Matúš Pikuliak
Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava, Bratislava, Slovakia
GenderBench: Evaluation Suite for Gender Biases in LLMs
May 17, 2025



Abstract:We present GenderBench -- a comprehensive evaluation suite designed to measure gender biases in LLMs. GenderBench includes 14 probes that quantify 19 gender-related harmful behaviors exhibited by LLMs. We release GenderBench as an open-source and extensible library to improve the reproducibility and robustness of benchmarking across the field. We also publish our evaluation of 12 LLMs. Our measurements reveal consistent patterns in their behavior. We show that LLMs struggle with stereotypical reasoning, equitable gender representation in generated texts, and occasionally also with discriminatory behavior in high-stakes scenarios, such as hiring.
Large Language Models for Multilingual Previously Fact-Checked Claim Detection
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:In our era of widespread false information, human fact-checkers often face the challenge of duplicating efforts when verifying claims that may have already been addressed in other countries or languages. As false information transcends linguistic boundaries, the ability to automatically detect previously fact-checked claims across languages has become an increasingly important task. This paper presents the first comprehensive evaluation of large language models (LLMs) for multilingual previously fact-checked claim detection. We assess seven LLMs across 20 languages in both monolingual and cross-lingual settings. Our results show that while LLMs perform well for high-resource languages, they struggle with low-resource languages. Moreover, translating original texts into English proved to be beneficial for low-resource languages. These findings highlight the potential of LLMs for multilingual previously fact-checked claim detection and provide a foundation for further research on this promising application of LLMs.
Generative Large Language Models in Automated Fact-Checking: A Survey
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:The dissemination of false information across online platforms poses a serious societal challenge, necessitating robust measures for information verification. While manual fact-checking efforts are still instrumental, the growing volume of false information requires automated methods. Large language models (LLMs) offer promising opportunities to assist fact-checkers, leveraging LLM's extensive knowledge and robust reasoning capabilities. In this survey paper, we investigate the utilization of generative LLMs in the realm of fact-checking, illustrating various approaches that have been employed and techniques for prompting or fine-tuning LLMs. By providing an overview of existing approaches, this survey aims to improve the understanding of utilizing LLMs in fact-checking and to facilitate further progress in LLMs' involvement in this process.
Women Are Beautiful, Men Are Leaders: Gender Stereotypes in Machine Translation and Language Modeling
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:We present GEST -- a new dataset for measuring gender-stereotypical reasoning in masked LMs and English-to-X machine translation systems. GEST contains samples that are compatible with 9 Slavic languages and English for 16 gender stereotypes about men and women (e.g., Women are beautiful, Men are leaders). The definition of said stereotypes was informed by gender experts. We used GEST to evaluate 11 masked LMs and 4 machine translation systems. We discovered significant and consistent amounts of stereotypical reasoning in almost all the evaluated models and languages.
Disinformation Capabilities of Large Language Models
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:Automated disinformation generation is often listed as one of the risks of large language models (LLMs). The theoretical ability to flood the information space with disinformation content might have dramatic consequences for democratic societies around the world. This paper presents a comprehensive study of the disinformation capabilities of the current generation of LLMs to generate false news articles in English language. In our study, we evaluated the capabilities of 10 LLMs using 20 disinformation narratives. We evaluated several aspects of the LLMs: how well they are at generating news articles, how strongly they tend to agree or disagree with the disinformation narratives, how often they generate safety warnings, etc. We also evaluated the abilities of detection models to detect these articles as LLM-generated. We conclude that LLMs are able to generate convincing news articles that agree with dangerous disinformation narratives.
MULTITuDE: Large-Scale Multilingual Machine-Generated Text Detection Benchmark
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:There is a lack of research into capabilities of recent LLMs to generate convincing text in languages other than English and into performance of detectors of machine-generated text in multilingual settings. This is also reflected in the available benchmarks which lack authentic texts in languages other than English and predominantly cover older generators. To fill this gap, we introduce MULTITuDE, a novel benchmarking dataset for multilingual machine-generated text detection comprising of 74,081 authentic and machine-generated texts in 11 languages (ar, ca, cs, de, en, es, nl, pt, ru, uk, and zh) generated by 8 multilingual LLMs. Using this benchmark, we compare the performance of zero-shot (statistical and black-box) and fine-tuned detectors. Considering the multilinguality, we evaluate 1) how these detectors generalize to unseen languages (linguistically similar as well as dissimilar) and unseen LLMs and 2) whether the detectors improve their performance when trained on multiple languages.
Multilingual Previously Fact-Checked Claim Retrieval
May 13, 2023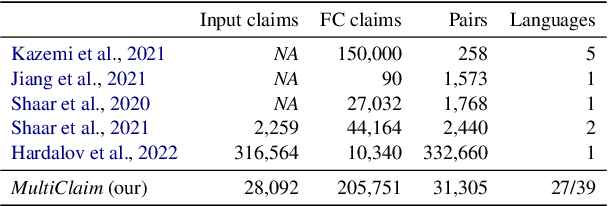



Abstract:Fact-checkers are often hampered by the sheer amount of online content that needs to be fact-checked. NLP can help them by retrieving already existing fact-checks relevant to the content being investigated. This paper introduces a new multilingual dataset -- MultiClaim -- for previously fact-checked claim retrieval. We collected 28k posts in 27 languages from social media, 206k fact-checks in 39 languages written by professional fact-checkers, as well as 31k connections between these two groups. This is the most extensive and the most linguistically diverse dataset of this kind to date. We evaluated how different unsupervised methods fare on this dataset and its various dimensions. We show that evaluating such a diverse dataset has its complexities and proper care needs to be taken before interpreting the results. We also evaluated a supervised fine-tuning approach, improving upon the unsupervised method significantly.
In-Depth Look at Word Filling Societal Bias Measures
Feb 24, 2023Abstract:Many measures of societal bias in language models have been proposed in recent years. A popular approach is to use a set of word filling prompts to evaluate the behavior of the language models. In this work, we analyze the validity of two such measures -- StereoSet and CrowS-Pairs. We show that these measures produce unexpected and illogical results when appropriate control group samples are constructed. Based on this, we believe that they are problematic and using them in the future should be reconsidered. We propose a way forward with an improved testing protocol. Finally, we also introduce a new gender bias dataset for Slovak.
Average Is Not Enough: Caveats of Multilingual Evaluation
Jan 03, 2023Abstract:This position paper discusses the problem of multilingual evaluation. Using simple statistics, such as average language performance, might inject linguistic biases in favor of dominant language families into evaluation methodology. We argue that a qualitative analysis informed by comparative linguistics is needed for multilingual results to detect this kind of bias. We show in our case study that results in published works can indeed be linguistically biased and we demonstrate that visualization based on URIEL typological database can detect it.
SlovakBERT: Slovak Masked Language Model
Sep 30, 2021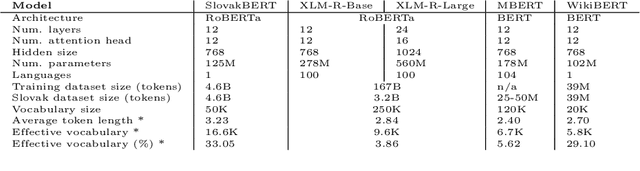
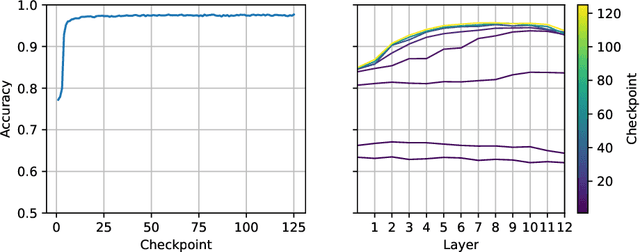

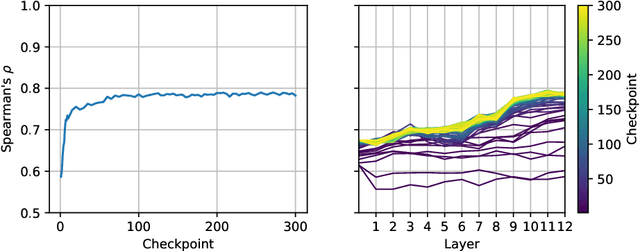
Abstract:We introduce a new Slovak masked language model called SlovakBERT in this paper. It is the first Slovak-only transformers-based model trained on a sizeable corpus. We evaluate the model on several NLP tasks and achieve state-of-the-art results. We publish the masked language model, as well as the subsequently fine-tuned models for part-of-speech tagging, sentiment analysis and semantic textual similarity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge