Lena Dankin
TAU-CS
Conversational Prompt Engineering
Aug 08, 2024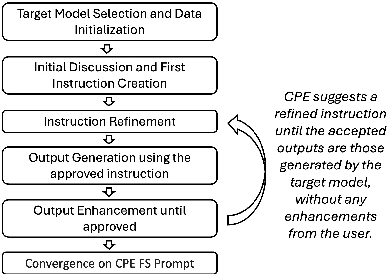
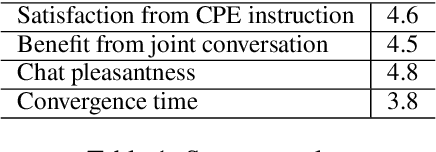
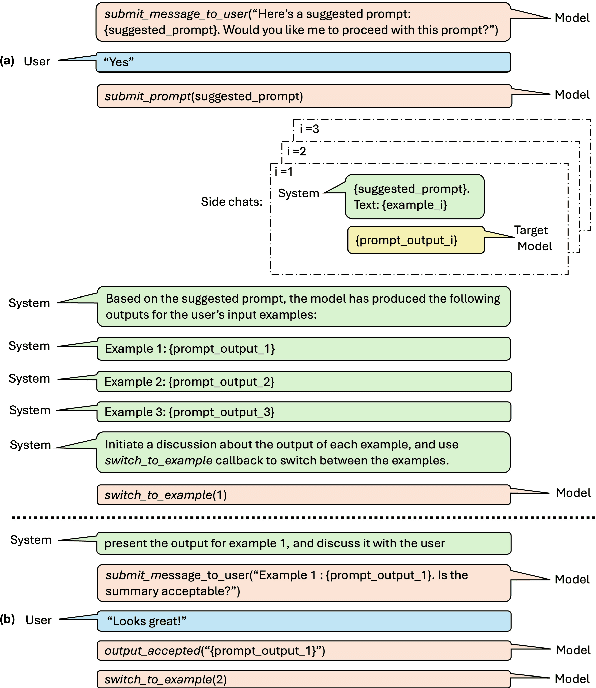
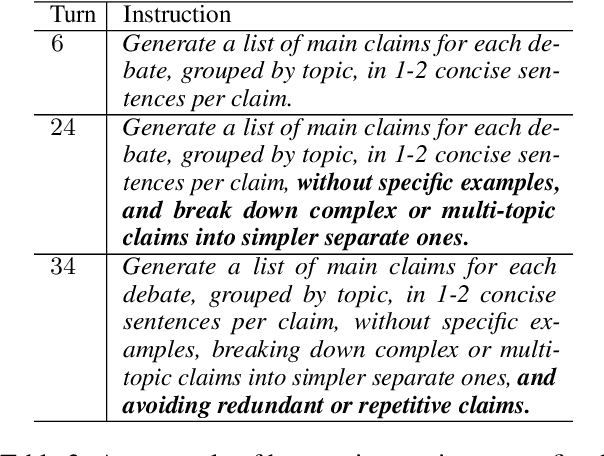
Abstract:Prompts are how humans communicate with LLMs. Informative prompts are essential for guiding LLMs to produce the desired output. However, prompt engineering is often tedious and time-consuming, requiring significant expertise, limiting its widespread use. We propose Conversational Prompt Engineering (CPE), a user-friendly tool that helps users create personalized prompts for their specific tasks. CPE uses a chat model to briefly interact with users, helping them articulate their output preferences and integrating these into the prompt. The process includes two main stages: first, the model uses user-provided unlabeled data to generate data-driven questions and utilize user responses to shape the initial instruction. Then, the model shares the outputs generated by the instruction and uses user feedback to further refine the instruction and the outputs. The final result is a few-shot prompt, where the outputs approved by the user serve as few-shot examples. A user study on summarization tasks demonstrates the value of CPE in creating personalized, high-performing prompts. The results suggest that the zero-shot prompt obtained is comparable to its - much longer - few-shot counterpart, indicating significant savings in scenarios involving repetitive tasks with large text volumes.
Label Sleuth: From Unlabeled Text to a Classifier in a Few Hours
Aug 02, 2022
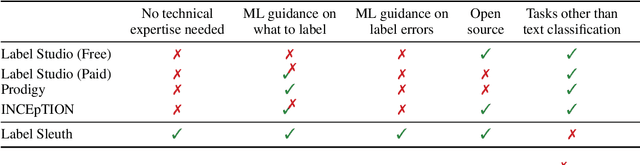


Abstract:Text classification can be useful in many real-world scenarios, saving a lot of time for end users. However, building a custom classifier typically requires coding skills and ML knowledge, which poses a significant barrier for many potential users. To lift this barrier, we introduce Label Sleuth, a free open source system for labeling and creating text classifiers. This system is unique for (a) being a no-code system, making NLP accessible to non-experts, (b) guiding users through the entire labeling process until they obtain a custom classifier, making the process efficient -- from cold start to classifier in a few hours, and (c) being open for configuration and extension by developers. By open sourcing Label Sleuth we hope to build a community of users and developers that will broaden the utilization of NLP models.
Cluster & Tune: Boost Cold Start Performance in Text Classification
Mar 20, 2022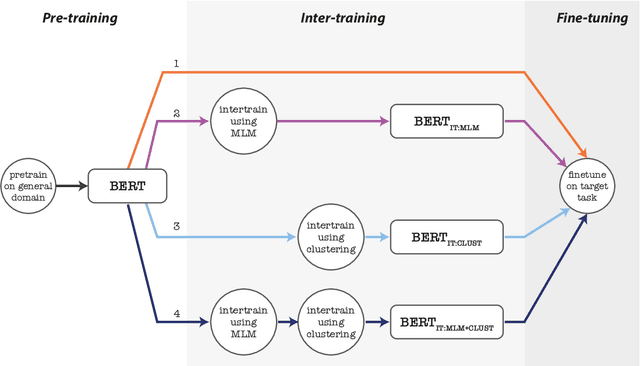
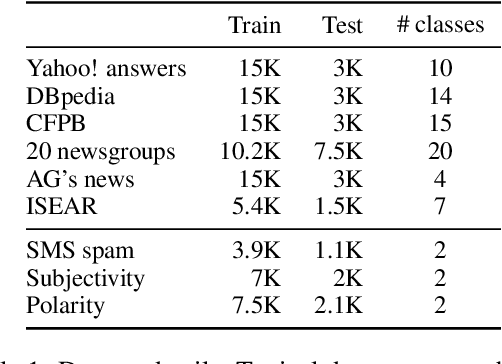
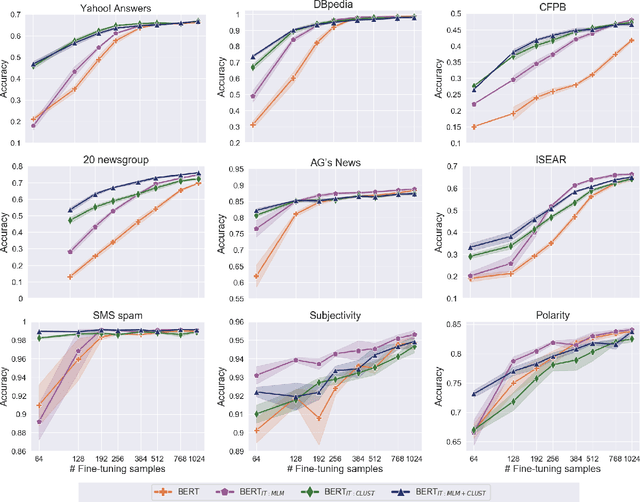
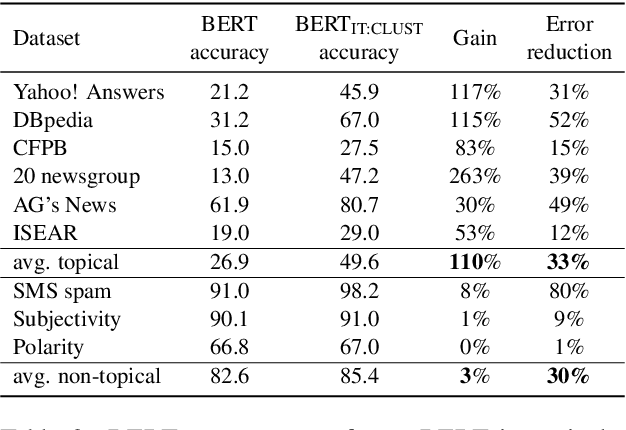
Abstract:In real-world scenarios, a text classification task often begins with a cold start, when labeled data is scarce. In such cases, the common practice of fine-tuning pre-trained models, such as BERT, for a target classification task, is prone to produce poor performance. We suggest a method to boost the performance of such models by adding an intermediate unsupervised classification task, between the pre-training and fine-tuning phases. As such an intermediate task, we perform clustering and train the pre-trained model on predicting the cluster labels. We test this hypothesis on various data sets, and show that this additional classification phase can significantly improve performance, mainly for topical classification tasks, when the number of labeled instances available for fine-tuning is only a couple of dozen to a few hundred.
Fortunately, Discourse Markers Can Enhance Language Models for Sentiment Analysis
Jan 06, 2022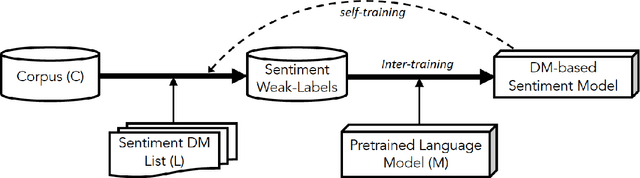
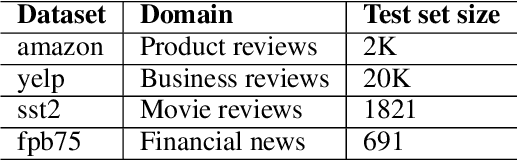
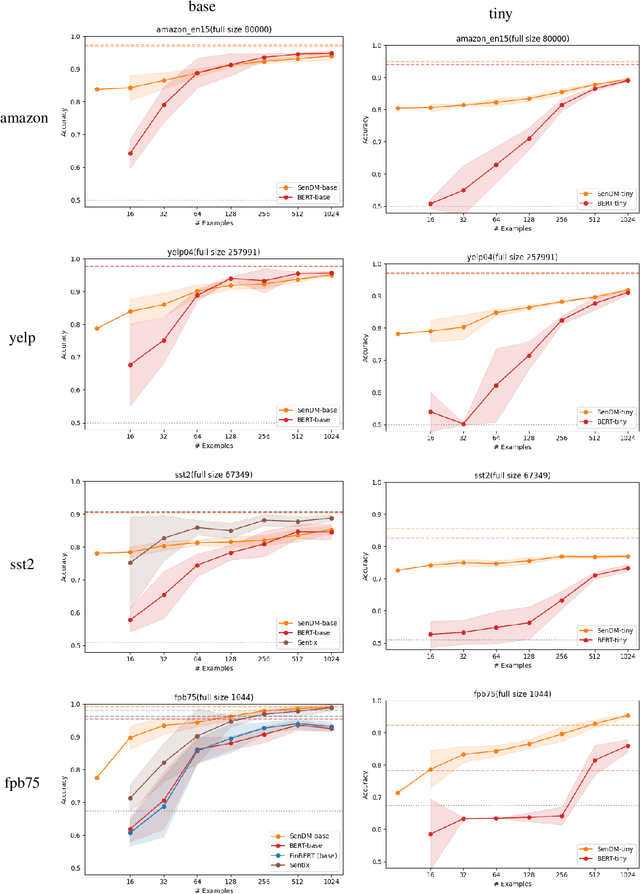
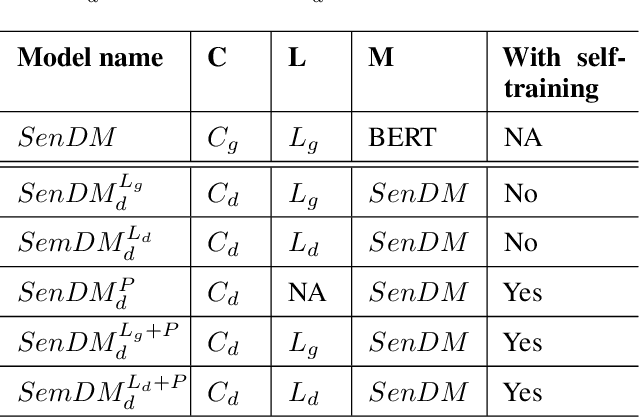
Abstract:In recent years, pretrained language models have revolutionized the NLP world, while achieving state of the art performance in various downstream tasks. However, in many cases, these models do not perform well when labeled data is scarce and the model is expected to perform in the zero or few shot setting. Recently, several works have shown that continual pretraining or performing a second phase of pretraining (inter-training) which is better aligned with the downstream task, can lead to improved results, especially in the scarce data setting. Here, we propose to leverage sentiment-carrying discourse markers to generate large-scale weakly-labeled data, which in turn can be used to adapt language models for sentiment analysis. Extensive experimental results show the value of our approach on various benchmark datasets, including the finance domain. Code, models and data are available at https://github.com/ibm/tslm-discourse-markers.
Overview of the 2021 Key Point Analysis Shared Task
Oct 20, 2021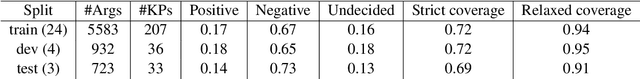
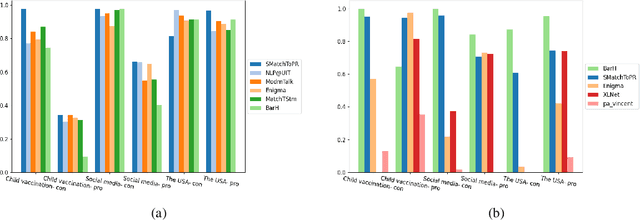
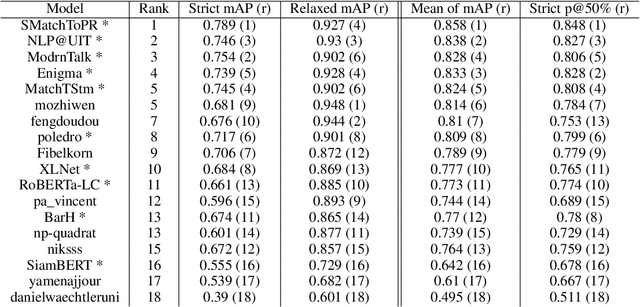
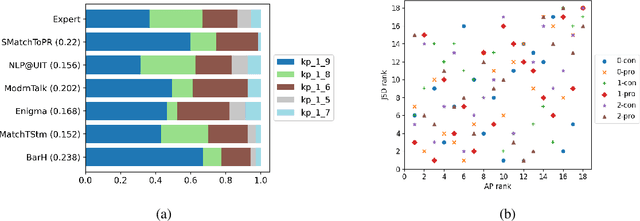
Abstract:We describe the 2021 Key Point Analysis (KPA-2021) shared task on key point analysis that we organized as a part of the 8th Workshop on Argument Mining (ArgMining 2021) at EMNLP 2021. We outline various approaches and discuss the results of the shared task. We expect the task and the findings reported in this paper to be relevant for researchers working on text summarization and argument mining.
Automatic Metaphor Interpretation Using Word Embeddings
Oct 06, 2020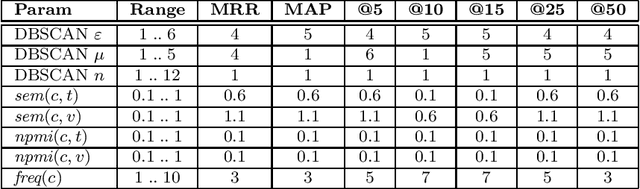
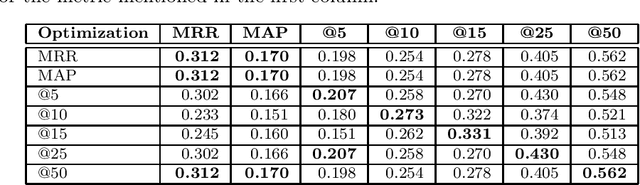
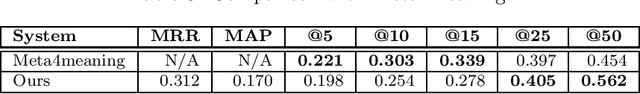
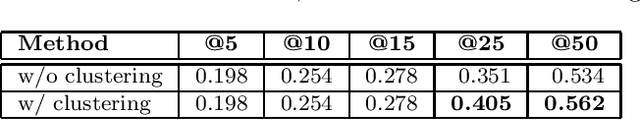
Abstract:We suggest a model for metaphor interpretation using word embeddings trained over a relatively large corpus. Our system handles nominal metaphors, like "time is money". It generates a ranked list of potential interpretations of given metaphors. Candidate meanings are drawn from collocations of the topic ("time") and vehicle ("money") components, automatically extracted from a dependency-parsed corpus. We explore adding candidates derived from word association norms (common human responses to cues). Our ranking procedure considers similarity between candidate interpretations and metaphor components, measured in a semantic vector space. Lastly, a clustering algorithm removes semantically related duplicates, thereby allowing other candidate interpretations to attain higher rank. We evaluate using a set of annotated metaphors.
Corpus Wide Argument Mining -- a Working Solution
Nov 25, 2019
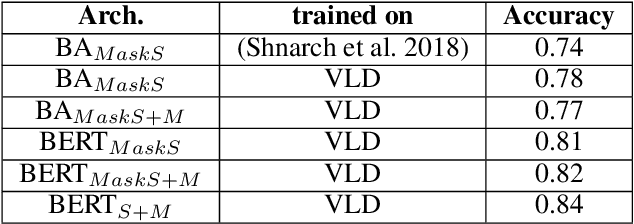


Abstract:One of the main tasks in argument mining is the retrieval of argumentative content pertaining to a given topic. Most previous work addressed this task by retrieving a relatively small number of relevant documents as the initial source for such content. This line of research yielded moderate success, which is of limited use in a real-world system. Furthermore, for such a system to yield a comprehensive set of relevant arguments, over a wide range of topics, it requires leveraging a large and diverse corpus in an appropriate manner. Here we present a first end-to-end high-precision, corpus-wide argument mining system. This is made possible by combining sentence-level queries over an appropriate indexing of a very large corpus of newspaper articles, with an iterative annotation scheme. This scheme addresses the inherent label bias in the data and pinpoints the regions of the sample space whose manual labeling is required to obtain high-precision among top-ranked candidates.
A Dataset of General-Purpose Rebuttal
Sep 01, 2019
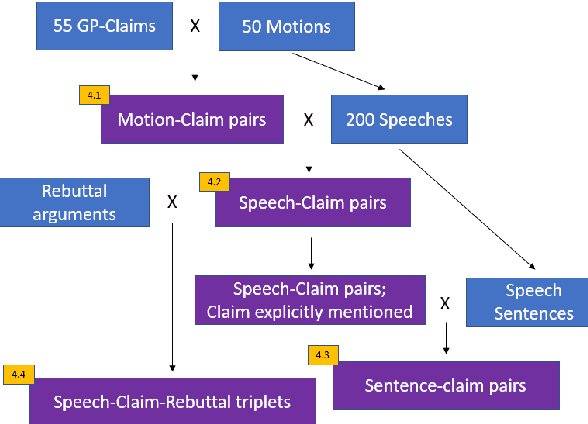
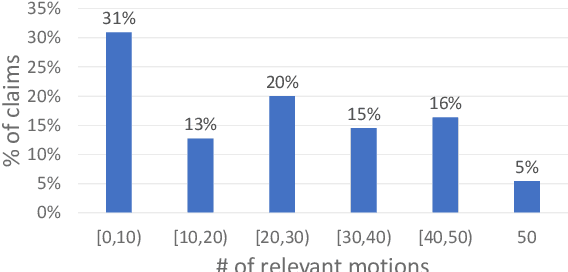
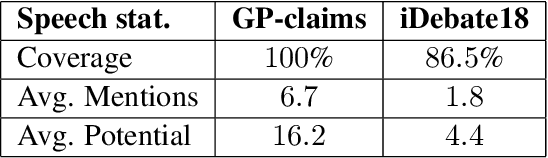
Abstract:In Natural Language Understanding, the task of response generation is usually focused on responses to short texts, such as tweets or a turn in a dialog. Here we present a novel task of producing a critical response to a long argumentative text, and suggest a method based on general rebuttal arguments to address it. We do this in the context of the recently-suggested task of listening comprehension over argumentative content: given a speech on some specified topic, and a list of relevant arguments, the goal is to determine which of the arguments appear in the speech. The general rebuttals we describe here (written in English) overcome the need for topic-specific arguments to be provided, by proving to be applicable for a large set of topics. This allows creating responses beyond the scope of topics for which specific arguments are available. All data collected during this work is freely available for research.
Towards Effective Rebuttal: Listening Comprehension using Corpus-Wide Claim Mining
Jul 27, 2019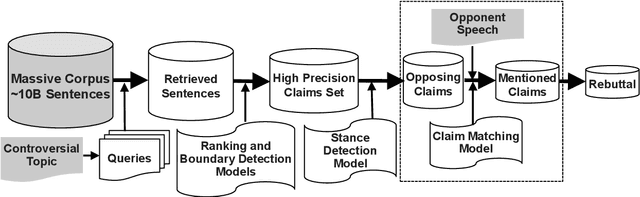
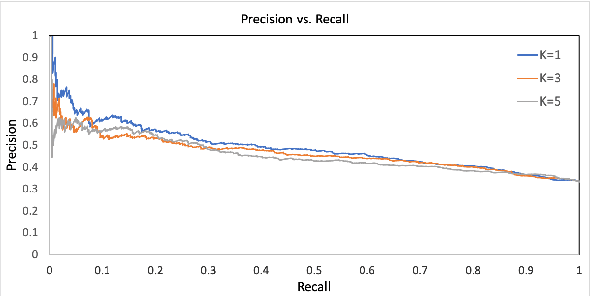
Abstract:Engaging in a live debate requires, among other things, the ability to effectively rebut arguments claimed by your opponent. In particular, this requires identifying these arguments. Here, we suggest doing so by automatically mining claims from a corpus of news articles containing billions of sentences, and searching for them in a given speech. This raises the question of whether such claims indeed correspond to those made in spoken speeches. To this end, we collected a large dataset of $400$ speeches in English discussing $200$ controversial topics, mined claims for each topic, and asked annotators to identify the mined claims mentioned in each speech. Results show that in the vast majority of speeches debaters indeed make use of such claims. In addition, we present several baselines for the automatic detection of mined claims in speeches, forming the basis for future work. All collected data is freely available for research.
Are You Convinced? Choosing the More Convincing Evidence with a Siamese Network
Jul 23, 2019



Abstract:With the advancement in argument detection, we suggest to pay more attention to the challenging task of identifying the more convincing arguments. Machines capable of responding and interacting with humans in helpful ways have become ubiquitous. We now expect them to discuss with us the more delicate questions in our world, and they should do so armed with effective arguments. But what makes an argument more persuasive? What will convince you? In this paper, we present a new data set, IBM-EviConv, of pairs of evidence labeled for convincingness, designed to be more challenging than existing alternatives. We also propose a Siamese neural network architecture shown to outperform several baselines on both a prior convincingness data set and our own. Finally, we provide insights into our experimental results and the various kinds of argumentative value our method is capable of detecting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge