Keren Fu
Samba+: General and Accurate Salient Object Detection via A More Unified Mamba-based Framework
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Existing salient object detection (SOD) models are generally constrained by the limited receptive fields of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and quadratic computational complexity of Transformers. Recently, the emerging state-space model, namely Mamba, has shown great potential in balancing global receptive fields and computational efficiency. As a solution, we propose Saliency Mamba (Samba), a pure Mamba-based architecture that flexibly handles various distinct SOD tasks, including RGB/RGB-D/RGB-T SOD, video SOD (VSOD), RGB-D VSOD, and visible-depth-thermal SOD. Specifically, we rethink the scanning strategy of Mamba for SOD, and introduce a saliency-guided Mamba block (SGMB) that features a spatial neighborhood scanning (SNS) algorithm to preserve the spatial continuity of salient regions. A context-aware upsampling (CAU) method is also proposed to promote hierarchical feature alignment and aggregation by modeling contextual dependencies. As one step further, to avoid the "task-specific" problem as in previous SOD solutions, we develop Samba+, which is empowered by training Samba in a multi-task joint manner, leading to a more unified and versatile model. Two crucial components that collaboratively tackle challenges encountered in input of arbitrary modalities and continual adaptation are investigated. Specifically, a hub-and-spoke graph attention (HGA) module facilitates adaptive cross-modal interactive fusion, and a modality-anchored continual learning (MACL) strategy alleviates inter-modal conflicts together with catastrophic forgetting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Samba individually outperforms existing methods across six SOD tasks on 22 datasets with lower computational cost, whereas Samba+ achieves even superior results on these tasks and datasets by using a single trained versatile model. Additional results further demonstrate the potential of our Samba framework.
Mamba-based Efficient Spatio-Frequency Motion Perception for Video Camouflaged Object Detection
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Existing video camouflaged object detection (VCOD) methods primarily rely on spatial appearance features to perceive motion cues for breaking camouflage. However, the high similarity between foreground and background in VCOD results in limited discriminability of spatial appearance features (e.g., color and texture), restricting detection accuracy and completeness. Recent studies demonstrate that frequency features can not only enhance feature representation to compensate for appearance limitations but also perceive motion through dynamic variations in frequency energy. Furthermore, the emerging state space model called Mamba, enables efficient perception of motion cues in frame sequences due to its linear-time long-sequence modeling capability. Motivated by this, we propose a novel visual camouflage Mamba (Vcamba) based on spatio-frequency motion perception that integrates frequency and spatial features for efficient and accurate VCOD. Specifically, we propose a receptive field visual state space (RFVSS) module to extract multi-scale spatial features after sequence modeling. For frequency learning, we introduce an adaptive frequency component enhancement (AFE) module with a novel frequency-domain sequential scanning strategy to maintain semantic consistency. Then we propose a space-based long-range motion perception (SLMP) module and a frequency-based long-range motion perception (FLMP) module to model spatio-temporal and frequency-temporal sequences in spatial and frequency phase domains. Finally, the space and frequency motion fusion module (SFMF) integrates dual-domain features for unified motion representation. Experimental results show that our Vcamba outperforms state-of-the-art methods across 6 evaluation metrics on 2 datasets with lower computation cost, confirming the superiority of Vcamba. Our code is available at: https://github.com/BoydeLi/Vcamba.
Unleashing the Power of Motion and Depth: A Selective Fusion Strategy for RGB-D Video Salient Object Detection
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Applying salient object detection (SOD) to RGB-D videos is an emerging task called RGB-D VSOD and has recently gained increasing interest, due to considerable performance gains of incorporating motion and depth and that RGB-D videos can be easily captured now in daily life. Existing RGB-D VSOD models have different attempts to derive motion cues, in which extracting motion information explicitly from optical flow appears to be a more effective and promising alternative. Despite this, there remains a key issue that how to effectively utilize optical flow and depth to assist the RGB modality in SOD. Previous methods always treat optical flow and depth equally with respect to model designs, without explicitly considering their unequal contributions in individual scenarios, limiting the potential of motion and depth. To address this issue and unleash the power of motion and depth, we propose a novel selective cross-modal fusion framework (SMFNet) for RGB-D VSOD, incorporating a pixel-level selective fusion strategy (PSF) that achieves optimal fusion of optical flow and depth based on their actual contributions. Besides, we propose a multi-dimensional selective attention module (MSAM) to integrate the fused features derived from PSF with the remaining RGB modality at multiple dimensions, effectively enhancing feature representation to generate refined features. We conduct comprehensive evaluation of SMFNet against 19 state-of-the-art models on both RDVS and DVisal datasets, making the evaluation the most comprehensive RGB-D VSOD benchmark up to date, and it also demonstrates the superiority of SMFNet over other models. Meanwhile, evaluation on five video benchmark datasets incorporating synthetic depth validates the efficacy of SMFNet as well. Our code and benchmark results are made publicly available at https://github.com/Jia-hao999/SMFNet.
CamoSAM2: Motion-Appearance Induced Auto-Refining Prompts for Video Camouflaged Object Detection
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:The Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2), a prompt-guided video foundation model, has remarkably performed in video object segmentation, drawing significant attention in the community. Due to the high similarity between camouflaged objects and their surroundings, which makes them difficult to distinguish even by the human eye, the application of SAM2 for automated segmentation in real-world scenarios faces challenges in camouflage perception and reliable prompts generation. To address these issues, we propose CamoSAM2, a motion-appearance prompt inducer (MAPI) and refinement framework to automatically generate and refine prompts for SAM2, enabling high-quality automatic detection and segmentation in VCOD task. Initially, we introduce a prompt inducer that simultaneously integrates motion and appearance cues to detect camouflaged objects, delivering more accurate initial predictions than existing methods. Subsequently, we propose a video-based adaptive multi-prompts refinement (AMPR) strategy tailored for SAM2, aimed at mitigating prompt error in initial coarse masks and further producing good prompts. Specifically, we introduce a novel three-step process to generate reliable prompts by camouflaged object determination, pivotal prompting frame selection, and multi-prompts formation. Extensive experiments conducted on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed model, CamoSAM2, significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving increases of 8.0% and 10.1% in mIoU metric. Additionally, our method achieves the fastest inference speed compared to current VCOD models.
MoEdit: On Learning Quantity Perception for Multi-object Image Editing
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Multi-object images are prevalent in various real-world scenarios, including augmented reality, advertisement design, and medical imaging. Efficient and precise editing of these images is critical for these applications. With the advent of Stable Diffusion (SD), high-quality image generation and editing have entered a new era. However, existing methods often struggle to consider each object both individually and part of the whole image editing, both of which are crucial for ensuring consistent quantity perception, resulting in suboptimal perceptual performance. To address these challenges, we propose MoEdit, an auxiliary-free multi-object image editing framework. MoEdit facilitates high-quality multi-object image editing in terms of style transfer, object reinvention, and background regeneration, while ensuring consistent quantity perception between inputs and outputs, even with a large number of objects. To achieve this, we introduce the Feature Compensation (FeCom) module, which ensures the distinction and separability of each object attribute by minimizing the in-between interlacing. Additionally, we present the Quantity Attention (QTTN) module, which perceives and preserves quantity consistency by effective control in editing, without relying on auxiliary tools. By leveraging the SD model, MoEdit enables customized preservation and modification of specific concepts in inputs with high quality. Experimental results demonstrate that our MoEdit achieves State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) performance in multi-object image editing. Data and codes will be available at https://github.com/Tear-kitty/MoEdit.
Patch-Depth Fusion: Dichotomous Image Segmentation via Fine-Grained Patch Strategy and Depth Integrity-Prior
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Dichotomous Image Segmentation (DIS) is a high-precision object segmentation task for high-resolution natural images. The current mainstream methods focus on the optimization of local details but overlook the fundamental challenge of modeling the integrity of objects. We have found that the depth integrity-prior implicit in the the pseudo-depth maps generated by Depth Anything Model v2 and the local detail features of image patches can jointly address the above dilemmas. Based on the above findings, we have designed a novel Patch-Depth Fusion Network (PDFNet) for high-precision dichotomous image segmentation. The core of PDFNet consists of three aspects. Firstly, the object perception is enhanced through multi-modal input fusion. By utilizing the patch fine-grained strategy, coupled with patch selection and enhancement, the sensitivity to details is improved. Secondly, by leveraging the depth integrity-prior distributed in the depth maps, we propose an integrity-prior loss to enhance the uniformity of the segmentation results in the depth maps. Finally, we utilize the features of the shared encoder and, through a simple depth refinement decoder, improve the ability of the shared encoder to capture subtle depth-related information in the images. Experiments on the DIS-5K dataset show that PDFNet significantly outperforms state-of-the-art non-diffusion methods. Due to the incorporation of the depth integrity-prior, PDFNet achieves or even surpassing the performance of the latest diffusion-based methods while using less than 11% of the parameters of diffusion-based methods. The source code at https://github.com/Tennine2077/PDFNet.
Uncertainty-aware sign language video retrieval with probability distribution modeling
May 30, 2024Abstract:Sign language video retrieval plays a key role in facilitating information access for the deaf community. Despite significant advances in video-text retrieval, the complexity and inherent uncertainty of sign language preclude the direct application of these techniques. Previous methods achieve the mapping between sign language video and text through fine-grained modal alignment. However, due to the scarcity of fine-grained annotation, the uncertainty inherent in sign language video is underestimated, limiting the further development of sign language retrieval tasks. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Uncertainty-aware Probability Distribution Retrieval (UPRet), that conceptualizes the mapping process of sign language video and text in terms of probability distributions, explores their potential interrelationships, and enables flexible mappings. Experiments on three benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which achieves state-of-the-art results on How2Sign (59.1%), PHOENIX-2014T (72.0%), and CSL-Daily (78.4%).
Effectiveness Assessment of Recent Large Vision-Language Models
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:The advent of large vision-language models (LVLMs) represents a noteworthy advancement towards the pursuit of artificial general intelligence. However, the extent of their efficacy across both specialized and general tasks warrants further investigation. This article endeavors to evaluate the competency of popular LVLMs in specialized and general tasks, respectively, aiming to offer a comprehensive comprehension of these innovative methodologies. To gauge their efficacy in specialized tasks, we tailor a comprehensive testbed comprising three distinct scenarios: natural, healthcare, and industrial, encompassing six challenging tasks. These tasks include salient, camouflaged, and transparent object detection, as well as polyp and skin lesion detection, alongside industrial anomaly detection. We examine the performance of three recent open-source LVLMs -- MiniGPT-v2, LLaVA-1.5, and Shikra -- in the realm of visual recognition and localization. Moreover, we conduct empirical investigations utilizing the aforementioned models alongside GPT-4V, assessing their multi-modal understanding capacities in general tasks such as object counting, absurd question answering, affordance reasoning, attribute recognition, and spatial relation reasoning. Our investigations reveal that these models demonstrate limited proficiency not only in specialized tasks but also in general tasks. We delve deeper into this inadequacy and suggest several potential factors, including limited cognition in specialized tasks, object hallucination, text-to-image interference, and decreased robustness in complex problems. We hope this study would provide valuable insights for the future development of LVLMs, augmenting their power in coping with both general and specialized applications.
Explicit Motion Handling and Interactive Prompting for Video Camouflaged Object Detection
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Camouflage poses challenges in distinguishing a static target, whereas any movement of the target can break this disguise. Existing video camouflaged object detection (VCOD) approaches take noisy motion estimation as input or model motion implicitly, restricting detection performance in complex dynamic scenes. In this paper, we propose a novel Explicit Motion handling and Interactive Prompting framework for VCOD, dubbed EMIP, which handles motion cues explicitly using a frozen pre-trained optical flow fundamental model. EMIP is characterized by a two-stream architecture for simultaneously conducting camouflaged segmentation and optical flow estimation. Interactions across the dual streams are realized in an interactive prompting way that is inspired by emerging visual prompt learning. Two learnable modules, i.e. the camouflaged feeder and motion collector, are designed to incorporate segmentation-to-motion and motion-to-segmentation prompts, respectively, and enhance outputs of the both streams. The prompt fed to the motion stream is learned by supervising optical flow in a self-supervised manner. Furthermore, we show that long-term historical information can also be incorporated as a prompt into EMIP and achieve more robust results with temporal consistency. Experimental results demonstrate that our EMIP achieves new state-of-the-art records on popular VCOD benchmarks. The code will be publicly available.
Dynamic Patch-aware Enrichment Transformer for Occluded Person Re-Identification
Feb 16, 2024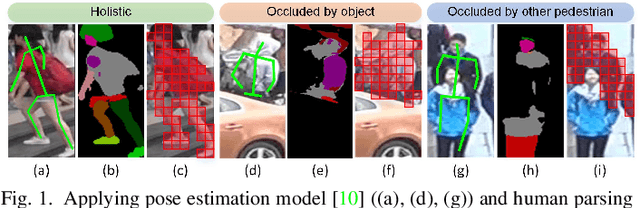
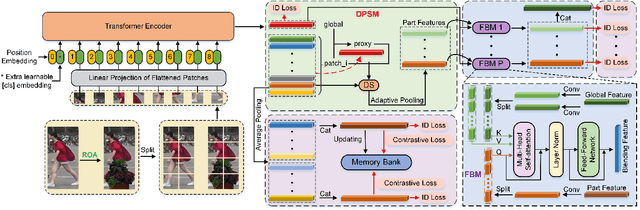
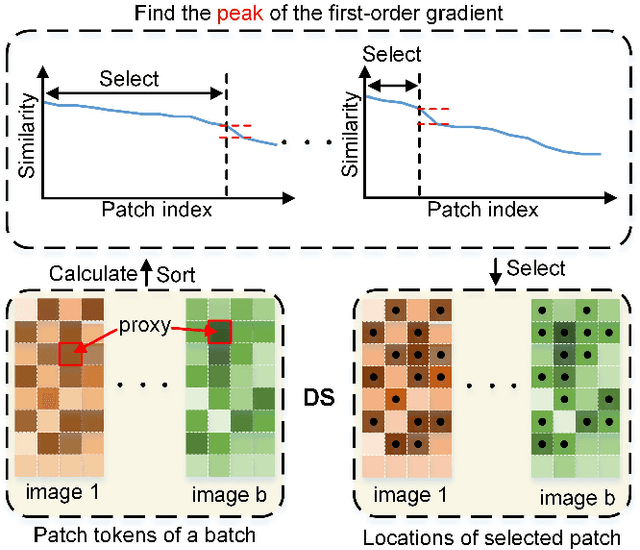

Abstract:Person re-identification (re-ID) continues to pose a significant challenge, particularly in scenarios involving occlusions. Prior approaches aimed at tackling occlusions have predominantly focused on aligning physical body features through the utilization of external semantic cues. However, these methods tend to be intricate and susceptible to noise. To address the aforementioned challenges, we present an innovative end-to-end solution known as the Dynamic Patch-aware Enrichment Transformer (DPEFormer). This model effectively distinguishes human body information from occlusions automatically and dynamically, eliminating the need for external detectors or precise image alignment. Specifically, we introduce a dynamic patch token selection module (DPSM). DPSM utilizes a label-guided proxy token as an intermediary to identify informative occlusion-free tokens. These tokens are then selected for deriving subsequent local part features. To facilitate the seamless integration of global classification features with the finely detailed local features selected by DPSM, we introduce a novel feature blending module (FBM). FBM enhances feature representation through the complementary nature of information and the exploitation of part diversity. Furthermore, to ensure that DPSM and the entire DPEFormer can effectively learn with only identity labels, we also propose a Realistic Occlusion Augmentation (ROA) strategy. This strategy leverages the recent advances in the Segment Anything Model (SAM). As a result, it generates occlusion images that closely resemble real-world occlusions, greatly enhancing the subsequent contrastive learning process. Experiments on occluded and holistic re-ID benchmarks signify a substantial advancement of DPEFormer over existing state-of-the-art approaches. The code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge