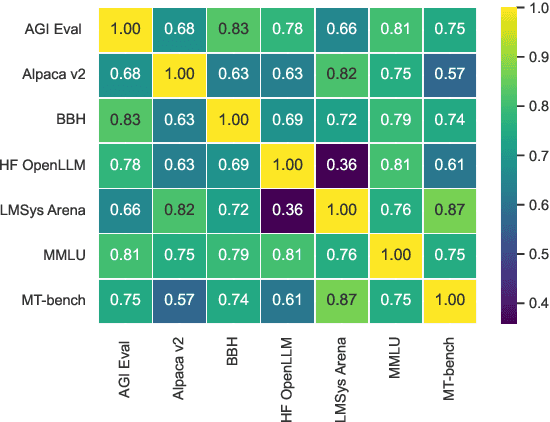
Abstract:Recent advancements in Language Models (LMs) have catalyzed the creation of multiple benchmarks, designed to assess these models' general capabilities. A crucial task, however, is assessing the validity of the benchmarks themselves. This is most commonly done via Benchmark Agreement Testing (BAT), where new benchmarks are validated against established ones using some agreement metric (e.g., rank correlation). Despite the crucial role of BAT for benchmark builders and consumers, there are no standardized procedures for such agreement testing. This deficiency can lead to invalid conclusions, fostering mistrust in benchmarks and upending the ability to properly choose the appropriate benchmark to use. By analyzing over 40 prominent benchmarks, we demonstrate how some overlooked methodological choices can significantly influence BAT results, potentially undermining the validity of conclusions. To address these inconsistencies, we propose a set of best practices for BAT and demonstrate how utilizing these methodologies greatly improves BAT robustness and validity. To foster adoption and facilitate future research,, we introduce BenchBench, a python package for BAT, and release the BenchBench-leaderboard, a meta-benchmark designed to evaluate benchmarks using their peers. Our findings underscore the necessity for standardized BAT, ensuring the robustness and validity of benchmark evaluations in the evolving landscape of language model research. BenchBench Package: https://github.com/IBM/BenchBench Leaderboard: https://huggingface.co/spaces/per/BenchBench
Unitxt: Flexible, Shareable and Reusable Data Preparation and Evaluation for Generative AI
Jan 25, 2024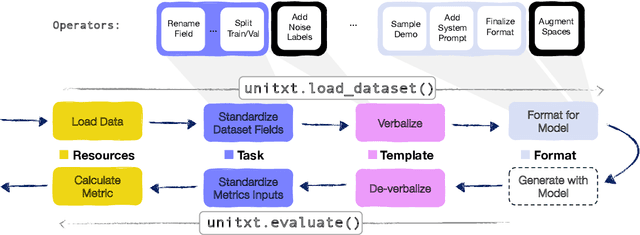

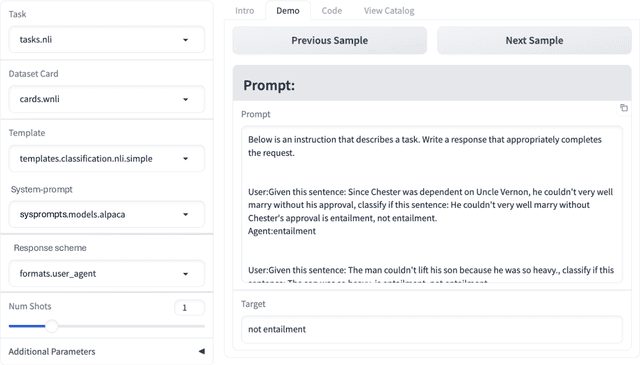

Abstract:In the dynamic landscape of generative NLP, traditional text processing pipelines limit research flexibility and reproducibility, as they are tailored to specific dataset, task, and model combinations. The escalating complexity, involving system prompts, model-specific formats, instructions, and more, calls for a shift to a structured, modular, and customizable solution. Addressing this need, we present Unitxt, an innovative library for customizable textual data preparation and evaluation tailored to generative language models. Unitxt natively integrates with common libraries like HuggingFace and LM-eval-harness and deconstructs processing flows into modular components, enabling easy customization and sharing between practitioners. These components encompass model-specific formats, task prompts, and many other comprehensive dataset processing definitions. The Unitxt-Catalog centralizes these components, fostering collaboration and exploration in modern textual data workflows. Beyond being a tool, Unitxt is a community-driven platform, empowering users to build, share, and advance their pipelines collaboratively. Join the Unitxt community at https://github.com/IBM/unitxt!
Efficient Benchmarking (of Language Models)
Aug 31, 2023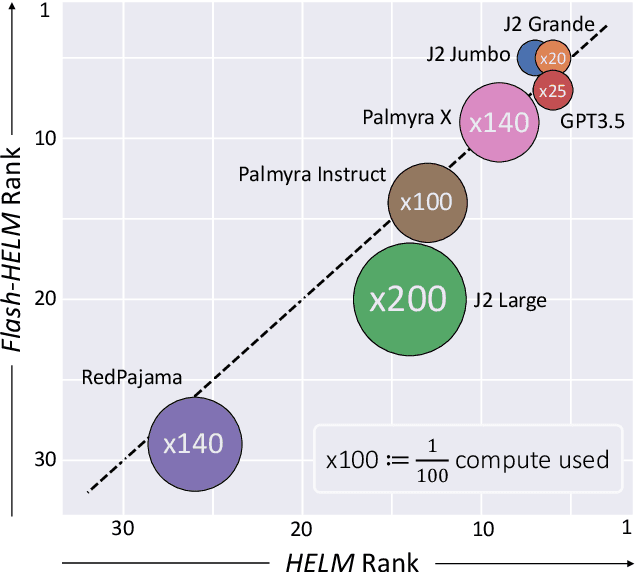
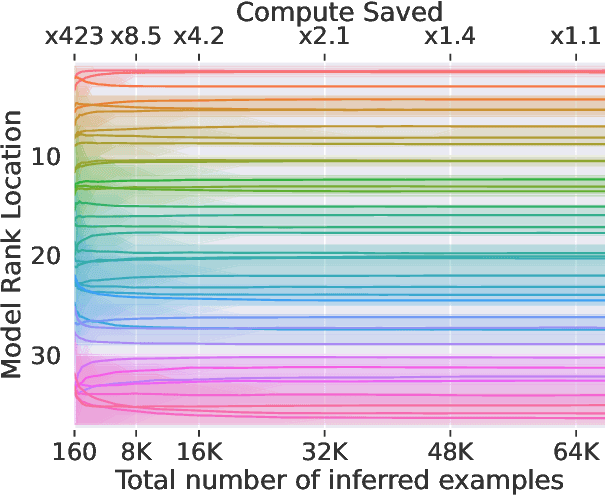
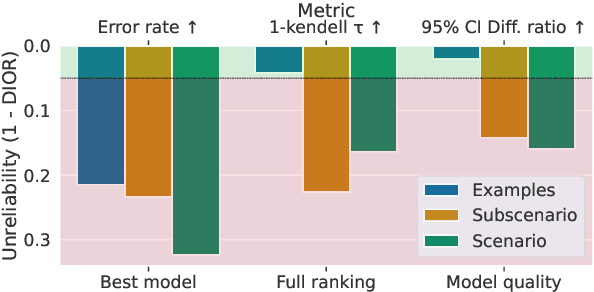
Abstract:The increasing versatility of language models LMs has given rise to a new class of benchmarks that comprehensively assess a broad range of capabilities. Such benchmarks are associated with massive computational costs reaching thousands of GPU hours per model. However the efficiency aspect of these evaluation efforts had raised little discussion in the literature. In this work we present the problem of Efficient Benchmarking namely intelligently reducing the computation costs of LM evaluation without compromising reliability. Using the HELM benchmark as a test case we investigate how different benchmark design choices affect the computation-reliability tradeoff. We propose to evaluate the reliability of such decisions by using a new measure Decision Impact on Reliability DIoR for short. We find for example that the current leader on HELM may change by merely removing a low-ranked model from the benchmark and observe that a handful of examples suffice to obtain the correct benchmark ranking. Conversely a slightly different choice of HELM scenarios varies ranking widely. Based on our findings we outline a set of concrete recommendations for more efficient benchmark design and utilization practices leading to dramatic cost savings with minimal loss of benchmark reliability often reducing computation by x100 or more.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge