Joseph M. Hellerstein
Operationalizing Machine Learning: An Interview Study
Sep 16, 2022



Abstract:Organizations rely on machine learning engineers (MLEs) to operationalize ML, i.e., deploy and maintain ML pipelines in production. The process of operationalizing ML, or MLOps, consists of a continual loop of (i) data collection and labeling, (ii) experimentation to improve ML performance, (iii) evaluation throughout a multi-staged deployment process, and (iv) monitoring of performance drops in production. When considered together, these responsibilities seem staggering -- how does anyone do MLOps, what are the unaddressed challenges, and what are the implications for tool builders? We conducted semi-structured ethnographic interviews with 18 MLEs working across many applications, including chatbots, autonomous vehicles, and finance. Our interviews expose three variables that govern success for a production ML deployment: Velocity, Validation, and Versioning. We summarize common practices for successful ML experimentation, deployment, and sustaining production performance. Finally, we discuss interviewees' pain points and anti-patterns, with implications for tool design.
Selectivity Estimation with Deep Likelihood Models
May 10, 2019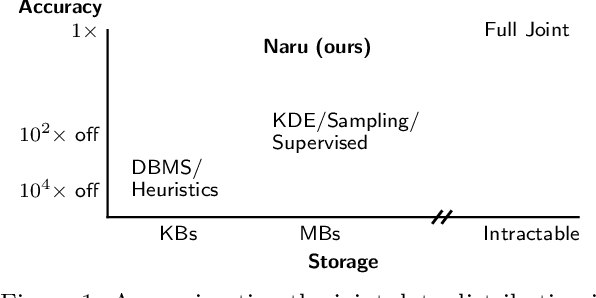
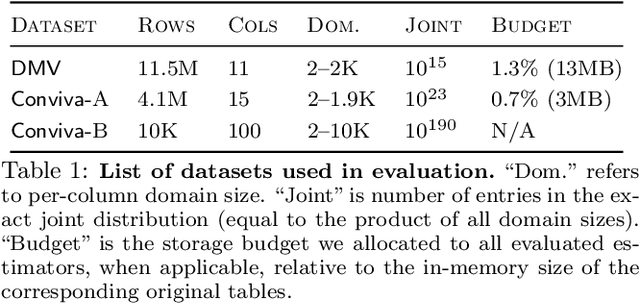
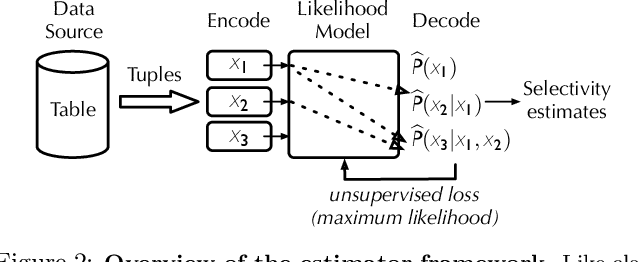
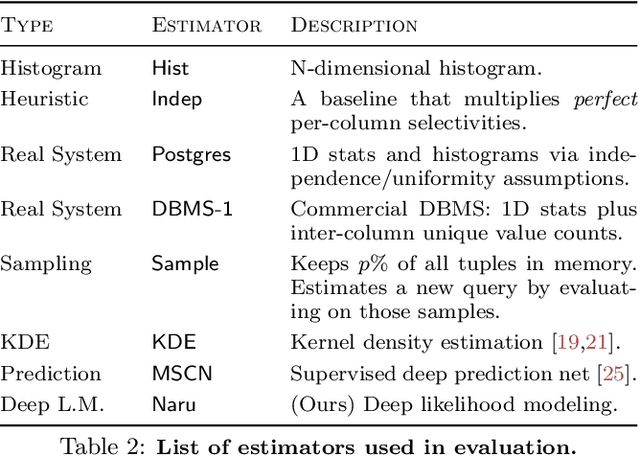
Abstract:Selectivity estimation has long been grounded in statistical tools for density estimation. To capture the rich multivariate distributions of relational tables, we propose the use of a new type of high-capacity statistical model: deep likelihood models. However, direct application of these models leads to a limited estimator that is prohibitively expensive to evaluate for range and wildcard predicates. To make a truly usable estimator, we develop a Monte Carlo integration scheme on top of likelihood models that can efficiently handle range queries with dozens of filters or more. Like classical synopses, our estimator summarizes the data without supervision. Unlike previous solutions, our estimator approximates the joint data distribution without any independence assumptions. When evaluated on real-world datasets and compared against real systems and dominant families of techniques, our likelihood model based estimator achieves single-digit multiplicative error at tail, a 40-200$\times$ accuracy improvement over the second best method, and is space- and runtime-efficient.
A Berkeley View of Systems Challenges for AI
Dec 15, 2017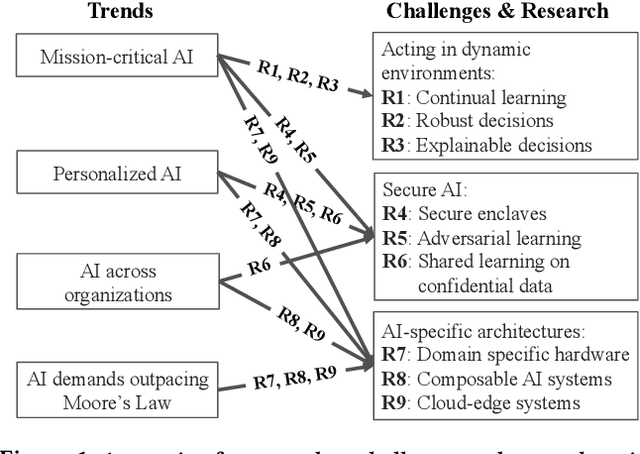
Abstract:With the increasing commoditization of computer vision, speech recognition and machine translation systems and the widespread deployment of learning-based back-end technologies such as digital advertising and intelligent infrastructures, AI (Artificial Intelligence) has moved from research labs to production. These changes have been made possible by unprecedented levels of data and computation, by methodological advances in machine learning, by innovations in systems software and architectures, and by the broad accessibility of these technologies. The next generation of AI systems promises to accelerate these developments and increasingly impact our lives via frequent interactions and making (often mission-critical) decisions on our behalf, often in highly personalized contexts. Realizing this promise, however, raises daunting challenges. In particular, we need AI systems that make timely and safe decisions in unpredictable environments, that are robust against sophisticated adversaries, and that can process ever increasing amounts of data across organizations and individuals without compromising confidentiality. These challenges will be exacerbated by the end of the Moore's Law, which will constrain the amount of data these technologies can store and process. In this paper, we propose several open research directions in systems, architectures, and security that can address these challenges and help unlock AI's potential to improve lives and society.
Distributed GraphLab: A Framework for Machine Learning in the Cloud
Apr 26, 2012



Abstract:While high-level data parallel frameworks, like MapReduce, simplify the design and implementation of large-scale data processing systems, they do not naturally or efficiently support many important data mining and machine learning algorithms and can lead to inefficient learning systems. To help fill this critical void, we introduced the GraphLab abstraction which naturally expresses asynchronous, dynamic, graph-parallel computation while ensuring data consistency and achieving a high degree of parallel performance in the shared-memory setting. In this paper, we extend the GraphLab framework to the substantially more challenging distributed setting while preserving strong data consistency guarantees. We develop graph based extensions to pipelined locking and data versioning to reduce network congestion and mitigate the effect of network latency. We also introduce fault tolerance to the GraphLab abstraction using the classic Chandy-Lamport snapshot algorithm and demonstrate how it can be easily implemented by exploiting the GraphLab abstraction itself. Finally, we evaluate our distributed implementation of the GraphLab abstraction on a large Amazon EC2 deployment and show 1-2 orders of magnitude performance gains over Hadoop-based implementations.
* VLDB2012
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge