Malu Zhang
Hyperspectral Image Fusion with Spectral-Band and Fusion-Scale Agnosticism
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Current deep learning models for Multispectral and Hyperspectral Image Fusion (MS/HS fusion) are typically designed for fixed spectral bands and spatial scales, which limits their transferability across diverse sensors. To address this, we propose SSA, a universal framework for MS/HS fusion with spectral-band and fusion-scale agnosticism. Specifically, we introduce Matryoshka Kernel (MK), a novel operator that enables a single model to adapt to arbitrary numbers of spectral channels. Meanwhile, we build SSA upon an Implicit Neural Representation (INR) backbone that models the HS signal as a continuous function, enabling reconstruction at arbitrary spatial resolutions. Together, these two forms of agnosticism enable a single MS/HS fusion model that generalizes effectively to unseen sensors and spatial scales. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our single model achieves state-of-the-art performance while generalizing well to unseen sensors and scales, paving the way toward future HS foundation models.
BSO: Binary Spiking Online Optimization Algorithm
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Binary Spiking Neural Networks (BSNNs) offer promising efficiency advantages for resource-constrained computing. However, their training algorithms often require substantial memory overhead due to latent weights storage and temporal processing requirements. To address this issue, we propose Binary Spiking Online (BSO) optimization algorithm, a novel online training algorithm that significantly reduces training memory. BSO directly updates weights through flip signals under the online training framework. These signals are triggered when the product of gradient momentum and weights exceeds a threshold, eliminating the need for latent weights during training. To enhance performance, we propose T-BSO, a temporal-aware variant that leverages the inherent temporal dynamics of BSNNs by capturing gradient information across time steps for adaptive threshold adjustment. Theoretical analysis establishes convergence guarantees for both BSO and T-BSO, with formal regret bounds characterizing their convergence rates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that both BSO and T-BSO achieve superior optimization performance compared to existing training methods for BSNNs. The codes are available at https://github.com/hamings1/BSO.
Training-Free ANN-to-SNN Conversion for High-Performance Spiking Transformer
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Leveraging the event-driven paradigm, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offer a promising approach for constructing energy-efficient Transformer architectures. Compared to directly trained Spiking Transformers, ANN-to-SNN conversion methods bypass the high training costs. However, existing methods still suffer from notable limitations, failing to effectively handle nonlinear operations in Transformer architectures and requiring additional fine-tuning processes for pre-trained ANNs. To address these issues, we propose a high-performance and training-free ANN-to-SNN conversion framework tailored for Transformer architectures. Specifically, we introduce a Multi-basis Exponential Decay (MBE) neuron, which employs an exponential decay strategy and multi-basis encoding method to efficiently approximate various nonlinear operations. It removes the requirement for weight modifications in pre-trained ANNs. Extensive experiments across diverse tasks (CV, NLU, NLG) and mainstream Transformer architectures (ViT, RoBERTa, GPT-2) demonstrate that our method achieves near-lossless conversion accuracy with significantly lower latency. This provides a promising pathway for the efficient and scalable deployment of Spiking Transformers in real-world applications.
What Is Next for LLMs? Next-Generation AI Computing Hardware Using Photonic Chips
May 09, 2025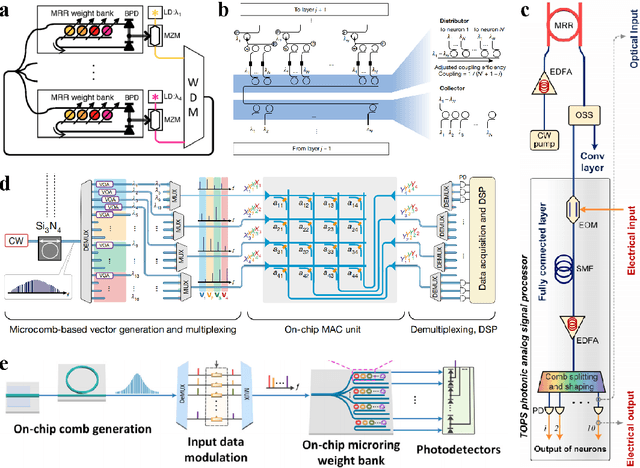
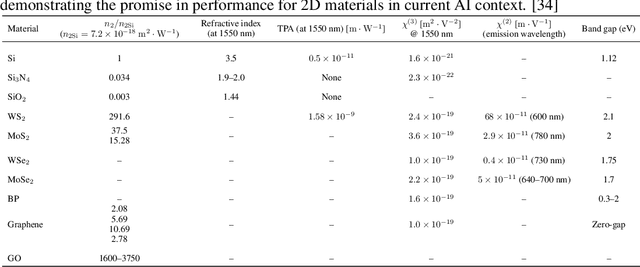
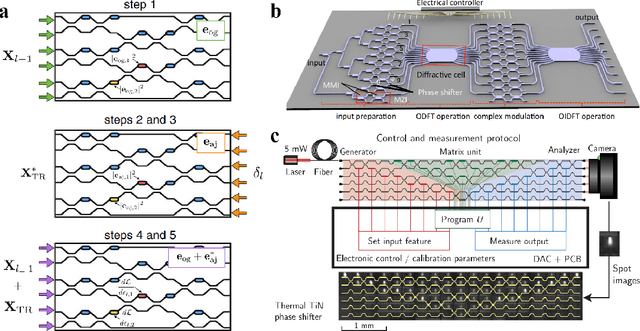
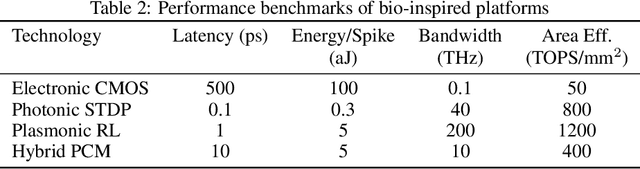
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly pushing the limits of contemporary computing hardware. For example, training GPT-3 has been estimated to consume around 1300 MWh of electricity, and projections suggest future models may require city-scale (gigawatt) power budgets. These demands motivate exploration of computing paradigms beyond conventional von Neumann architectures. This review surveys emerging photonic hardware optimized for next-generation generative AI computing. We discuss integrated photonic neural network architectures (e.g., Mach-Zehnder interferometer meshes, lasers, wavelength-multiplexed microring resonators) that perform ultrafast matrix operations. We also examine promising alternative neuromorphic devices, including spiking neural network circuits and hybrid spintronic-photonic synapses, which combine memory and processing. The integration of two-dimensional materials (graphene, TMDCs) into silicon photonic platforms is reviewed for tunable modulators and on-chip synaptic elements. Transformer-based LLM architectures (self-attention and feed-forward layers) are analyzed in this context, identifying strategies and challenges for mapping dynamic matrix multiplications onto these novel hardware substrates. We then dissect the mechanisms of mainstream LLMs, such as ChatGPT, DeepSeek, and LLaMA, highlighting their architectural similarities and differences. We synthesize state-of-the-art components, algorithms, and integration methods, highlighting key advances and open issues in scaling such systems to mega-sized LLM models. We find that photonic computing systems could potentially surpass electronic processors by orders of magnitude in throughput and energy efficiency, but require breakthroughs in memory, especially for long-context windows and long token sequences, and in storage of ultra-large datasets.
Towards Accurate Binary Spiking Neural Networks: Learning with Adaptive Gradient Modulation Mechanism
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Binary Spiking Neural Networks (BSNNs) inherit the eventdriven paradigm of SNNs, while also adopting the reduced storage burden of binarization techniques. These distinct advantages grant BSNNs lightweight and energy-efficient characteristics, rendering them ideal for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. However, due to the binary synaptic weights and non-differentiable spike function, effectively training BSNNs remains an open question. In this paper, we conduct an in-depth analysis of the challenge for BSNN learning, namely the frequent weight sign flipping problem. To mitigate this issue, we propose an Adaptive Gradient Modulation Mechanism (AGMM), which is designed to reduce the frequency of weight sign flipping by adaptively adjusting the gradients during the learning process. The proposed AGMM can enable BSNNs to achieve faster convergence speed and higher accuracy, effectively narrowing the gap between BSNNs and their full-precision equivalents. We validate AGMM on both static and neuromorphic datasets, and results indicate that it achieves state-of-the-art results among BSNNs. This work substantially reduces storage demands and enhances SNNs' inherent energy efficiency, making them highly feasible for resource-constrained environments.
Spiking Vision Transformer with Saccadic Attention
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:The combination of Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) holds potential for achieving both energy efficiency and high performance, particularly suitable for edge vision applications. However, a significant performance gap still exists between SNN-based ViTs and their ANN counterparts. Here, we first analyze why SNN-based ViTs suffer from limited performance and identify a mismatch between the vanilla self-attention mechanism and spatio-temporal spike trains. This mismatch results in degraded spatial relevance and limited temporal interactions. To address these issues, we draw inspiration from biological saccadic attention mechanisms and introduce an innovative Saccadic Spike Self-Attention (SSSA) method. Specifically, in the spatial domain, SSSA employs a novel spike distribution-based method to effectively assess the relevance between Query and Key pairs in SNN-based ViTs. Temporally, SSSA employs a saccadic interaction module that dynamically focuses on selected visual areas at each timestep and significantly enhances whole scene understanding through temporal interactions. Building on the SSSA mechanism, we develop a SNN-based Vision Transformer (SNN-ViT). Extensive experiments across various visual tasks demonstrate that SNN-ViT achieves state-of-the-art performance with linear computational complexity. The effectiveness and efficiency of the SNN-ViT highlight its potential for power-critical edge vision applications.
QP-SNN: Quantized and Pruned Spiking Neural Networks
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Brain-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) leverage sparse spikes to encode information and operate in an asynchronous event-driven manner, offering a highly energy-efficient paradigm for machine intelligence. However, the current SNN community focuses primarily on performance improvement by developing large-scale models, which limits the applicability of SNNs in resource-limited edge devices. In this paper, we propose a hardware-friendly and lightweight SNN, aimed at effectively deploying high-performance SNN in resource-limited scenarios. Specifically, we first develop a baseline model that integrates uniform quantization and structured pruning, called QP-SNN baseline. While this baseline significantly reduces storage demands and computational costs, it suffers from performance decline. To address this, we conduct an in-depth analysis of the challenges in quantization and pruning that lead to performance degradation and propose solutions to enhance the baseline's performance. For weight quantization, we propose a weight rescaling strategy that utilizes bit width more effectively to enhance the model's representation capability. For structured pruning, we propose a novel pruning criterion using the singular value of spatiotemporal spike activities to enable more accurate removal of redundant kernels. Extensive experiments demonstrate that integrating two proposed methods into the baseline allows QP-SNN to achieve state-of-the-art performance and efficiency, underscoring its potential for enhancing SNN deployment in edge intelligence computing.
Mixed-Precision Graph Neural Quantization for Low Bit Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) is pivotal for deploying large language models (LLMs) within resource-limited settings by significantly reducing resource demands. However, existing PTQ strategies underperform at low bit levels < 3 bits due to the significant difference between the quantized and original weights. To enhance the quantization performance at low bit widths, we introduce a Mixed-precision Graph Neural PTQ (MG-PTQ) approach, employing a graph neural network (GNN) module to capture dependencies among weights and adaptively assign quantization bit-widths. Through the information propagation of the GNN module, our method more effectively captures dependencies among target weights, leading to a more accurate assessment of weight importance and optimized allocation of quantization strategies. Extensive experiments on the WikiText2 and C4 datasets demonstrate that our MG-PTQ method outperforms previous state-of-the-art PTQ method GPTQ, setting new benchmarks for quantization performance under low-bit conditions.
Binary Event-Driven Spiking Transformer
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Transformer-based Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) introduce a novel event-driven self-attention paradigm that combines the high performance of Transformers with the energy efficiency of SNNs. However, the larger model size and increased computational demands of the Transformer structure limit their practicality in resource-constrained scenarios. In this paper, we integrate binarization techniques into Transformer-based SNNs and propose the Binary Event-Driven Spiking Transformer, i.e. BESTformer. The proposed BESTformer can significantly reduce storage and computational demands by representing weights and attention maps with a mere 1-bit. However, BESTformer suffers from a severe performance drop from its full-precision counterpart due to the limited representation capability of binarization. To address this issue, we propose a Coupled Information Enhancement (CIE) method, which consists of a reversible framework and information enhancement distillation. By maximizing the mutual information between the binary model and its full-precision counterpart, the CIE method effectively mitigates the performance degradation of the BESTformer. Extensive experiments on static and neuromorphic datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance to other binary SNNs, showcasing its potential as a compact yet high-performance model for resource-limited edge devices.
A Compressive Memory-based Retrieval Approach for Event Argument Extraction
Sep 14, 2024



Abstract:Recent works have demonstrated the effectiveness of retrieval augmentation in the Event Argument Extraction (EAE) task. However, existing retrieval-based EAE methods have two main limitations: (1) input length constraints and (2) the gap between the retriever and the inference model. These issues limit the diversity and quality of the retrieved information. In this paper, we propose a Compressive Memory-based Retrieval (CMR) mechanism for EAE, which addresses the two limitations mentioned above. Our compressive memory, designed as a dynamic matrix that effectively caches retrieved information and supports continuous updates, overcomes the limitations of the input length. Additionally, after pre-loading all candidate demonstrations into the compressive memory, the model further retrieves and filters relevant information from memory based on the input query, bridging the gap between the retriever and the inference model. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves new state-of-the-art performance on three public datasets (RAMS, WikiEvents, ACE05), significantly outperforming existing retrieval-based EAE methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge