Ivan Srba
Beyond the Checkbox: Strengthening DSA Compliance Through Social Media Algorithmic Auditing
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Algorithms of online platforms are required under the Digital Services Act (DSA) to comply with specific obligations concerning algorithmic transparency, user protection and privacy. To verify compliance with these requirements, DSA mandates platforms to undergo independent audits. Little is known about current auditing practices and their effectiveness in ensuring such compliance. To this end, we bridge regulatory and technical perspectives by critically examining selected audit reports across three critical algorithmic-related provisions: restrictions on profiling minors, transparency in recommender systems, and limitations on targeted advertising using sensitive data. Our analysis shows significant inconsistencies in methodologies and lack of technical depth when evaluating AI-powered systems. To enhance the depth, scale, and independence of compliance assessments, we propose to employ algorithmic auditing -- a process of behavioural assessment of AI algorithms by means of simulating user behaviour, observing algorithm responses and analysing them for audited phenomena.
Better as Generators Than Classifiers: Leveraging LLMs and Synthetic Data for Low-Resource Multilingual Classification
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable multilingual capabilities, making them promising tools in both high- and low-resource languages. One particularly valuable use case is generating synthetic samples that can be used to train smaller models in low-resource scenarios where human-labelled data is scarce. In this work, we investigate whether these synthetic data generation capabilities can serve as a form of distillation, producing smaller models that perform on par with or even better than massive LLMs across languages and tasks. To this end, we use a state-of-the-art multilingual LLM to generate synthetic datasets covering 11 languages and 4 classification tasks. These datasets are then used to train smaller models via fine-tuning or instruction tuning, or as synthetic in-context examples for compact LLMs. Our experiments show that even small amounts of synthetic data enable smaller models to outperform the large generator itself, particularly in low-resource languages. Overall, the results suggest that LLMs are best utilised as generators (teachers) rather than classifiers, producing data that empowers smaller and more efficient multilingual models.
SemEval-2025 Task 7: Multilingual and Crosslingual Fact-Checked Claim Retrieval
May 15, 2025Abstract:The rapid spread of online disinformation presents a global challenge, and machine learning has been widely explored as a potential solution. However, multilingual settings and low-resource languages are often neglected in this field. To address this gap, we conducted a shared task on multilingual claim retrieval at SemEval 2025, aimed at identifying fact-checked claims that match newly encountered claims expressed in social media posts across different languages. The task includes two subtracks: (1) a monolingual track, where social posts and claims are in the same language, and (2) a crosslingual track, where social posts and claims might be in different languages. A total of 179 participants registered for the task contributing to 52 test submissions. 23 out of 31 teams have submitted their system papers. In this paper, we report the best-performing systems as well as the most common and the most effective approaches across both subtracks. This shared task, along with its dataset and participating systems, provides valuable insights into multilingual claim retrieval and automated fact-checking, supporting future research in this field.
Revisiting Algorithmic Audits of TikTok: Poor Reproducibility and Short-term Validity of Findings
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Social media platforms are constantly shifting towards algorithmically curated content based on implicit or explicit user feedback. Regulators, as well as researchers, are calling for systematic social media algorithmic audits as this shift leads to enclosing users in filter bubbles and leading them to more problematic content. An important aspect of such audits is the reproducibility and generalisability of their findings, as it allows to draw verifiable conclusions and audit potential changes in algorithms over time. In this work, we study the reproducibility of the existing sockpuppeting audits of TikTok recommender systems, and the generalizability of their findings. In our efforts to reproduce the previous works, we find multiple challenges stemming from social media platform changes and content evolution, but also the research works themselves. These drawbacks limit the audit reproducibility and require an extensive effort altogether with inevitable adjustments to the auditing methodology. Our experiments also reveal that these one-shot audit findings often hold only in the short term, implying that the reproducibility and generalizability of the audits heavily depend on the methodological choices and the state of algorithms and content on the platform. This highlights the importance of reproducible audits that allow us to determine how the situation changes in time.
Beyond speculation: Measuring the growing presence of LLM-generated texts in multilingual disinformation
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Increased sophistication of large language models (LLMs) and the consequent quality of generated multilingual text raises concerns about potential disinformation misuse. While humans struggle to distinguish LLM-generated content from human-written texts, the scholarly debate about their impact remains divided. Some argue that heightened fears are overblown due to natural ecosystem limitations, while others contend that specific "longtail" contexts face overlooked risks. Our study bridges this debate by providing the first empirical evidence of LLM presence in the latest real-world disinformation datasets, documenting the increase of machine-generated content following ChatGPT's release, and revealing crucial patterns across languages, platforms, and time periods.
Increasing the Robustness of the Fine-tuned Multilingual Machine-Generated Text Detectors
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Since the proliferation of LLMs, there have been concerns about their misuse for harmful content creation and spreading. Recent studies justify such fears, providing evidence of LLM vulnerabilities and high potential of their misuse. Humans are no longer able to distinguish between high-quality machine-generated and authentic human-written texts. Therefore, it is crucial to develop automated means to accurately detect machine-generated content. It would enable to identify such content in online information space, thus providing an additional information about its credibility. This work addresses the problem by proposing a robust fine-tuning process of LLMs for the detection task, making the detectors more robust against obfuscation and more generalizable to out-of-distribution data.
Evaluation of LLM Vulnerabilities to Being Misused for Personalized Disinformation Generation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:The capabilities of recent large language models (LLMs) to generate high-quality content indistinguishable by humans from human-written texts rises many concerns regarding their misuse. Previous research has shown that LLMs can be effectively misused for generating disinformation news articles following predefined narratives. Their capabilities to generate personalized (in various aspects) content have also been evaluated and mostly found usable. However, a combination of personalization and disinformation abilities of LLMs has not been comprehensively studied yet. Such a dangerous combination should trigger integrated safety filters of the LLMs, if there are some. This study fills this gap by evaluation of vulnerabilities of recent open and closed LLMs, and their willingness to generate personalized disinformation news articles in English. We further explore whether the LLMs can reliably meta-evaluate the personalization quality and whether the personalization affects the generated-texts detectability. Our results demonstrate the need for stronger safety-filters and disclaimers, as those are not properly functioning in most of the evaluated LLMs. Additionally, our study revealed that the personalization actually reduces the safety-filter activations; thus effectively functioning as a jailbreak. Such behavior must be urgently addressed by LLM developers and service providers.
A Survey on Automatic Credibility Assessment of Textual Credibility Signals in the Era of Large Language Models
Oct 28, 2024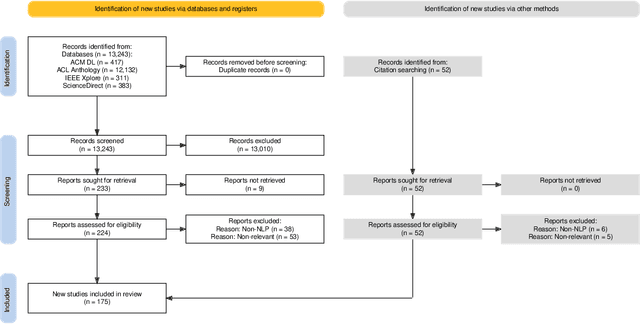
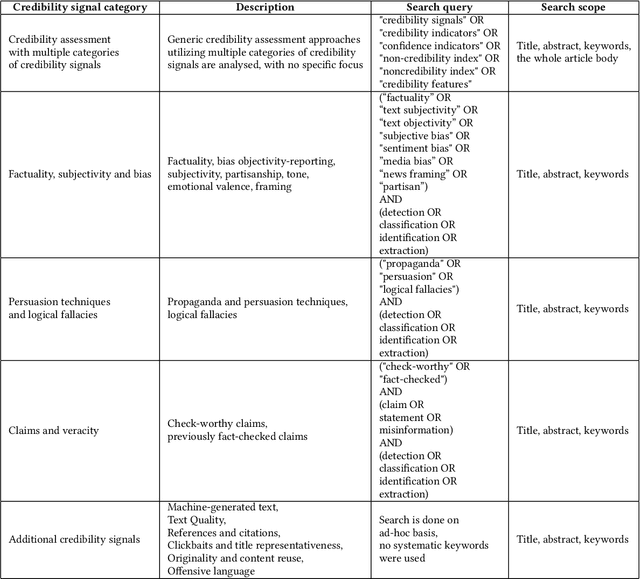
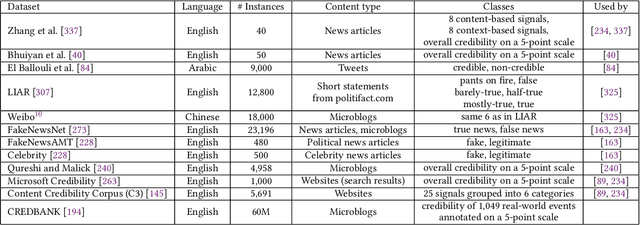
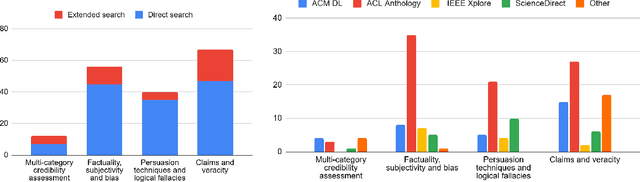
Abstract:In the current era of social media and generative AI, an ability to automatically assess the credibility of online social media content is of tremendous importance. Credibility assessment is fundamentally based on aggregating credibility signals, which refer to small units of information, such as content factuality, bias, or a presence of persuasion techniques, into an overall credibility score. Credibility signals provide a more granular, more easily explainable and widely utilizable information in contrast to currently predominant fake news detection, which utilizes various (mostly latent) features. A growing body of research on automatic credibility assessment and detection of credibility signals can be characterized as highly fragmented and lacking mutual interconnections. This issue is even more prominent due to a lack of an up-to-date overview of research works on automatic credibility assessment. In this survey, we provide such systematic and comprehensive literature review of 175 research papers while focusing on textual credibility signals and Natural Language Processing (NLP), which undergoes a significant advancement due to Large Language Models (LLMs). While positioning the NLP research into the context of other multidisciplinary research works, we tackle with approaches for credibility assessment as well as with 9 categories of credibility signals (we provide a thorough analysis for 3 of them, namely: 1) factuality, subjectivity and bias, 2) persuasion techniques and logical fallacies, and 3) claims and veracity). Following the description of the existing methods, datasets and tools, we identify future challenges and opportunities, while paying a specific attention to recent rapid development of generative AI.
Use Random Selection for Now: Investigation of Few-Shot Selection Strategies in LLM-based Text Augmentation for Classification
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:The generative large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used for data augmentation tasks, where text samples are paraphrased (or generated anew) and then used for classifier fine-tuning. Existing works on augmentation leverage the few-shot scenarios, where samples are given to LLMs as part of prompts, leading to better augmentations. Yet, the samples are mostly selected randomly and a comprehensive overview of the effects of other (more ``informed'') sample selection strategies is lacking. In this work, we compare sample selection strategies existing in few-shot learning literature and investigate their effects in LLM-based textual augmentation. We evaluate this on in-distribution and out-of-distribution classifier performance. Results indicate, that while some ``informed'' selection strategies increase the performance of models, especially for out-of-distribution data, it happens only seldom and with marginal performance increases. Unless further advances are made, a default of random sample selection remains a good option for augmentation practitioners.
Task Prompt Vectors: Effective Initialization through Multi-Task Soft-Prompt Transfer
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Prompt tuning is a modular and efficient solution for training large language models (LLMs). One of its main advantages is task modularity, making it suitable for multi-task problems. However, current soft-prompt-based methods often sacrifice multi-task modularity, requiring the training process to be fully or partially repeated for each newly added task. While recent work on task vectors applied arithmetic operations on full model weights to achieve the desired multi-task performance, a similar approach for soft-prompts is still missing. To this end, we introduce Task Prompt Vectors, created by element-wise difference between weights of tuned soft-prompts and their random initialization. Experimental results on 12 NLU datasets show that task prompt vectors can be used in low-resource settings to effectively initialize prompt tuning on similar tasks. In addition, we show that task prompt vectors are independent of the random initialization of prompt tuning. This allows prompt arithmetics with the pre-trained vectors from different tasks. In this way, by arithmetic addition of task prompt vectors from multiple tasks, we are able to outperform a state-of-the-art baseline in some cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge