Ruixiang Zhao
Hybrid-Tower: Fine-grained Pseudo-query Interaction and Generation for Text-to-Video Retrieval
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:The Text-to-Video Retrieval (T2VR) task aims to retrieve unlabeled videos by textual queries with the same semantic meanings. Recent CLIP-based approaches have explored two frameworks: Two-Tower versus Single-Tower framework, yet the former suffers from low effectiveness, while the latter suffers from low efficiency. In this study, we explore a new Hybrid-Tower framework that can hybridize the advantages of the Two-Tower and Single-Tower framework, achieving high effectiveness and efficiency simultaneously. We propose a novel hybrid method, Fine-grained Pseudo-query Interaction and Generation for T2VR, ie, PIG, which includes a new pseudo-query generator designed to generate a pseudo-query for each video. This enables the video feature and the textual features of pseudo-query to interact in a fine-grained manner, similar to the Single-Tower approaches to hold high effectiveness, even before the real textual query is received. Simultaneously, our method introduces no additional storage or computational overhead compared to the Two-Tower framework during the inference stage, thus maintaining high efficiency. Extensive experiments on five commonly used text-video retrieval benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves a significant improvement over the baseline, with an increase of $1.6\% \sim 3.9\%$ in R@1. Furthermore, our method matches the efficiency of Two-Tower models while achieving near state-of-the-art performance, highlighting the advantages of the Hybrid-Tower framework.
Multi-Object Sketch Animation by Scene Decomposition and Motion Planning
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Sketch animation, which brings static sketches to life by generating dynamic video sequences, has found widespread applications in GIF design, cartoon production, and daily entertainment. While current sketch animation methods perform well in single-object sketch animation, they struggle in multi-object scenarios. By analyzing their failures, we summarize two challenges of transitioning from single-object to multi-object sketch animation: object-aware motion modeling and complex motion optimization. For multi-object sketch animation, we propose MoSketch based on iterative optimization through Score Distillation Sampling (SDS), without any other data for training. We propose four modules: LLM-based scene decomposition, LLM-based motion planning, motion refinement network and compositional SDS, to tackle the two challenges in a divide-and-conquer strategy. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method over existing sketch animation approaches. MoSketch takes a pioneering step towards multi-object sketch animation, opening new avenues for future research and applications. The code will be released.
ASR-enhanced Multimodal Representation Learning for Cross-Domain Product Retrieval
Aug 06, 2024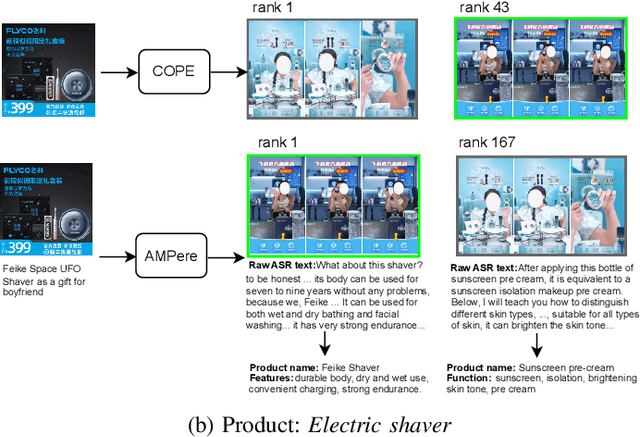
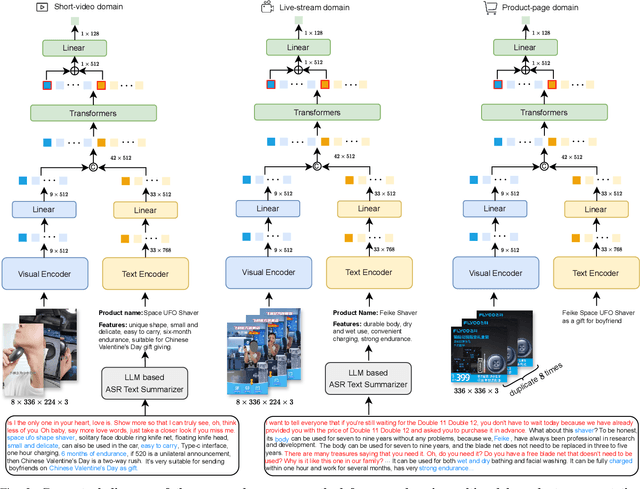

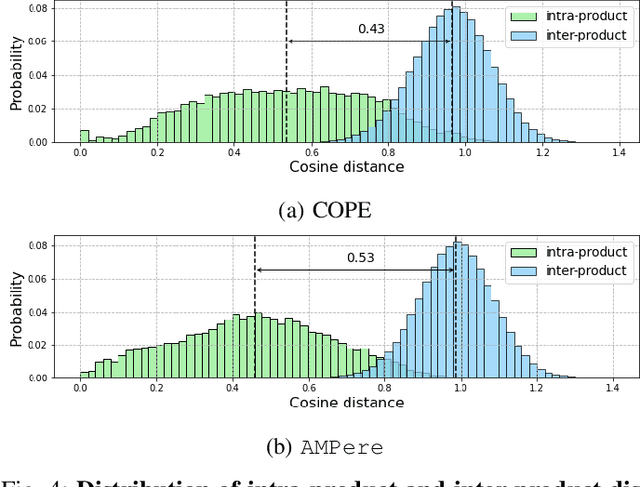
Abstract:E-commerce is increasingly multimedia-enriched, with products exhibited in a broad-domain manner as images, short videos, or live stream promotions. A unified and vectorized cross-domain production representation is essential. Due to large intra-product variance and high inter-product similarity in the broad-domain scenario, a visual-only representation is inadequate. While Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) text derived from the short or live-stream videos is readily accessible, how to de-noise the excessively noisy text for multimodal representation learning is mostly untouched. We propose ASR-enhanced Multimodal Product Representation Learning (AMPere). In order to extract product-specific information from the raw ASR text, AMPere uses an easy-to-implement LLM-based ASR text summarizer. The LLM-summarized text, together with visual data, is then fed into a multi-branch network to generate compact multimodal embeddings. Extensive experiments on a large-scale tri-domain dataset verify the effectiveness of AMPere in obtaining a unified multimodal product representation that clearly improves cross-domain product retrieval.
TeachCLIP: Multi-Grained Teaching for Efficient Text-to-Video Retrieval
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:For text-to-video retrieval (T2VR), which aims to retrieve unlabeled videos by ad-hoc textual queries, CLIP-based methods are dominating. Compared to CLIP4Clip which is efficient and compact, the state-of-the-art models tend to compute video-text similarity by fine-grained cross-modal feature interaction and matching, putting their scalability for large-scale T2VR into doubt. For efficient T2VR, we propose TeachCLIP with multi-grained teaching to let a CLIP4Clip based student network learn from more advanced yet computationally heavy models such as X-CLIP, TS2-Net and X-Pool . To improve the student's learning capability, we add an Attentional frame-Feature Aggregation (AFA) block, which by design adds no extra storage/computation overhead at the retrieval stage. While attentive weights produced by AFA are commonly used for combining frame-level features, we propose a novel use of the weights to let them imitate frame-text relevance estimated by the teacher network. As such, AFA provides a fine-grained learning (teaching) channel for the student (teacher). Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets justify the viability of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge