Robert Moro
Multilingual vs Crosslingual Retrieval of Fact-Checked Claims: A Tale of Two Approaches
May 28, 2025Abstract:Retrieval of previously fact-checked claims is a well-established task, whose automation can assist professional fact-checkers in the initial steps of information verification. Previous works have mostly tackled the task monolingually, i.e., having both the input and the retrieved claims in the same language. However, especially for languages with a limited availability of fact-checks and in case of global narratives, such as pandemics, wars, or international politics, it is crucial to be able to retrieve claims across languages. In this work, we examine strategies to improve the multilingual and crosslingual performance, namely selection of negative examples (in the supervised) and re-ranking (in the unsupervised setting). We evaluate all approaches on a dataset containing posts and claims in 47 languages (283 language combinations). We observe that the best results are obtained by using LLM-based re-ranking, followed by fine-tuning with negative examples sampled using a sentence similarity-based strategy. Most importantly, we show that crosslinguality is a setup with its own unique characteristics compared to the multilingual setup.
SemEval-2025 Task 7: Multilingual and Crosslingual Fact-Checked Claim Retrieval
May 15, 2025Abstract:The rapid spread of online disinformation presents a global challenge, and machine learning has been widely explored as a potential solution. However, multilingual settings and low-resource languages are often neglected in this field. To address this gap, we conducted a shared task on multilingual claim retrieval at SemEval 2025, aimed at identifying fact-checked claims that match newly encountered claims expressed in social media posts across different languages. The task includes two subtracks: (1) a monolingual track, where social posts and claims are in the same language, and (2) a crosslingual track, where social posts and claims might be in different languages. A total of 179 participants registered for the task contributing to 52 test submissions. 23 out of 31 teams have submitted their system papers. In this paper, we report the best-performing systems as well as the most common and the most effective approaches across both subtracks. This shared task, along with its dataset and participating systems, provides valuable insights into multilingual claim retrieval and automated fact-checking, supporting future research in this field.
Eye Movements as Indicators of Deception: A Machine Learning Approach
May 05, 2025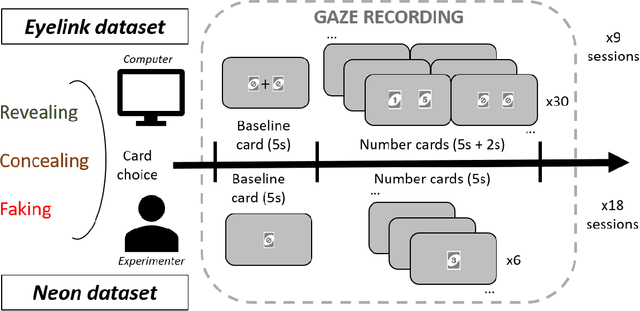
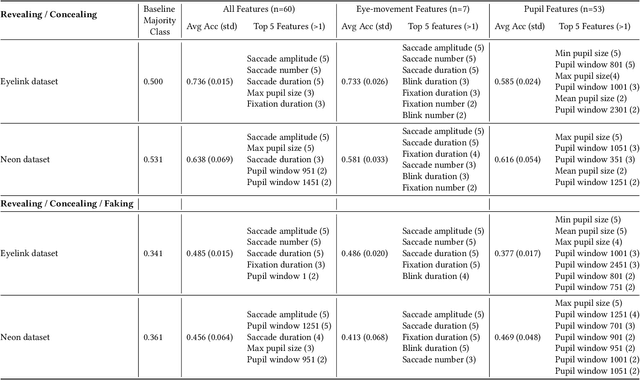
Abstract:Gaze may enhance the robustness of lie detectors but remains under-studied. This study evaluated the efficacy of AI models (using fixations, saccades, blinks, and pupil size) for detecting deception in Concealed Information Tests across two datasets. The first, collected with Eyelink 1000, contains gaze data from a computerized experiment where 87 participants revealed, concealed, or faked the value of a previously selected card. The second, collected with Pupil Neon, involved 36 participants performing a similar task but facing an experimenter. XGBoost achieved accuracies up to 74% in a binary classification task (Revealing vs. Concealing) and 49% in a more challenging three-classification task (Revealing vs. Concealing vs. Faking). Feature analysis identified saccade number, duration, amplitude, and maximum pupil size as the most important for deception prediction. These results demonstrate the feasibility of using gaze and AI to enhance lie detectors and encourage future research that may improve on this.
A Generative-AI-Driven Claim Retrieval System Capable of Detecting and Retrieving Claims from Social Media Platforms in Multiple Languages
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Online disinformation poses a global challenge, placing significant demands on fact-checkers who must verify claims efficiently to prevent the spread of false information. A major issue in this process is the redundant verification of already fact-checked claims, which increases workload and delays responses to newly emerging claims. This research introduces an approach that retrieves previously fact-checked claims, evaluates their relevance to a given input, and provides supplementary information to support fact-checkers. Our method employs large language models (LLMs) to filter irrelevant fact-checks and generate concise summaries and explanations, enabling fact-checkers to faster assess whether a claim has been verified before. In addition, we evaluate our approach through both automatic and human assessments, where humans interact with the developed tool to review its effectiveness. Our results demonstrate that LLMs are able to filter out many irrelevant fact-checks and, therefore, reduce effort and streamline the fact-checking process.
RecGaze: The First Eye Tracking and User Interaction Dataset for Carousel Interfaces
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Carousel interfaces are widely used in e-commerce and streaming services, but little research has been devoted to them. Previous studies of interfaces for presenting search and recommendation results have focused on single ranked lists, but it appears their results cannot be extrapolated to carousels due to the added complexity. Eye tracking is a highly informative approach to understanding how users click, yet there are no eye tracking studies concerning carousels. There are very few interaction datasets on recommenders with carousel interfaces and none that contain gaze data. We introduce the RecGaze dataset: the first comprehensive feedback dataset on carousels that includes eye tracking results, clicks, cursor movements, and selection explanations. The dataset comprises of interactions from 3 movie selection tasks with 40 different carousel interfaces per user. In total, 87 users and 3,477 interactions are logged. In addition to the dataset, its description and possible use cases, we provide results of a survey on carousel design and the first analysis of gaze data on carousels, which reveals a golden triangle or F-pattern browsing behavior. Our work seeks to advance the field of carousel interfaces by providing the first dataset with eye tracking results on carousels. In this manner, we provide and encourage an empirical understanding of interactions with carousel interfaces, for building better recommender systems through gaze information, and also encourage the development of gaze-based recommenders.
Beyond speculation: Measuring the growing presence of LLM-generated texts in multilingual disinformation
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Increased sophistication of large language models (LLMs) and the consequent quality of generated multilingual text raises concerns about potential disinformation misuse. While humans struggle to distinguish LLM-generated content from human-written texts, the scholarly debate about their impact remains divided. Some argue that heightened fears are overblown due to natural ecosystem limitations, while others contend that specific "longtail" contexts face overlooked risks. Our study bridges this debate by providing the first empirical evidence of LLM presence in the latest real-world disinformation datasets, documenting the increase of machine-generated content following ChatGPT's release, and revealing crucial patterns across languages, platforms, and time periods.
Increasing the Robustness of the Fine-tuned Multilingual Machine-Generated Text Detectors
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Since the proliferation of LLMs, there have been concerns about their misuse for harmful content creation and spreading. Recent studies justify such fears, providing evidence of LLM vulnerabilities and high potential of their misuse. Humans are no longer able to distinguish between high-quality machine-generated and authentic human-written texts. Therefore, it is crucial to develop automated means to accurately detect machine-generated content. It would enable to identify such content in online information space, thus providing an additional information about its credibility. This work addresses the problem by proposing a robust fine-tuning process of LLMs for the detection task, making the detectors more robust against obfuscation and more generalizable to out-of-distribution data.
Evaluation of LLM Vulnerabilities to Being Misused for Personalized Disinformation Generation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:The capabilities of recent large language models (LLMs) to generate high-quality content indistinguishable by humans from human-written texts rises many concerns regarding their misuse. Previous research has shown that LLMs can be effectively misused for generating disinformation news articles following predefined narratives. Their capabilities to generate personalized (in various aspects) content have also been evaluated and mostly found usable. However, a combination of personalization and disinformation abilities of LLMs has not been comprehensively studied yet. Such a dangerous combination should trigger integrated safety filters of the LLMs, if there are some. This study fills this gap by evaluation of vulnerabilities of recent open and closed LLMs, and their willingness to generate personalized disinformation news articles in English. We further explore whether the LLMs can reliably meta-evaluate the personalization quality and whether the personalization affects the generated-texts detectability. Our results demonstrate the need for stronger safety-filters and disclaimers, as those are not properly functioning in most of the evaluated LLMs. Additionally, our study revealed that the personalization actually reduces the safety-filter activations; thus effectively functioning as a jailbreak. Such behavior must be urgently addressed by LLM developers and service providers.
A Survey on Automatic Credibility Assessment of Textual Credibility Signals in the Era of Large Language Models
Oct 28, 2024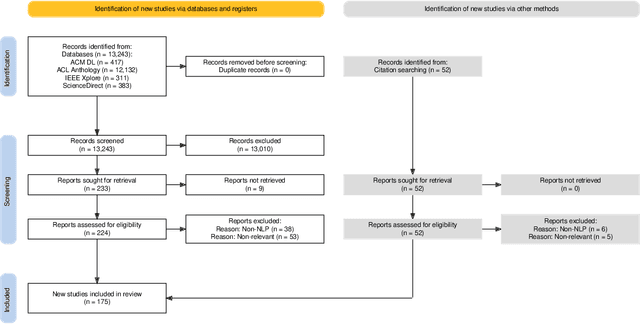
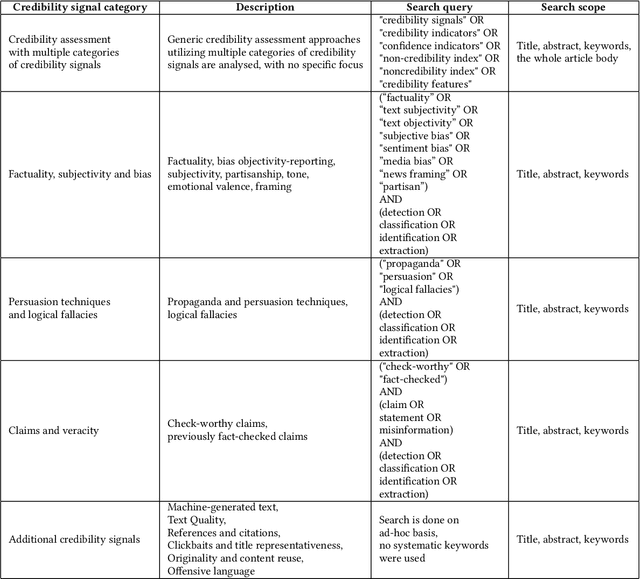
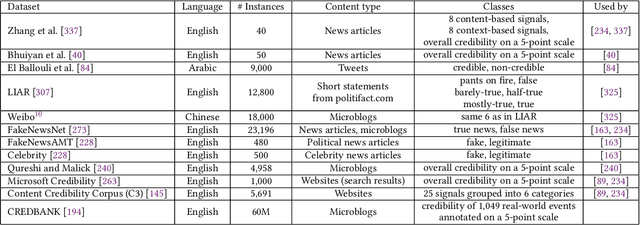
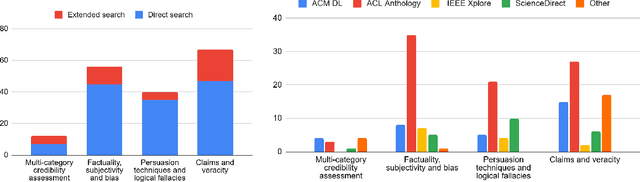
Abstract:In the current era of social media and generative AI, an ability to automatically assess the credibility of online social media content is of tremendous importance. Credibility assessment is fundamentally based on aggregating credibility signals, which refer to small units of information, such as content factuality, bias, or a presence of persuasion techniques, into an overall credibility score. Credibility signals provide a more granular, more easily explainable and widely utilizable information in contrast to currently predominant fake news detection, which utilizes various (mostly latent) features. A growing body of research on automatic credibility assessment and detection of credibility signals can be characterized as highly fragmented and lacking mutual interconnections. This issue is even more prominent due to a lack of an up-to-date overview of research works on automatic credibility assessment. In this survey, we provide such systematic and comprehensive literature review of 175 research papers while focusing on textual credibility signals and Natural Language Processing (NLP), which undergoes a significant advancement due to Large Language Models (LLMs). While positioning the NLP research into the context of other multidisciplinary research works, we tackle with approaches for credibility assessment as well as with 9 categories of credibility signals (we provide a thorough analysis for 3 of them, namely: 1) factuality, subjectivity and bias, 2) persuasion techniques and logical fallacies, and 3) claims and veracity). Following the description of the existing methods, datasets and tools, we identify future challenges and opportunities, while paying a specific attention to recent rapid development of generative AI.
MultiSocial: Multilingual Benchmark of Machine-Generated Text Detection of Social-Media Texts
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Recent LLMs are able to generate high-quality multilingual texts, indistinguishable for humans from authentic human-written ones. Research in machine-generated text detection is however mostly focused on the English language and longer texts, such as news articles, scientific papers or student essays. Social-media texts are usually much shorter and often feature informal language, grammatical errors, or distinct linguistic items (e.g., emoticons, hashtags). There is a gap in studying the ability of existing methods in detection of such texts, reflected also in the lack of existing multilingual benchmark datasets. To fill this gap we propose the first multilingual (22 languages) and multi-platform (5 social media platforms) dataset for benchmarking machine-generated text detection in the social-media domain, called MultiSocial. It contains 472,097 texts, of which about 58k are human-written and approximately the same amount is generated by each of 7 multilingual LLMs. We use this benchmark to compare existing detection methods in zero-shot as well as fine-tuned form. Our results indicate that the fine-tuned detectors have no problem to be trained on social-media texts and that the platform selection for training matters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge