Wenjie Wei
BSO: Binary Spiking Online Optimization Algorithm
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Binary Spiking Neural Networks (BSNNs) offer promising efficiency advantages for resource-constrained computing. However, their training algorithms often require substantial memory overhead due to latent weights storage and temporal processing requirements. To address this issue, we propose Binary Spiking Online (BSO) optimization algorithm, a novel online training algorithm that significantly reduces training memory. BSO directly updates weights through flip signals under the online training framework. These signals are triggered when the product of gradient momentum and weights exceeds a threshold, eliminating the need for latent weights during training. To enhance performance, we propose T-BSO, a temporal-aware variant that leverages the inherent temporal dynamics of BSNNs by capturing gradient information across time steps for adaptive threshold adjustment. Theoretical analysis establishes convergence guarantees for both BSO and T-BSO, with formal regret bounds characterizing their convergence rates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that both BSO and T-BSO achieve superior optimization performance compared to existing training methods for BSNNs. The codes are available at https://github.com/hamings1/BSO.
Training-Free ANN-to-SNN Conversion for High-Performance Spiking Transformer
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Leveraging the event-driven paradigm, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offer a promising approach for constructing energy-efficient Transformer architectures. Compared to directly trained Spiking Transformers, ANN-to-SNN conversion methods bypass the high training costs. However, existing methods still suffer from notable limitations, failing to effectively handle nonlinear operations in Transformer architectures and requiring additional fine-tuning processes for pre-trained ANNs. To address these issues, we propose a high-performance and training-free ANN-to-SNN conversion framework tailored for Transformer architectures. Specifically, we introduce a Multi-basis Exponential Decay (MBE) neuron, which employs an exponential decay strategy and multi-basis encoding method to efficiently approximate various nonlinear operations. It removes the requirement for weight modifications in pre-trained ANNs. Extensive experiments across diverse tasks (CV, NLU, NLG) and mainstream Transformer architectures (ViT, RoBERTa, GPT-2) demonstrate that our method achieves near-lossless conversion accuracy with significantly lower latency. This provides a promising pathway for the efficient and scalable deployment of Spiking Transformers in real-world applications.
What Is Next for LLMs? Next-Generation AI Computing Hardware Using Photonic Chips
May 09, 2025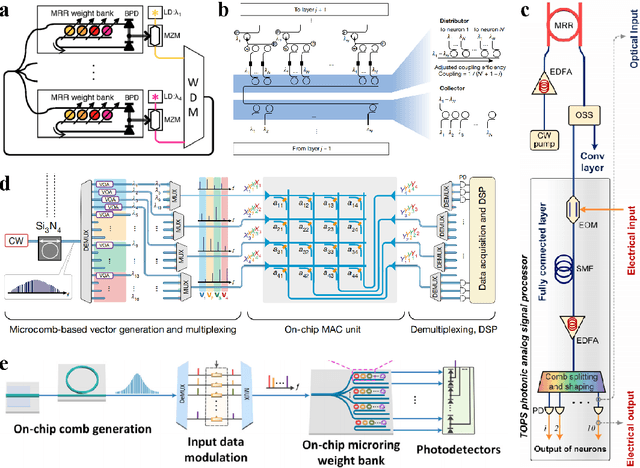
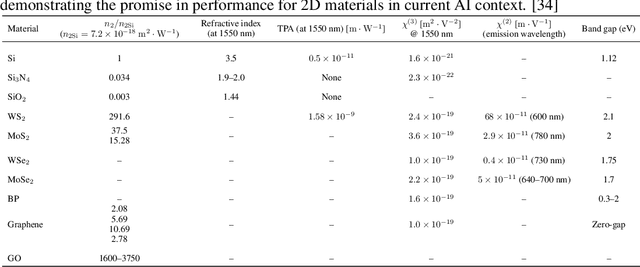
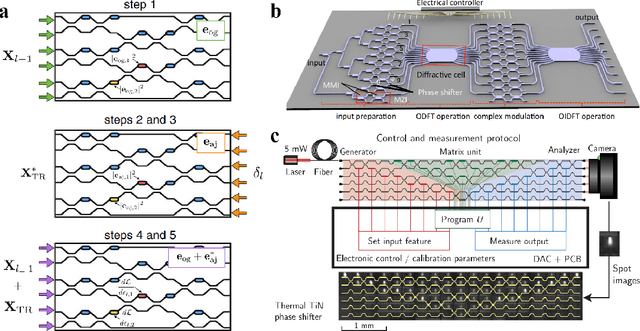
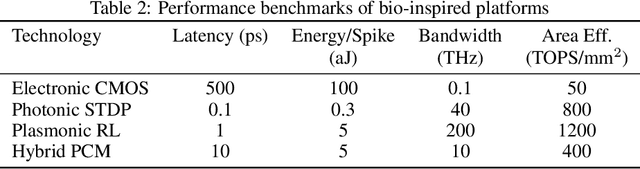
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly pushing the limits of contemporary computing hardware. For example, training GPT-3 has been estimated to consume around 1300 MWh of electricity, and projections suggest future models may require city-scale (gigawatt) power budgets. These demands motivate exploration of computing paradigms beyond conventional von Neumann architectures. This review surveys emerging photonic hardware optimized for next-generation generative AI computing. We discuss integrated photonic neural network architectures (e.g., Mach-Zehnder interferometer meshes, lasers, wavelength-multiplexed microring resonators) that perform ultrafast matrix operations. We also examine promising alternative neuromorphic devices, including spiking neural network circuits and hybrid spintronic-photonic synapses, which combine memory and processing. The integration of two-dimensional materials (graphene, TMDCs) into silicon photonic platforms is reviewed for tunable modulators and on-chip synaptic elements. Transformer-based LLM architectures (self-attention and feed-forward layers) are analyzed in this context, identifying strategies and challenges for mapping dynamic matrix multiplications onto these novel hardware substrates. We then dissect the mechanisms of mainstream LLMs, such as ChatGPT, DeepSeek, and LLaMA, highlighting their architectural similarities and differences. We synthesize state-of-the-art components, algorithms, and integration methods, highlighting key advances and open issues in scaling such systems to mega-sized LLM models. We find that photonic computing systems could potentially surpass electronic processors by orders of magnitude in throughput and energy efficiency, but require breakthroughs in memory, especially for long-context windows and long token sequences, and in storage of ultra-large datasets.
Towards Accurate Binary Spiking Neural Networks: Learning with Adaptive Gradient Modulation Mechanism
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Binary Spiking Neural Networks (BSNNs) inherit the eventdriven paradigm of SNNs, while also adopting the reduced storage burden of binarization techniques. These distinct advantages grant BSNNs lightweight and energy-efficient characteristics, rendering them ideal for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. However, due to the binary synaptic weights and non-differentiable spike function, effectively training BSNNs remains an open question. In this paper, we conduct an in-depth analysis of the challenge for BSNN learning, namely the frequent weight sign flipping problem. To mitigate this issue, we propose an Adaptive Gradient Modulation Mechanism (AGMM), which is designed to reduce the frequency of weight sign flipping by adaptively adjusting the gradients during the learning process. The proposed AGMM can enable BSNNs to achieve faster convergence speed and higher accuracy, effectively narrowing the gap between BSNNs and their full-precision equivalents. We validate AGMM on both static and neuromorphic datasets, and results indicate that it achieves state-of-the-art results among BSNNs. This work substantially reduces storage demands and enhances SNNs' inherent energy efficiency, making them highly feasible for resource-constrained environments.
QP-SNN: Quantized and Pruned Spiking Neural Networks
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Brain-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) leverage sparse spikes to encode information and operate in an asynchronous event-driven manner, offering a highly energy-efficient paradigm for machine intelligence. However, the current SNN community focuses primarily on performance improvement by developing large-scale models, which limits the applicability of SNNs in resource-limited edge devices. In this paper, we propose a hardware-friendly and lightweight SNN, aimed at effectively deploying high-performance SNN in resource-limited scenarios. Specifically, we first develop a baseline model that integrates uniform quantization and structured pruning, called QP-SNN baseline. While this baseline significantly reduces storage demands and computational costs, it suffers from performance decline. To address this, we conduct an in-depth analysis of the challenges in quantization and pruning that lead to performance degradation and propose solutions to enhance the baseline's performance. For weight quantization, we propose a weight rescaling strategy that utilizes bit width more effectively to enhance the model's representation capability. For structured pruning, we propose a novel pruning criterion using the singular value of spatiotemporal spike activities to enable more accurate removal of redundant kernels. Extensive experiments demonstrate that integrating two proposed methods into the baseline allows QP-SNN to achieve state-of-the-art performance and efficiency, underscoring its potential for enhancing SNN deployment in edge intelligence computing.
Binary Event-Driven Spiking Transformer
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Transformer-based Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) introduce a novel event-driven self-attention paradigm that combines the high performance of Transformers with the energy efficiency of SNNs. However, the larger model size and increased computational demands of the Transformer structure limit their practicality in resource-constrained scenarios. In this paper, we integrate binarization techniques into Transformer-based SNNs and propose the Binary Event-Driven Spiking Transformer, i.e. BESTformer. The proposed BESTformer can significantly reduce storage and computational demands by representing weights and attention maps with a mere 1-bit. However, BESTformer suffers from a severe performance drop from its full-precision counterpart due to the limited representation capability of binarization. To address this issue, we propose a Coupled Information Enhancement (CIE) method, which consists of a reversible framework and information enhancement distillation. By maximizing the mutual information between the binary model and its full-precision counterpart, the CIE method effectively mitigates the performance degradation of the BESTformer. Extensive experiments on static and neuromorphic datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance to other binary SNNs, showcasing its potential as a compact yet high-performance model for resource-limited edge devices.
Q-SNNs: Quantized Spiking Neural Networks
Jun 19, 2024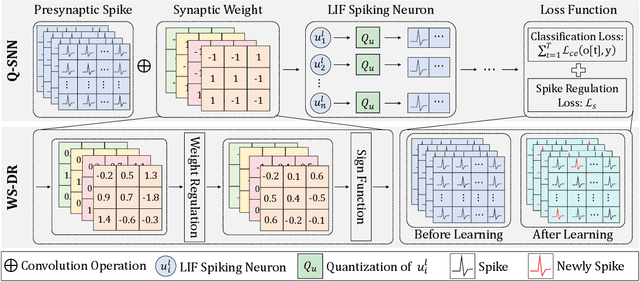
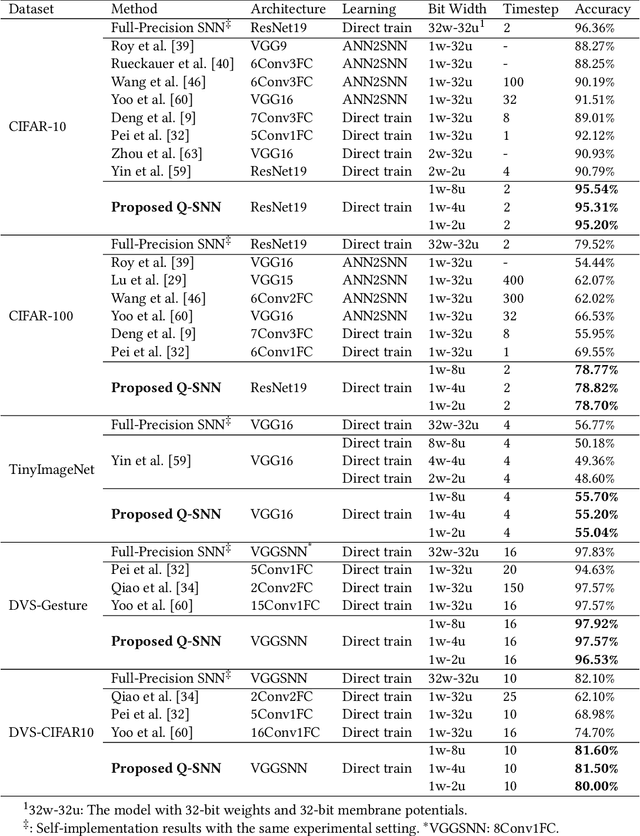
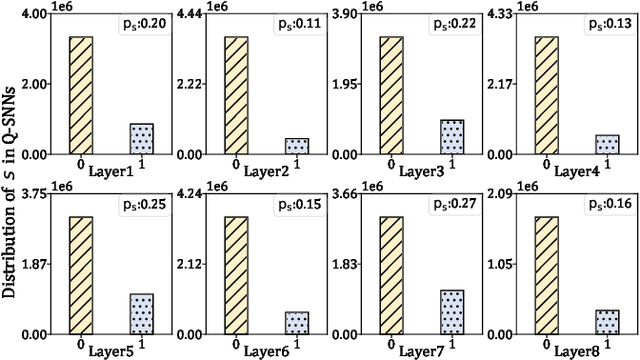
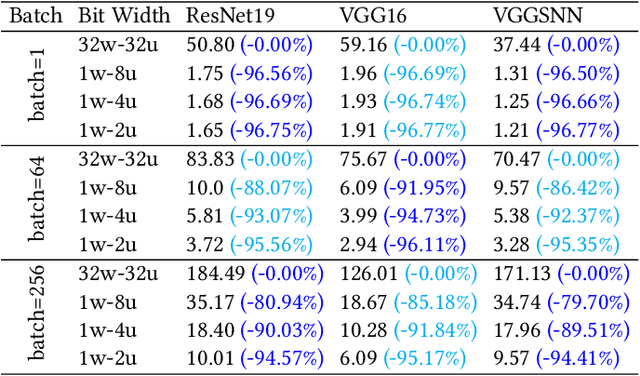
Abstract:Brain-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) leverage sparse spikes to represent information and process them in an asynchronous event-driven manner, offering an energy-efficient paradigm for the next generation of machine intelligence. However, the current focus within the SNN community prioritizes accuracy optimization through the development of large-scale models, limiting their viability in resource-constrained and low-power edge devices. To address this challenge, we introduce a lightweight and hardware-friendly Quantized SNN (Q-SNN) that applies quantization to both synaptic weights and membrane potentials. By significantly compressing these two key elements, the proposed Q-SNNs substantially reduce both memory usage and computational complexity. Moreover, to prevent the performance degradation caused by this compression, we present a new Weight-Spike Dual Regulation (WS-DR) method inspired by information entropy theory. Experimental evaluations on various datasets, including static and neuromorphic, demonstrate that our Q-SNNs outperform existing methods in terms of both model size and accuracy. These state-of-the-art results in efficiency and efficacy suggest that the proposed method can significantly improve edge intelligent computing.
Global-Local Convolution with Spiking Neural Networks for Energy-efficient Keyword Spotting
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:Thanks to Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), the accuracy of Keyword Spotting (KWS) has made substantial progress. However, as KWS systems are usually implemented on edge devices, energy efficiency becomes a critical requirement besides performance. Here, we take advantage of spiking neural networks' energy efficiency and propose an end-to-end lightweight KWS model. The model consists of two innovative modules: 1) Global-Local Spiking Convolution (GLSC) module and 2) Bottleneck-PLIF module. Compared to the hand-crafted feature extraction methods, the GLSC module achieves speech feature extraction that is sparser, more energy-efficient, and yields better performance. The Bottleneck-PLIF module further processes the signals from GLSC with the aim to achieve higher accuracy with fewer parameters. Extensive experiments are conducted on the Google Speech Commands Dataset (V1 and V2). The results show our method achieves competitive performance among SNN-based KWS models with fewer parameters.
Sensitivity-Informed Augmentation for Robust Segmentation
Jun 04, 2024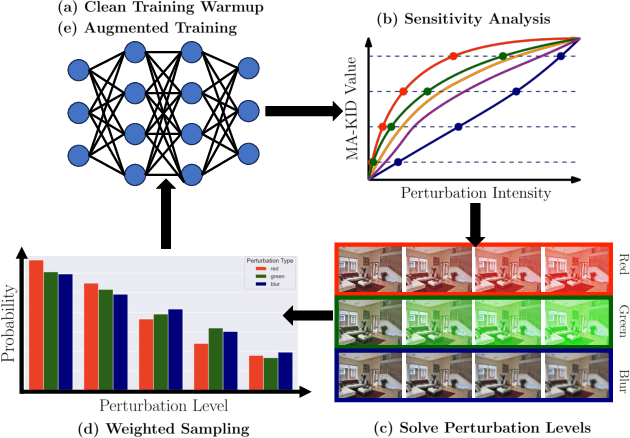
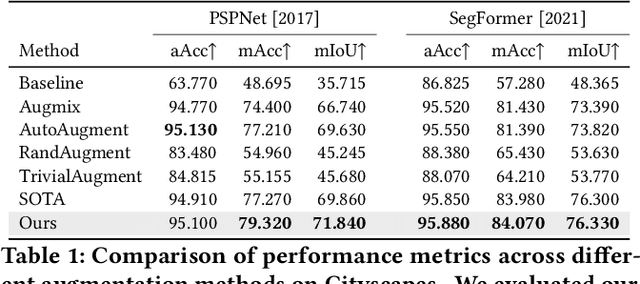
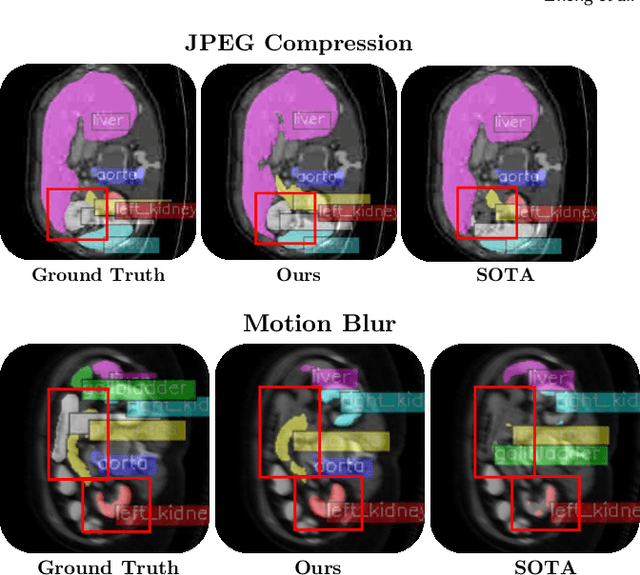
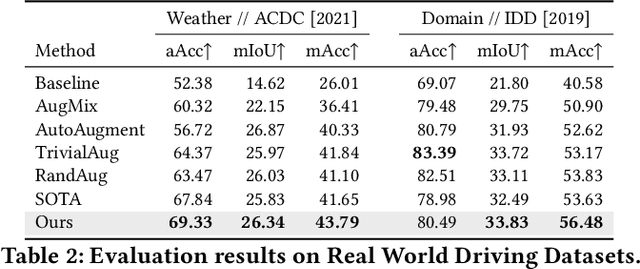
Abstract:Segmentation is an integral module in many visual computing applications such as virtual try-on, medical imaging, autonomous driving, and agricultural automation. These applications often involve either widespread consumer use or highly variable environments, both of which can degrade the quality of visual sensor data, whether from a common mobile phone or an expensive satellite imaging camera. In addition to external noises like user difference or weather conditions, internal noises such as variations in camera quality or lens distortion can affect the performance of segmentation models during both development and deployment. In this work, we present an efficient, adaptable, and gradient-free method to enhance the robustness of learning-based segmentation models across training. First, we introduce a novel adaptive sensitivity analysis (ASA) using Kernel Inception Distance (KID) on basis perturbations to benchmark perturbation sensitivity of pre-trained segmentation models. Then, we model the sensitivity curve using the adaptive SA and sample perturbation hyperparameter values accordingly. Finally, we conduct adversarial training with the selected perturbation values and dynamically re-evaluate robustness during online training. Our method, implemented end-to-end with minimal fine-tuning required, consistently outperforms state-of-the-art data augmentation techniques for segmentation. It shows significant improvement in both clean data evaluation and real-world adverse scenario evaluation across various segmentation datasets used in visual computing and computer graphics applications.
Event-Driven Learning for Spiking Neural Networks
Mar 01, 2024


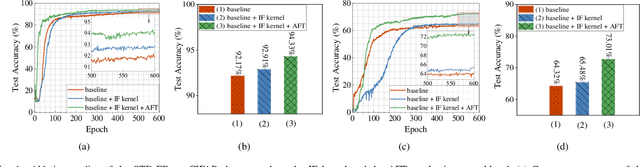
Abstract:Brain-inspired spiking neural networks (SNNs) have gained prominence in the field of neuromorphic computing owing to their low energy consumption during feedforward inference on neuromorphic hardware. However, it remains an open challenge how to effectively benefit from the sparse event-driven property of SNNs to minimize backpropagation learning costs. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive examination of the existing event-driven learning algorithms, reveal their limitations, and propose novel solutions to overcome them. Specifically, we introduce two novel event-driven learning methods: the spike-timing-dependent event-driven (STD-ED) and membrane-potential-dependent event-driven (MPD-ED) algorithms. These proposed algorithms leverage precise neuronal spike timing and membrane potential, respectively, for effective learning. The two methods are extensively evaluated on static and neuromorphic datasets to confirm their superior performance. They outperform existing event-driven counterparts by up to 2.51% for STD-ED and 6.79% for MPD-ED on the CIFAR-100 dataset. In addition, we theoretically and experimentally validate the energy efficiency of our methods on neuromorphic hardware. On-chip learning experiments achieved a remarkable 30-fold reduction in energy consumption over time-step-based surrogate gradient methods. The demonstrated efficiency and efficacy of the proposed event-driven learning methods emphasize their potential to significantly advance the fields of neuromorphic computing, offering promising avenues for energy-efficiency applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge