Kaibin Tian
Towards Efficient and Effective Text-to-Video Retrieval with Coarse-to-Fine Visual Representation Learning
Jan 01, 2024Abstract:In recent years, text-to-video retrieval methods based on CLIP have experienced rapid development. The primary direction of evolution is to exploit the much wider gamut of visual and textual cues to achieve alignment. Concretely, those methods with impressive performance often design a heavy fusion block for sentence (words)-video (frames) interaction, regardless of the prohibitive computation complexity. Nevertheless, these approaches are not optimal in terms of feature utilization and retrieval efficiency. To address this issue, we adopt multi-granularity visual feature learning, ensuring the model's comprehensiveness in capturing visual content features spanning from abstract to detailed levels during the training phase. To better leverage the multi-granularity features, we devise a two-stage retrieval architecture in the retrieval phase. This solution ingeniously balances the coarse and fine granularity of retrieval content. Moreover, it also strikes a harmonious equilibrium between retrieval effectiveness and efficiency. Specifically, in training phase, we design a parameter-free text-gated interaction block (TIB) for fine-grained video representation learning and embed an extra Pearson Constraint to optimize cross-modal representation learning. In retrieval phase, we use coarse-grained video representations for fast recall of top-k candidates, which are then reranked by fine-grained video representations. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness. Notably, our method achieves comparable performance with the current state-of-the-art methods while being nearly 50 times faster.
TeachCLIP: Multi-Grained Teaching for Efficient Text-to-Video Retrieval
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:For text-to-video retrieval (T2VR), which aims to retrieve unlabeled videos by ad-hoc textual queries, CLIP-based methods are dominating. Compared to CLIP4Clip which is efficient and compact, the state-of-the-art models tend to compute video-text similarity by fine-grained cross-modal feature interaction and matching, putting their scalability for large-scale T2VR into doubt. For efficient T2VR, we propose TeachCLIP with multi-grained teaching to let a CLIP4Clip based student network learn from more advanced yet computationally heavy models such as X-CLIP, TS2-Net and X-Pool . To improve the student's learning capability, we add an Attentional frame-Feature Aggregation (AFA) block, which by design adds no extra storage/computation overhead at the retrieval stage. While attentive weights produced by AFA are commonly used for combining frame-level features, we propose a novel use of the weights to let them imitate frame-text relevance estimated by the teacher network. As such, AFA provides a fine-grained learning (teaching) channel for the student (teacher). Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets justify the viability of the proposed method.
Renmin University of China at TRECVID 2022: Improving Video Search by Feature Fusion and Negation Understanding
Nov 28, 2022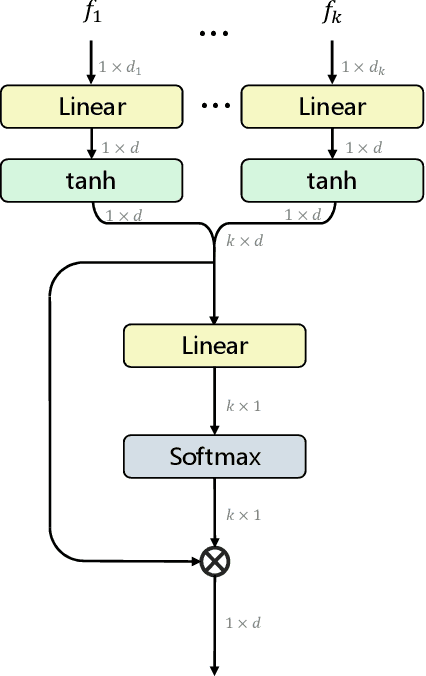

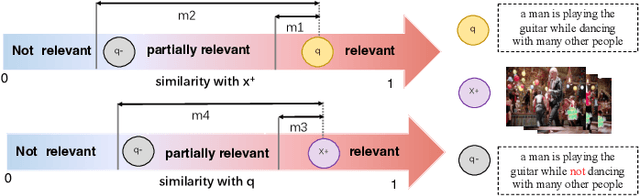

Abstract:We summarize our TRECVID 2022 Ad-hoc Video Search (AVS) experiments. Our solution is built with two new techniques, namely Lightweight Attentional Feature Fusion (LAFF) for combining diverse visual / textual features and Bidirectional Negation Learning (BNL) for addressing queries that contain negation cues. In particular, LAFF performs feature fusion at both early and late stages and at both text and video ends to exploit diverse (off-the-shelf) features. Compared to multi-head self attention, LAFF is much more compact yet more effective. Its attentional weights can also be used for selecting fewer features, with the retrieval performance mostly preserved. BNL trains a negation-aware video retrieval model by minimizing a bidirectionally constrained loss per triplet, where a triplet consists of a given training video, its original description and a partially negated description. For video feature extraction, we use pre-trained CLIP, BLIP, BEiT, ResNeXt-101 and irCSN. As for text features, we adopt bag-of-words, word2vec, CLIP and BLIP. Our training data consists of MSR-VTT, TGIF and VATEX that were used in our previous participation. In addition, we automatically caption the V3C1 collection for pre-training. The 2022 edition of the TRECVID benchmark has again been a fruitful participation for the RUCMM team. Our best run, with an infAP of 0.262, is ranked at the second place teamwise.
MVP: Robust Multi-View Practice for Driving Action Localization
Jul 05, 2022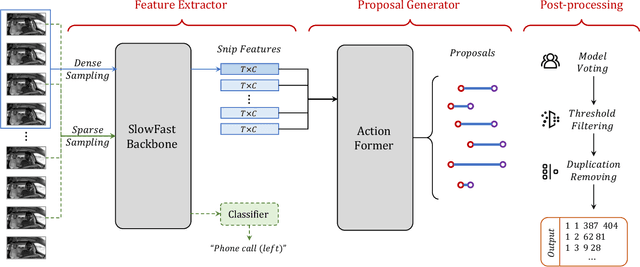
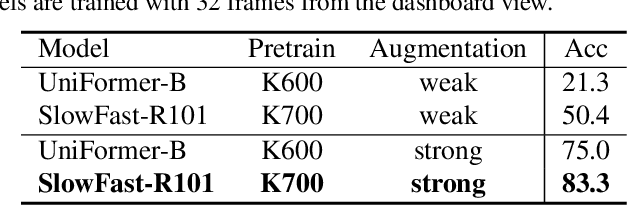
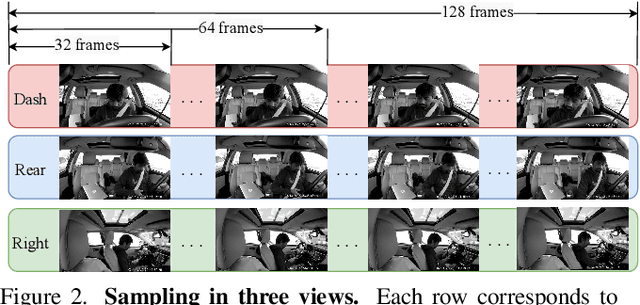
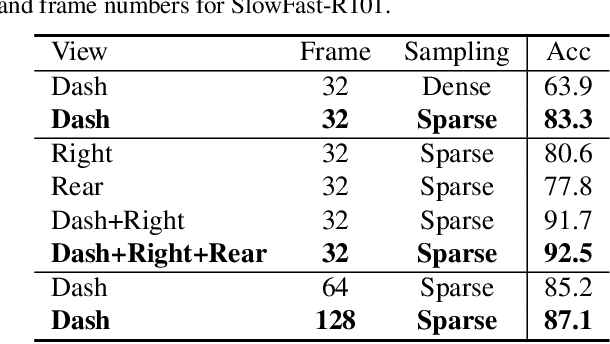
Abstract:Distracted driving causes thousands of deaths per year, and how to apply deep-learning methods to prevent these tragedies has become a crucial problem. In Track3 of the 6th AI City Challenge, researchers provide a high-quality video dataset with densely action annotations. Due to the small data scale and unclear action boundary, the dataset presents a unique challenge to precisely localize all the different actions and classify their categories. In this paper, we make good use of the multi-view synchronization among videos, and conduct robust Multi-View Practice (MVP) for driving action localization. To avoid overfitting, we fine-tune SlowFast with Kinetics-700 pre-training as the feature extractor. Then the features of different views are passed to ActionFormer to generate candidate action proposals. For precisely localizing all the actions, we design elaborate post-processing, including model voting, threshold filtering and duplication removal. The results show that our MVP is robust for driving action localization, which achieves 28.49% F1-score in the Track3 test set.
Co-Teaching for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation and Expansion
Apr 04, 2022
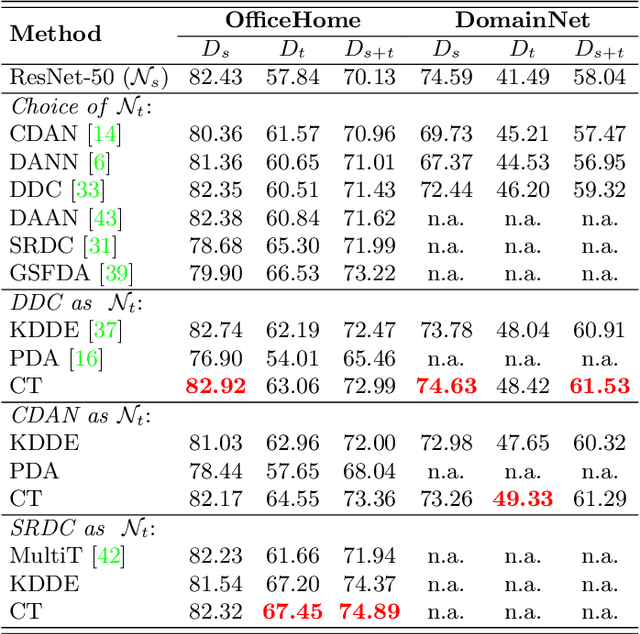
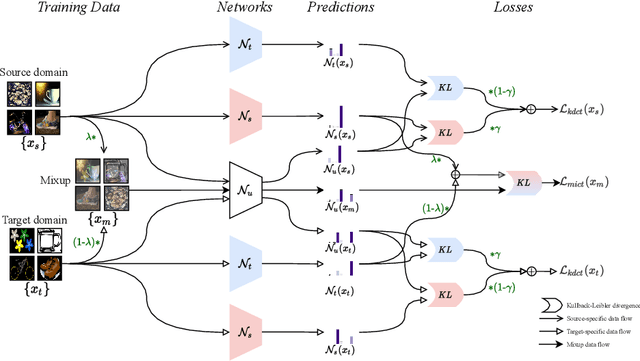
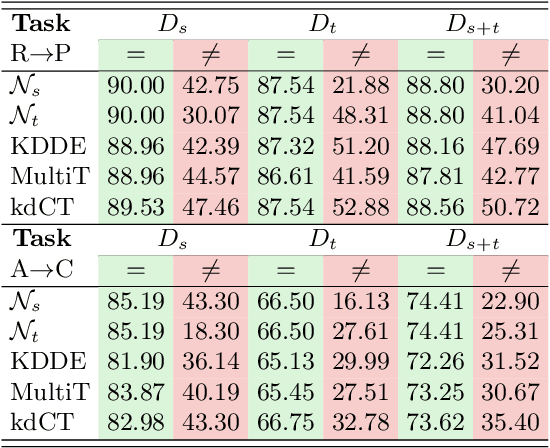
Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is known to trade a model's performance on a source domain for improving its performance on a target domain. To resolve the issue, Unsupervised Domain Expansion (UDE) has been proposed recently to adapt the model for the target domain as UDA does, and in the meantime maintain its performance on the source domain. For both UDA and UDE, a model tailored to a given domain, let it be the source or the target domain, is assumed to well handle samples from the given domain. We question the assumption by reporting the existence of cross-domain visual ambiguity: Due to the lack of a crystally clear boundary between the two domains, samples from one domain can be visually close to the other domain. We exploit this finding and accordingly propose in this paper Co-Teaching (CT) that consists of knowledge distillation based CT (kdCT) and mixup based CT (miCT). Specifically, kdCT transfers knowledge from a leader-teacher network and an assistant-teacher network to a student network, so the cross-domain visual ambiguity will be better handled by the student. Meanwhile, miCT further enhances the generalization ability of the student. Comprehensive experiments on two image-classification benchmarks and two driving-scene-segmentation benchmarks justify the viability of the proposed method.
Unsupervised Domain Expansion for Visual Categorization
Apr 01, 2021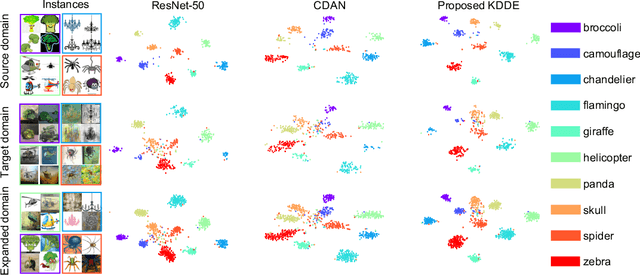
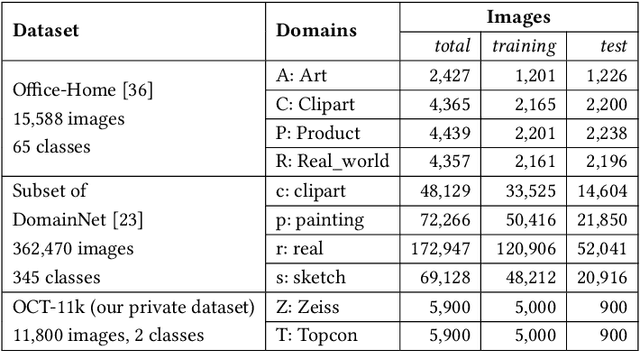
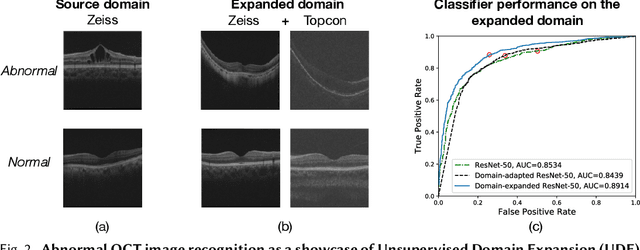
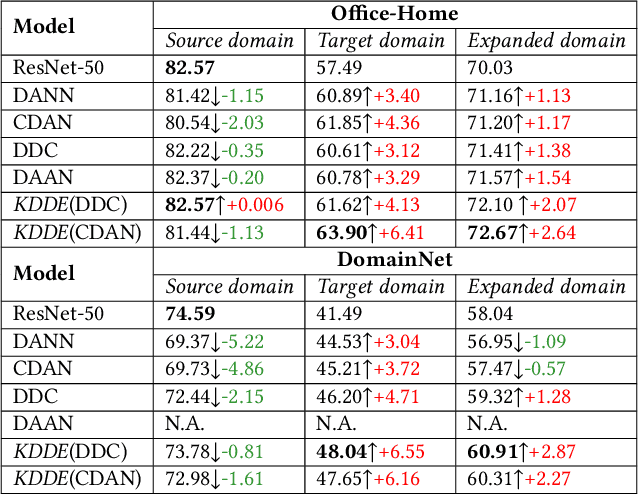
Abstract:Expanding visual categorization into a novel domain without the need of extra annotation has been a long-term interest for multimedia intelligence. Previously, this challenge has been approached by unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA). Given labeled data from a source domain and unlabeled data from a target domain, UDA seeks for a deep representation that is both discriminative and domain-invariant. While UDA focuses on the target domain, we argue that the performance on both source and target domains matters, as in practice which domain a test example comes from is unknown. In this paper we extend UDA by proposing a new task called unsupervised domain expansion (UDE), which aims to adapt a deep model for the target domain with its unlabeled data, meanwhile maintaining the model's performance on the source domain. We propose Knowledge Distillation Domain Expansion (KDDE) as a general method for the UDE task. Its domain-adaptation module can be instantiated with any existing model. We develop a knowledge distillation based learning mechanism, enabling KDDE to optimize a single objective wherein the source and target domains are equally treated. Extensive experiments on two major benchmarks, i.e., Office-Home and DomainNet, show that KDDE compares favorably against four competitive baselines, i.e., DDC, DANN, DAAN, and CDAN, for both UDA and UDE tasks. Our study also reveals that the current UDA models improve their performance on the target domain at the cost of noticeable performance loss on the source domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge