Jungwook Choi
Enhancing Generalization in Data-free Quantization via Mixup-class Prompting
Jul 29, 2025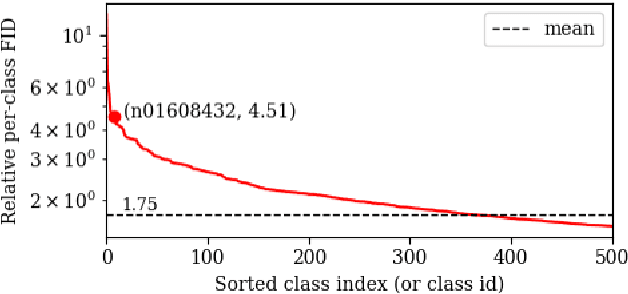
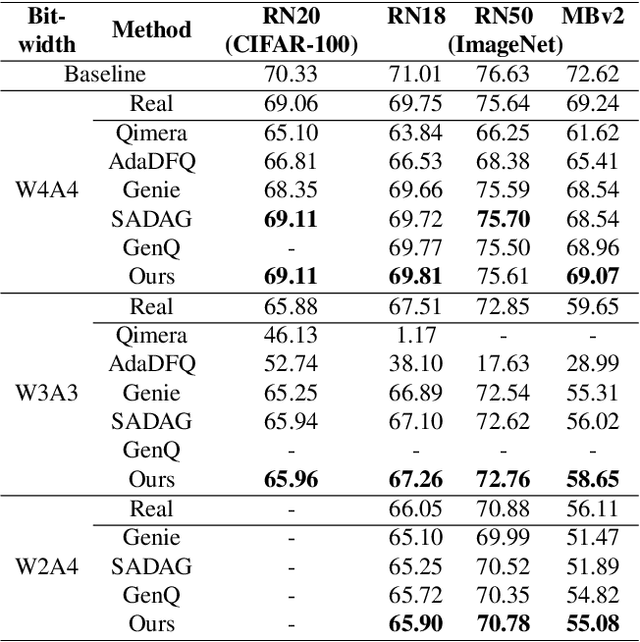
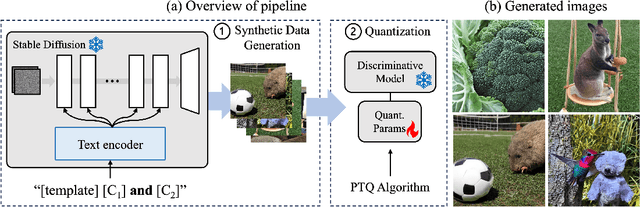
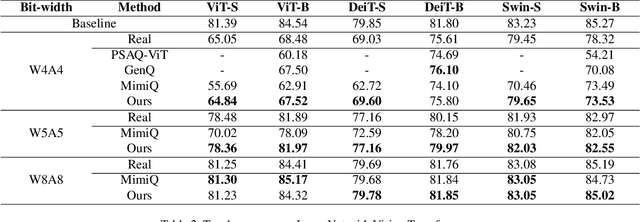
Abstract:Post-training quantization (PTQ) improves efficiency but struggles with limited calibration data, especially under privacy constraints. Data-free quantization (DFQ) mitigates this by generating synthetic images using generative models such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and text-conditioned latent diffusion models (LDMs), while applying existing PTQ algorithms. However, the relationship between generated synthetic images and the generalizability of the quantized model during PTQ remains underexplored. Without investigating this relationship, synthetic images generated by previous prompt engineering methods based on single-class prompts suffer from issues such as polysemy, leading to performance degradation. We propose \textbf{mixup-class prompt}, a mixup-based text prompting strategy that fuses multiple class labels at the text prompt level to generate diverse, robust synthetic data. This approach enhances generalization, and improves optimization stability in PTQ. We provide quantitative insights through gradient norm and generalization error analysis. Experiments on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art DFQ methods like GenQ. Furthermore, it pushes the performance boundary in extremely low-bit scenarios, achieving new state-of-the-art accuracy in challenging 2-bit weight, 4-bit activation (W2A4) quantization.
Saliency-Aware Quantized Imitation Learning for Efficient Robotic Control
May 21, 2025Abstract:Deep neural network (DNN)-based policy models, such as vision-language-action (VLA) models, excel at automating complex decision-making from multi-modal inputs. However, scaling these models greatly increases computational overhead, complicating deployment in resource-constrained settings like robot manipulation and autonomous driving. To address this, we propose Saliency-Aware Quantized Imitation Learning (SQIL), which combines quantization-aware training with a selective loss-weighting strategy for mission-critical states. By identifying these states via saliency scores and emphasizing them in the training loss, SQIL preserves decision fidelity under low-bit precision. We validate SQIL's generalization capability across extensive simulation benchmarks with environment variations, real-world tasks, and cross-domain tasks (self-driving, physics simulation), consistently recovering full-precision performance. Notably, a 4-bit weight-quantized VLA model for robotic manipulation achieves up to 2.5x speedup and 2.5x energy savings on an edge GPU with minimal accuracy loss. These results underline SQIL's potential for efficiently deploying large IL-based policy models on resource-limited devices.
LoL-PIM: Long-Context LLM Decoding with Scalable DRAM-PIM System
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:The expansion of large language models (LLMs) with hundreds of billions of parameters presents significant challenges to computational resources, particularly data movement and memory bandwidth. Long-context LLMs, which process sequences of tens of thousands of tokens, further increase the demand on the memory system as the complexity in attention layers and key-value cache sizes is proportional to the context length. Processing-in-Memory (PIM) maximizes memory bandwidth by moving compute to the data and can address the memory bandwidth challenges; however, PIM is not necessarily scalable to accelerate long-context LLM because of limited per-module memory capacity and the inflexibility of fixed-functional unit PIM architecture and static memory management. In this work, we propose LoL-PIM which is a multi-node PIM architecture that accelerates long context LLM through hardware-software co-design. In particular, we propose how pipeline parallelism can be exploited across a multi-PIM module while a direct PIM access (DPA) controller (or DMA for PIM) is proposed that enables dynamic PIM memory management and results in efficient PIM utilization across a diverse range of context length. We developed an MLIR-based compiler for LoL-PIM extending a commercial PIM-based compiler where the software modifications were implemented and evaluated, while the hardware changes were modeled in the simulator. Our evaluations demonstrate that LoL-PIM significantly improves throughput and reduces latency for long-context LLM inference, outperforming both multi-GPU and GPU-PIM systems (up to 8.54x and 16.0x speedup, respectively), thereby enabling more efficient deployment of LLMs in real-world applications.
RILQ: Rank-Insensitive LoRA-based Quantization Error Compensation for Boosting 2-bit Large Language Model Accuracy
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) has become the dominant method for parameter-efficient LLM fine-tuning, with LoRA-based quantization error compensation (LQEC) emerging as a powerful tool for recovering accuracy in compressed LLMs. However, LQEC has underperformed in sub-4-bit scenarios, with no prior investigation into understanding this limitation. We propose RILQ (Rank-Insensitive LoRA-based Quantization Error Compensation) to understand fundamental limitation and boost 2-bit LLM accuracy. Based on rank analysis revealing model-wise activation discrepancy loss's rank-insensitive nature, RILQ employs this loss to adjust adapters cooperatively across layers, enabling robust error compensation with low-rank adapters. Evaluations on LLaMA-2 and LLaMA-3 demonstrate RILQ's consistent improvements in 2-bit quantized inference across various state-of-the-art quantizers and enhanced accuracy in task-specific fine-tuning. RILQ maintains computational efficiency comparable to existing LoRA methods, enabling adapter-merged weight-quantized LLM inference with significantly enhanced accuracy, making it a promising approach for boosting 2-bit LLM performance.
Quantization-Aware Imitation-Learning for Resource-Efficient Robotic Control
Dec 02, 2024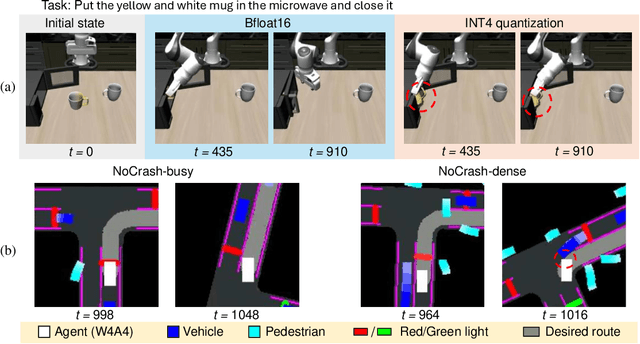
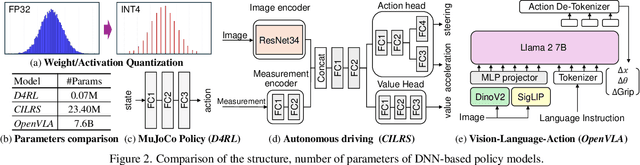
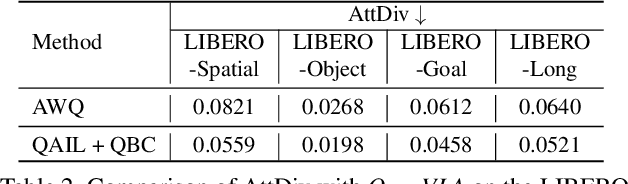
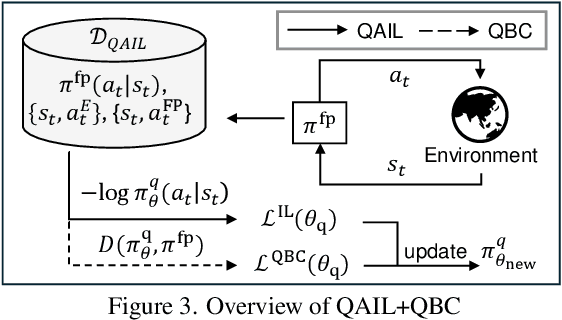
Abstract:Deep neural network (DNN)-based policy models like vision-language-action (VLA) models are transformative in automating complex decision-making across applications by interpreting multi-modal data. However, scaling these models greatly increases computational costs, which presents challenges in fields like robot manipulation and autonomous driving that require quick, accurate responses. To address the need for deployment on resource-limited hardware, we propose a new quantization framework for IL-based policy models that fine-tunes parameters to enhance robustness against low-bit precision errors during training, thereby maintaining efficiency and reliability under constrained conditions. Our evaluations with representative robot manipulation for 4-bit weight-quantization on a real edge GPU demonstrate that our framework achieves up to 2.5x speedup and 2.5x energy savings while preserving accuracy. For 4-bit weight and activation quantized self-driving models, the framework achieves up to 3.7x speedup and 3.1x energy saving on a low-end GPU. These results highlight the practical potential of deploying IL-based policy models on resource-constrained devices.
AMXFP4: Taming Activation Outliers with Asymmetric Microscaling Floating-Point for 4-bit LLM Inference
Nov 15, 2024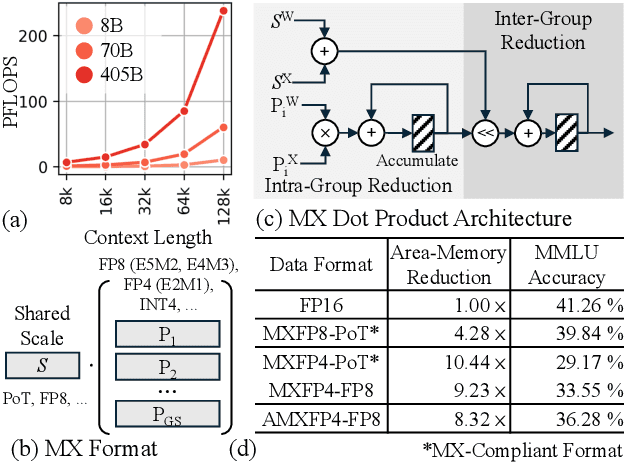
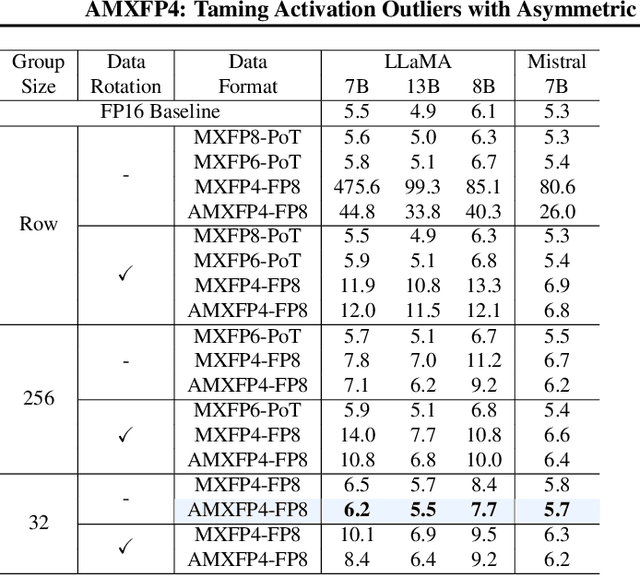
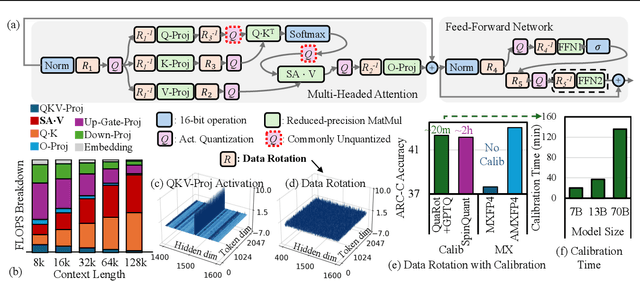
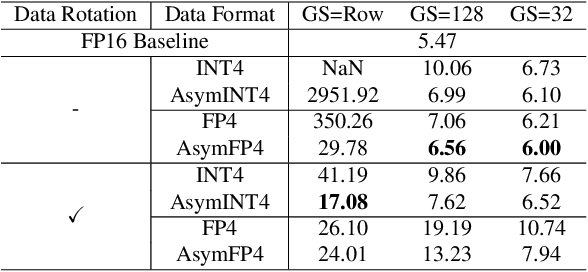
Abstract:Scaling Large Language Models (LLMs) with extended context lengths has increased the need for efficient low-bit quantization to manage their substantial computational demands. However, reducing precision to 4 bits frequently degrades performance due to activation outliers. To address this, we propose Asymmetric Microscaling 4-bit Floating-Point (AMXFP4) for efficient LLM inference. This novel data format leverages asymmetric shared scales to mitigate outliers while naturally capturing the asymmetry introduced by group-wise quantization. Unlike conventional 4-bit quantization methods that rely on data rotation and costly calibration, AMXFP4 uses asymmetric shared scales for direct 4-bit casting, achieving near-ideal quantization accuracy across various LLM tasks, including multi-turn conversations, long-context reasoning, and visual question answering. Our AMXFP4 format significantly outperforms MXFP4 and other leading quantization techniques, enabling robust, calibration-free 4-bit inference.
InfiniPot: Infinite Context Processing on Memory-Constrained LLMs
Oct 02, 2024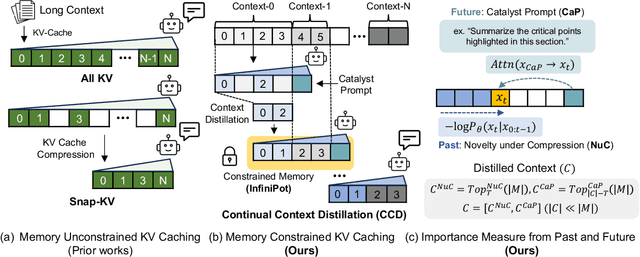
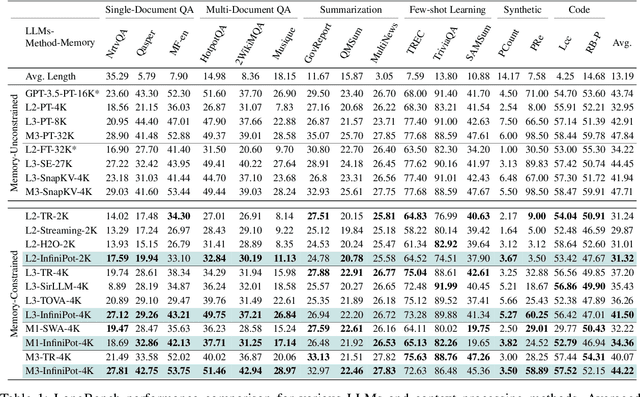
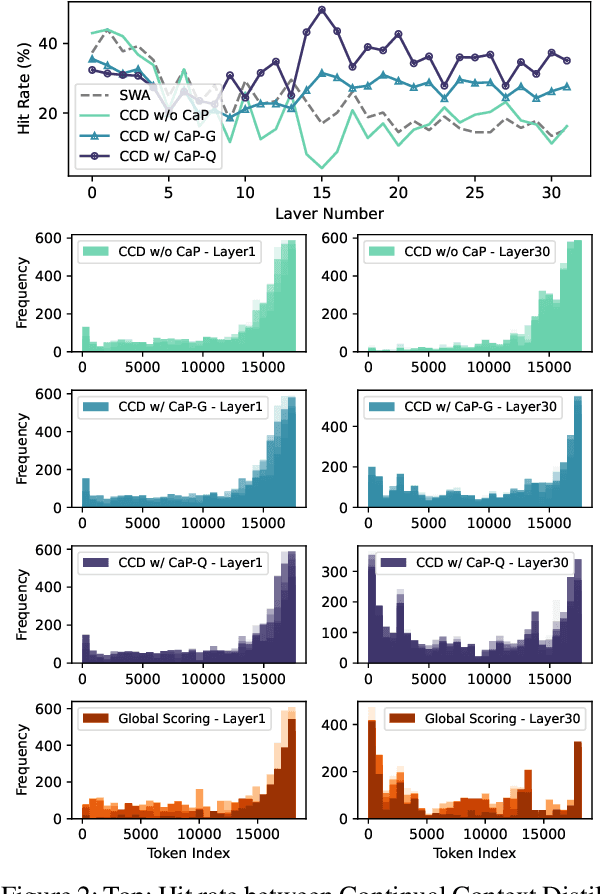
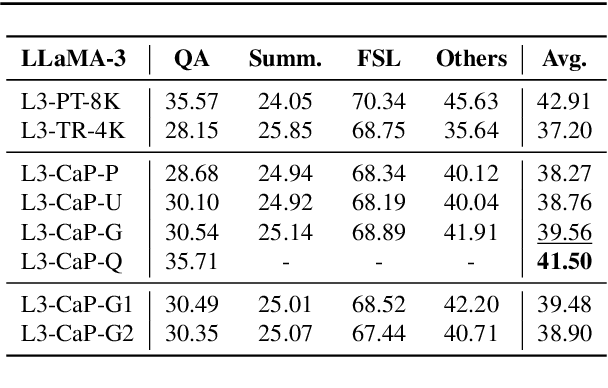
Abstract:Handling long input contexts remains a significant challenge for Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly in resource-constrained environments such as mobile devices. Our work aims to address this limitation by introducing InfiniPot, a novel KV cache control framework designed to enable pre-trained LLMs to manage extensive sequences within fixed memory constraints efficiently, without requiring additional training. InfiniPot leverages Continual Context Distillation (CCD), an iterative process that compresses and retains essential information through novel importance metrics, effectively maintaining critical data even without access to future context. Our comprehensive evaluations indicate that InfiniPot significantly outperforms models trained for long contexts in various NLP tasks, establishing its efficacy and versatility. This work represents a substantial advancement toward making LLMs applicable to a broader range of real-world scenarios.
Selectively Dilated Convolution for Accuracy-Preserving Sparse Pillar-based Embedded 3D Object Detection
Aug 25, 2024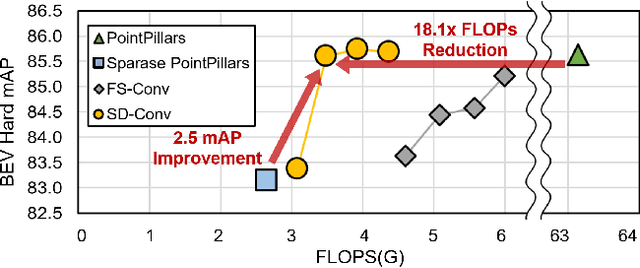
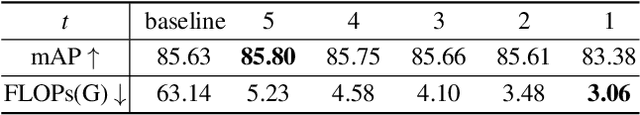
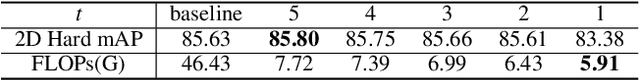
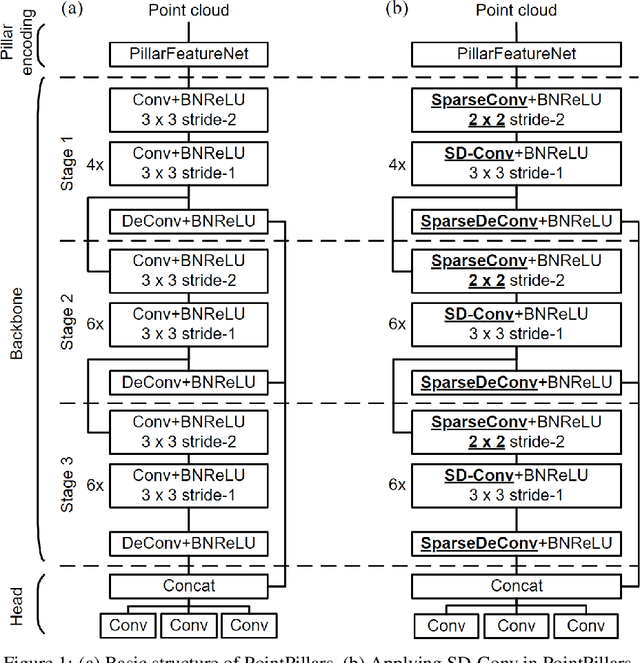
Abstract:Pillar-based 3D object detection has gained traction in self-driving technology due to its speed and accuracy facilitated by the artificial densification of pillars for GPU-friendly processing. However, dense pillar processing fundamentally wastes computation since it ignores the inherent sparsity of pillars derived from scattered point cloud data. Motivated by recent embedded accelerators with native sparsity support, sparse pillar convolution methods like submanifold convolution (SubM-Conv) aimed to reduce these redundant computations by applying convolution only on active pillars but suffered considerable accuracy loss. Our research identifies that this accuracy loss is due to the restricted fine-grained spatial information flow (fSIF) of SubM-Conv in sparse pillar networks. To overcome this restriction, we propose a selectively dilated (SD-Conv) convolution that evaluates the importance of encoded pillars and selectively dilates the convolution output, enhancing the receptive field for critical pillars and improving object detection accuracy. To facilitate actual acceleration with this novel convolution approach, we designed SPADE+ as a cost-efficient augmentation to existing embedded sparse convolution accelerators. This design supports the SD-Conv without significant demands in area and SRAM size, realizing superior trade-off between the speedup and model accuracy. This strategic enhancement allows our method to achieve extreme pillar sparsity, leading to up to 18.1x computational savings and 16.2x speedup on the embedded accelerators, without compromising object detection accuracy.
Improving Conversational Abilities of Quantized Large Language Models via Direct Preference Alignment
Jul 03, 2024Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has facilitated their transformation into conversational chatbots that can grasp contextual nuances and generate pertinent sentences, closely mirroring human values through advanced techniques such as instruction tuning and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). However, the computational efficiency required for LLMs, achieved through techniques like post-training quantization (PTQ), presents challenges such as token-flipping that can impair chatbot performance. In response, we propose a novel preference alignment approach, quantization-aware direct preference optimization (QDPO), that aligns quantized LLMs with their full-precision counterparts, improving conversational abilities. Evaluated on two instruction-tuned LLMs in various languages, QDPO demonstrated superior performance in improving conversational abilities compared to established PTQ and knowledge-distillation fine-tuning techniques, marking a significant step forward in the development of efficient and effective conversational LLMs.
Enhancing Computation Efficiency in Large Language Models through Weight and Activation Quantization
Nov 09, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are proficient in natural language processing tasks, but their deployment is often restricted by extensive parameter sizes and computational demands. This paper focuses on post-training quantization (PTQ) in LLMs, specifically 4-bit weight and 8-bit activation (W4A8) quantization, to enhance computational efficiency -- a topic less explored compared to weight-only quantization. We present two innovative techniques: activation-quantization-aware scaling (AQAS) and sequence-length-aware calibration (SLAC) to enhance PTQ by considering the combined effects on weights and activations and aligning calibration sequence lengths to target tasks. Moreover, we introduce dINT, a hybrid data format combining integer and denormal representations, to address the underflow issue in W4A8 quantization, where small values are rounded to zero. Through rigorous evaluations of LLMs, including OPT and LLaMA, we demonstrate that our techniques significantly boost task accuracies to levels comparable with full-precision models. By developing arithmetic units compatible with dINT, we further confirm that our methods yield a 2$\times$ hardware efficiency improvement compared to 8-bit integer MAC unit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge